Abstract
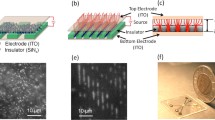
The paper presents a dielectrophoretic method for cell patterning using dielectrophoretic–hydrodynamic trap. A distinctive characteristic of the device is that the dielectrophoretic (DEP) force is generated using a structure that combines conventional electrode-based DEP (eDEP) with insulator-based DEP method (iDEP). The conventional eDEP force is generated across the microfluidic channel between a top plate indium tin oxide electrode and a thin CrAu electrode. Meantime, an isolating cage built from SU8 photoresist around the thin electrode modifies the electric field generating an iDEP force. The cells that are flowing through a microfluidic channel are trapped in the SU8 cage by the total DEP force. As a result, according to the cell dimension and the thickness of the SU8 layer, different cell patterns can be achieved. If the cell’s size is sensitively smaller than the dimensions of the hydrodynamic trap, due to the dipole–dipole interaction, the cell can be organized in 3D structures. The trapping method can be used for conducting genetic, biochemical or physiological studies on cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht DR, Tsang VL, Sah RL, Bhatia SN (2005) Photo- and electropatterning of hydrogel-encapsulated living cell arrays. Lab Chip 5:111–118. doi:10.1039/b406953f
Albrecht DR, Underhill GH, Wassermann TB, Sah RL, Bhatia SN (2006) Probing the role of multicellular organization in three-dimensional microenvironments. Nat Methods 3:369–375
Albrecht DR, Underhill GH, Mendelson A, Bhatia SN (2007) Multiphase electropatterning of cells and biomaterials. Lab Chip 7:702–709
Arora A, Simone G, Salieb-Beugelaar GB, Kim JT, Manz A (2010) Latest developments in micro total analysis systems. Anal Chem 82:4830–4847
Bhadriraju K, Chen CS (2002) Engineering cellular microenvironments to improve cell-based drug testing. Drug Discov Today 7:612–620
Bhatia S, Balis U, Yarmush M, Toner M (1999) Effect of cell–cell interactions in preservation of cellular phenotype: cocultivation of hepatocytes and nonparenchymal cells. FASEB J 13:1883–1900
Birkbeck AL, Flynn RA, Ozkan M, Song D, Gross M, Esener SC (2003) VCSEL arrays as micromanipulators in chip-based biosystems. Biomed Microdevices 5:47–54
Čemažar J, Miklavčič D, Kotnik T (2013) Microfluidic devices for manipulation, modification and characterization of biological cells in electric fields—a review. Informacije MIDEM 43:143–161
Choi J-W, Rosset S, Niklaus M, Adleman JR, Shea H, Psaltis D (2010) 3-dimensional electrode patterning within a microfluidic channel using metal ion implantation. Lab Chip 10:783–788
Choudhury D, Mo X, Iliescu C, Tan LL, Tong WH, Yu H (2011) Exploitation of physical and chemical constraints for three-dimensional microtissue construction in microfluidics. Biomicrofluidics 5:022203
Chow KS, Du H (2011) Dielectrophoretic characterization and trapping of different waterborne pathogen in continuous flow manner. Sens Actuators A 170:24–31
Cima I, Yee CW, Iliescu FS, Phyo WM, Lim KH, Iliescu C, Tan MH (2013) Label-free isolation of circulating tumor cells in microfluidic devices: current research and perspectives. Biomicrofluidics 7:011810
Di Carlo D, Aghdam N, Lee LP (2006) Single-cell enzyme concentrations, kinetics, and inhibition analysis using high-density hydrodynamic cell isolation arrays. Anal Chem 78:4925–4930
Dittrich PS, Manz A (2006) Lab-on-a-chip: microfluidics in drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:210–218
Flanagan LA, Lu J, Wang L, Marchenko SA, Jeon NL, Lee AP, Monuki ES (2008) Unique dielectric properties distinguish stem cells and their differentiated progeny. Stem Cells 26:656–665
Haeberle S, Zengerle R (2007) Microfluidic platforms for lab-on-a-chip applications. Lab Chip 7:1094–1110
Higginbotham SN, Sweatman DR (2008) A combined travelling wave dielectrophoresis and impedance sensing device for sensing biological cell suspensions. J Phys D Appl Phys 41:175503
Ho C-T, Lin R-Z, Chang W-Y, Chang H-Y, Liu C-H (2006) Rapid heterogeneous liver-cell on-chip patterning via the enhanced field-induced dielectrophoresis trap. Lab Chip 6:724–734
Hsiung L-C et al (2008) A planar interdigitated ring electrode array via dielectrophoresis for uniform patterning of cells. Biosens Bioelectron 24:869–875
Huang Y, Williams JC, Johnson SM (2012) Brain slice on a chip: opportunities and challenges of applying microfluidic technology to intact tissues. Lab Chip 12:2103–2117
Hwang H, Lee D-H, Choi W, Park J-K (2009) Enhanced discrimination of normal oocytes using optically induced pulling-up dielectrophoretic force. Biomicrofluidics 3:014103
Iliescu C, Xu GL, Samper V, Tay FE (2005) Fabrication of a dielectrophoretic chip with 3D silicon electrodes. J Micromech Microeng 15:494–500
Iliescu C, Tay FE, Xu G, Yu LM, Samper V (2006a) A dielectrophoretic chip packaged at wafer level. Microsyst Technol 12:987–992
Iliescu C, Yu L, Xu G, Tay FE (2006b) A dielectrophoretic chip with a 3-D electric field gradient. J Microelectromech Syst 15:1506–1513
Iliescu C, Xu GL, Loe FC, Ong PL, Tay FEH (2007) A 3 dimensional dielectrophoretic filter chip. Electrophoresis 28:1107–1114
Iliescu C, Xu GL, Barbarini E, Avram M, Avram A (2009a) Microfluidic device for continuous magnetophoretic separation of white blood cells. Microsyst Technol 15:1157–1162
Iliescu C, Tresset G, Xu G (2009b) Dielectrophoretic field-flow method for separating particle populations in a chip with asymmetric electrodes. Biomicrofluidics 3:044104
Ino K et al (2008) Cell culture arrays using magnetic force-based cell patterning for dynamic single cell analysis. Lab Chip 8:134–142
Ito A, Akiyama H, Kawabe Y, Kamihira M (2007) Magnetic force-based cell patterning using Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) peptide-conjugated magnetite cationic liposomes. J Biosci Bioeng 104:288–293
Iwasa J, Ochi M, Uchio Y, Katsube K, Adachi N, Kawasaki K (2003) Effects of cell density on proliferation and matrix synthesis of chondrocytes embedded in atelocollagen gel. Artif Org 27:249–255
Jen C-P, Huang C-T, Shih H-Y (2010) Hydrodynamic separation of cells utilizing insulator-based dielectrophoresis. Microsyst Technol 16:1097–1104
Johann RM (2006) Cell trapping in microfluidic chips. Anal Bioanal Chem 385:408–412
Jones TB (2005) Electromechanics of particles. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Khademhosseini A, Suh KY, Jon S, Eng G, Yeh J, Chen G-J, Langer R (2004) A soft lithographic approach to fabricate patterned microfluidic channels. Anal Chem 76:3675–3681
Khademhosseini A, Yeh J, Eng G, Karp J, Kaji H, Borenstein J, Farokhzad OC, Langer R (2005) Cell docking inside microwells within reversibly sealed microfluidic channels for fabricating multiphenotype cell arrays. Lab Chip 5:1380
Lewpiriyawong N, Yang C (2014) Continuous separation of multiple particles by negative and positive dielectrophoresis in a modified H filter. Electrophoresis 35(5):214–220
Li S, Li M, Hui YS, Cao W, Li W, Wen W (2013) A novel method to construct 3D electrodes at the sidewall of microfluidic channel. Microfluid Nanofluid 14:499–508
Li M, Li W, Zhang J, Alici G, Wen W (2014) A review of microfabrication techniques and dielectrophoretic microdevices for particle manipulation and separation. J Phys D Appl Phys 47:063001
Lin RZ, Ho CT, Liu CH, Chang HY (2006) Dielectrophoresis based-cell patterning for tissue engineering. Biotechnol J 1:949–957
Lindquist S (1986) The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem 55:1151–1191
Manneberg O, Vanherberghen B, Svennebring J, Hertz HM, Önfelt B, Wiklund M (2008) A three-dimensional ultrasonic cage for characterization of individual cells. Appl Phys Lett 93:063901
Markx GH, Rousselet J, Pethig R (1997) DEP-FFF: field-flow fractionation using non-uniform electric fields. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 20:2857–2872
Martinez-Duarte R (2012) Microfabrication technologies in dielectrophoresis applications—a review. Electrophoresis 33:3110–3132
Masuda S, Washizu M, Nanba T (1989) Novel method of cell fusion in field constriction area in fluid integration circuit. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 25:732–737
Mittal N, Rosenthal A, Voldman J (2007) nDEP microwells for single-cell patterning in physiological media. Lab Chip 7:1146–1153
Mo X et al (2010) Rapid construction of mechanically-confined multi-cellular structures using dendrimeric intercellular linker. Biomaterials 31:7455–7467
Morimoto Y, Takeuchi S (2013) Three-dimensional cell culture based on microfluidic techniques to mimic living tissues. Biomater Sci 1:257–264
Nasabi M, Khoshmanesh K, Tovar-Lopez FJ, Kalantar-zadeh K, Mitchell A (2013) Dielectrophoresis with 3D microelectrodes fabricated by surface tension assisted lithography. Electrophoresis 34:3150–3154
Neužil P, Giselbrecht S, Länge K, Huang TJ, Manz A (2012) Revisiting lab-on-a-chip technology for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 11:620–632
Ni M, Tong WH, Choudhury D, Rahim NAA, Iliescu C, Yu H (2009) Cell culture on MEMS platforms: a review. Int J Mol Sci 10:5411–5441
Nilsson J, Evander M, Hammarström B, Laurell T (2009) Review of cell and particle trapping in microfluidic systems. Anal Chim Acta 649:141–157
Pethig R (2010) Review article—dielectrophoresis: status of the theory, technology, and applications. Biomicrofluidics 4:022811
Pethig R, Talary MS, Lee RS (2003) Enhancing traveling-wave dielectrophoresis with signal superposition. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag 22:43–50
Piggee C (2009) Optical tweezers: not just for physicists anymore. Anal Chem 81(1):16–19
Ramos A, Morgan H, Green N, Castellanos A (1998) Ac electrokinetics: a review of forces in microelectrode structures. J Phys D Appl Phys 31:2338
Rosenthal A, Voldman J (2005) Dielectrophoretic traps for single-particle patterning. Biophys J 88:2193–2205
Skelley AM, Kirak O, Suh H, Jaenisch R, Voldman J (2009) Microfluidic control of cell pairing and fusion. Nat Methods 6:147–152
Sun T, Morgan H (2010) Single-cell microfluidic impedance cytometry: a review. Microfluid Nanofluid 8:423–443
Suzuki M, Yasukawa T, Shiku H, Matsue T (2008) Negative dielectrophoretic patterning with different cell types. Biosens Bioelectron 24:1043–1047
Taff BM, Desai SP, Voldman J (2009) Electroactive hydrodynamic weirs for microparticle manipulation and patterning. Appl Phys Lett 94:084102
Tan WH, Takeuchi S (2007) A trap-and-release integrated microfluidic system for dynamic microarray applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:1146–1151
Tay FE, Yu L, Pang AJ, Iliescu C (2007) Electrical and thermal characterization of a dielectrophoretic chip with 3D electrodes for cells manipulation. Electrochim Acta 52:2862–2868
Tresset G, Iliescu C (2007) Electrical control of loaded biomimetic femtoliter vesicles in microfluidic system. Appl Phys Lett 90:173901
Voldman J (2006) Electrical forces for microscale cell manipulation. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 8:425–454
Voldman J, Toner M, Gray M, Schmidt M (2003) Design and analysis of extruded quadrupolar dielectrophoretic traps. J Electrostat 57:69–90
Wang L, Lu J, Marchenko SA, Monuki ES, Flanagan LA, Lee AP (2009) Dual frequency dielectrophoresis with interdigitated sidewall electrodes for microfluidic flow-through separation of beads and cells. Electrophoresis 30:782–791
Wong I, Ho C-M (2009) Surface molecular property modifications for poly (dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) based microfluidic devices. Microfluid Nanofluid 7:291–306
Wu J et al (2011) A sandwiched microarray platform for benchtop cell-based high throughput screening Biomaterials 32:841–848
Xing X, Zhang M, Yobas L (2013) Interdigitated 3-D Silicon ring microelectrodes for DEP-based particle manipulation. J Microelectromech Syst 22:363–371
Yang M, Li C-W, Yang J (2002) Cell docking and on-chip monitoring of cellular reactions with a controlled concentration gradient on a microfluidic device. Anal Chem 74:3991–4001
Yeo LY, Hou D, Maheshswari S, Chang HC (2006) Electrohydrodynamic surface microvortices for mixing and particle trapping. Appl Phys Lett 88:233512
Yeo LY, Chang HC, Chan PP, Friend JR (2011) Microfluidic devices for bioapplications. Small 7:12–48
Yu L, Tay FE, Xu G, Chen B, Avram M, Iliescu C (2006) Adhesive bonding with SU-8 at wafer level for microfluidic devices. J Phys Conf Ser 34:776–780
Zhang S et al (2011) A robust high-throughput sandwich cell-based drug screening platform. Biomaterials 32:1229–1241
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iliescu, C., Xu, G., Tong, W.H. et al. Cell patterning using a dielectrophoretic–hydrodynamic trap. Microfluid Nanofluid 19, 363–373 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-015-1568-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-015-1568-2