Abstract
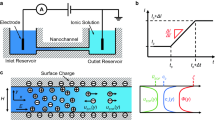
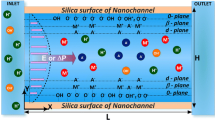
Considering recent widespread applications in nanofluidics, we analyze the ionic current in a pH-regulated nanochannel, using an aqueous NaCl solution in an SiO2 nanochannel with pH adjusted by HCl and NaOH as an example. The model assumed is closer to reality than that in previous analyses, where the channel surface is maintained either at constant potential or constant charge, and only ionic species coming from background salt are considered. The electrical potential, velocity distribution, and ionic current under various conditions are examined by varying the pH, the density of surface functional groups, and the background salt concentration. We show that neglecting ionic species other than those from back ground salt might yield appreciable deviation in ionic current. The mechanisms involved in ionic transport are discussed, and we show that the effects of double-layer thickness and surface potential yield complicated and interesting behaviors in ionic current.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai Y, Qian SZ (2011) Electrokinetic particle translocation through a nanopore. PCCP 13:4060–4071
Ai Y, Liu J, Zhang BK, Qian SZ (2010) Field effect regulation of DNA translocation through a nanopore. Anal Chem 82:8217–8225
Binner J, Zhang Y (2011) Characterization of silicon carbide and silicon powders by XPS and zeta potential measurement. J Mater Sci Lett 20:123–126
Chen Z, Wang P, Chang HC (2005) An electro-osmotic micro-pump based on monolithic silica for micro-flow analyses and electro-sprays. Anal Bioanal Chem 382:817–824
Choi YS, Kim SJ (2009) Electrokinetic flow-induced currents in silica nanofluidic channels. J Colloid Interface Sci 333:672–678
Choi Y, Olsen TJ, Sims PC, Moody IS, Corso BL, Dang MN, Weiss GA, Collins PG (2013) Dissecting single-molecule signal transduction in carbon nanotube circuits with protein engineering. Nano Lett 13:625–631
Daiguji H, Yang PD, Majumdar A (2004) Ion transport in nanofluidic channels. Nano Lett 4:137–142
Dekker C (2007) Solid-state nanopores. Nat Nanotech 2:209–215
Dolnik V (2004) Wall coating for capillary electrophoresis on microchips. Electrophoresis 25:3589–3601
FlexPDE (2000) version 2.22; PDE Solutions Inc.: Spokane Valley
Gasparac R, Kohli P, Mota MO, Trofin L, Martin CR (2004) Template synthesis of nano test tubes. Nano Lett 4:513–516
Holland BT, Blanford CF, Do T, Stein A (1999) Synthesis of highly ordered, three-dimensional, macroporous structures of amorphous or crystalline inorganic oxides, phosphates, and hybrid composites. Chem Mater 11:795–805
Hsu JP, Chen ZS (2007) Electrophoresis of a sphere along the axis of a cylindrical pore: effects of double-layer polarization and electroosmotic flow. Langmuir 23:6198–6204
Hsu JP, Tai YH (2010) Effect of multiple ionic species on the electrophoretic behavior of a charge-regulated particle. Langmuir 26:16857–16864
Hsu JP, Lee E, Yen FY (2000) Electrophoresis of concentrated spherical particles with a charge-regulated surface. J Chem Phys 112:6404–6410
Hsu JP, Tai YH, Yeh LH, Tseng S (2011) Electrophoresis of a charge-regulated sphere in a narrow cylindrical pore filled with multiple ionic species. J Phys Chem B 115:3972–3980
Huang KD, Yang RJ (2007) Electrokinetic behaviour of overlapped electric double layers in nanofluidic channels. Nanotechnology 18:115701
Jacobsa S, Regaa F, Burkhoffb D, Meynsa B (2012) The use of a CircuLite micro-pump for congenitally corrected transposition of the great arteries. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 42:741–743
Karenga S, El Rassi Z (2010) A novel, neutral hydroxylated octadecyl acrylate monolith with fast electroosmotic flow velocity and its application to the separation of various solutes including peptides and proteins in the absence of electrostatic interactions. Electrophoresis 31:3192–3199
Karnik R, Fan R, Yue M, Li D, Yang P, Majumdar A (2005) Electrostatic control of ions and molecules in nanofluidic transistors. Nano Lett 5:943–948
Kim SJ, Wang YC, Lee JH, Jang H, Han J (2007) Concentration polarization and nonlinear electrokinetic flow near a nanofluidic channel. Phys Rev Lett 99:044501
Kirby BJ, Hasselbrink EF (2004) Zeta potential of microfluidic substrates: 1. Theory, experimental techniques, and effects on separations. Electrophoresis 25:187–202
Kutter JP (2000) Current developments in electrophoretic and chromatographic separation methods on microfabricated devices. Trends Anal Chem 19:352–363
Lam ET, Hastie A, Lin C, Ehrlich D, Das SK, Austin MD, Deshpande P, Cao H, Nagarajan N, Xiao M, Kwok PY (2012) Genome mapping on nanochannel arrays for structural variation analysis and sequence assembly. Nat Biotechnol 30:771–776
Lee SM, Kuan YD, Sung MF (2013) Diaphragm air–liquid micro pump applicable to the direct methanol fuel cell. J Power Sources 238:290–295
Li CY, Ma FX, Wu ZQ, Gao HL, Shao WT, Wang K, Xia XH (2013) Solution-pH-modulated rectification of ionic current in highly ordered nanochannel arrays patterned with chemical functional groups at designed positions. Adv Funct Mater 23:3836–3844
Liu H, Qian SZ, Bau HH (2007) The effect of translocating cylindrical particles on the ionic current through a nanopore. Biophys J 92:1164–1177
Mei J, Xu JR, Xiao YX, Liao XY, Qiu GF, Feng YQ (2008) A novel covalent coupling method for coating of capillaries with liposomes in capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 29:3825–3833
O’Brien RW, White LR (1978) Electrophoretic mobility of a spherical colloidal particle. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 2(74):1607–1626
Ohshima H (1995) Electrophoresis of soft particles. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 62:189–235
Ohshima H (2006) Electrophoresis of soft particles: analytic approximations. Electrophoresis 27:526–533
Park HM, Lee JS, Kim TW (2007) Comparison of the Nernst–Planck model and the Poisson–Boltzmann model for electroosmotic flows in microchannels. J Colloid Interface Sci 315:731–739
Pevarnik M, Healy K, Davenport M, Yen J, Siwy ZS (2012) A hydrophobic entrance enhances ion current rectification and induces dewetting in asymmetric nanopores. Analyst 137:2944–2950
Qian SZ, Wang AH, Afonien JK (2006) Electrophoretic motion of a spherical particle in a converging-diverging nanotube. J Colloid Interface Sci 303:579–592
Rice CL, Whitehead R (1965) Electrokinetic flow in a narrow cylindrical capillary. J Phys Chem 69:4017–4024
Shugai AA, Carnie SL (1999) Electrophoretic motion of a spherical particle with a thick double layer in bounded flows. J Colloid Interface Sci 213:298–315
So HM, Won K, Kim YH, Kim BK, Ryu BH, Na PS, Kim H, Lee JO (2005) Single-walled carbon nanotube biosensors using aptamers as molecular recognition elements. J Am Chem Soc 127:11906–11907
Sorgenfrei S, Chiu CY, Johnston M, Nuckolls C, Shepard KL (2011) Debye screening in single-molecule carbon nanotube field-effect sensors. Nano Lett 11:3739–3743
Stein D, Kruithof M, Dekker C (2004) Surface-charge-governed ion transport in nanofluidic channels. Phys Rev Lett 93:035901
Storm AJ, Chen JH, Zandbergen HW, Dekker C (2005) Translocation of double-strand DNA through a silicon oxide nanopore. Phys Rev E 71:051903
Tseng S, Lo TW, Hsu C, Fu YK, Hsu JP (2013a) Importance of temperature on the diffusiophoretic behavior of a charge-regulated zwitterionic particle. PCCP 15:7512–7519
Tseng S, Tai YH, Hsu JP (2013b) Electrokinetic flow in a pH-regulated, cylindrical nanochannel containing multiple ionic species. Microfluid Nanofluidics 15:847–857
van der Heyden FHJ, Bonthuis DJ, Stein D, Meyer C, Dekker C (2007) Power generation by pressure-driven transport of ions in nanofluidic channels. Nano Lett 7:1022–1025
Wall S (2010) The history of electrokinetic phenomena. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 15:119–124
Wang M, Revil A (2010) Electrochemical charge of silica surfaces at high ionic strength in narrow channels. J Colloid Interface Sci 343:381–386
Wang XY, Cheng C, Wang SL, Liu SR (2009) Electroosmotic pumps and their applications in microfluidic systems. Microfluid Nanifluid 6:145–162
Wang M, Kang QJ, Ben-Naim E (2010) Modeling of electrokinetic transport in silica nanofluidic channels. Anal Chim Acta 664:158–164
Wang X, Zheng G, Xu L, Cheng W, Xu B, Huang Y, Sun D (2012) Fabrication of nanochannels via near-field electrospinning. Appl Phys A 108:825–828
White HS, Bund A (2008) Ion current rectification at nanopores in glass membranes. Langmuir 24:2212–2218
Xia Y, Gates B, Yin Y, Lu Y (2000) Monodispersed colloidal spheres: old materials with new applications. Adv Mater 12:693–713
Xia D, Yan J, Hou S (2012) Fabrication of nanofluidic biochips with nanochannels for applications in DNA analysis. Small 8:2787–2801
Xu BY, Xu JJ, Xia XH, Chen HY (2010) Large scale lithography-free nano channel array on polystyrene. Lab Chip 10:2894–2901
Yan Y, Wang L, Xue J, Chang HC (2013) Ion current rectification inversion in conic nanopores: nonequilibrium ion transport biased by ion selectivity and spatial asymmetry. J Chem Phys 138:044706
Yaroshchuk A (2012) Current-induced concentration polarization of interfaces between non-ideally perm-selective ion-exchange media and electrolyte solutions. J Membr Sci 396:43–49
Yeh LH, Zhang M, Qian S (2013) Ion transport in a pH-regulated nanopore. Anal Chem 85:7527–7534
Yu HY, Hung SH, Hsu JP (2004) Electrophoresis of a charge-regulated particle at an arbitrary position in a spherical cavity. Colloid Polym Sci 283:10–14
Yusko EC, An R, Mayer M (2010) Electroosmotic flow can generate ion current rectification in nano- and micropores. ACS Nano 4:477–487
Zangle TA, Mani A, Santiago JG (2010) Theory and experiments of concentration polarization and ion focusing at microchannel and nanochannel interfaces. Chem Soc Rev 39:1014–1035
Zhao C, Yang C (2012) Advances in electrokinetics and their applications in micro/nano fluidics. Microfluid Nanofluidics 13:179–203
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tseng, S., Tai, YH. & Hsu, JP. Ionic current in a pH-regulated nanochannel filled with multiple ionic species. Microfluid Nanofluid 17, 933–941 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-014-1384-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-014-1384-0