Abstract
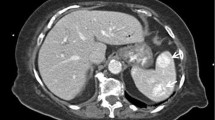
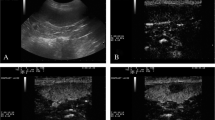
Detection of reticuloendothelial system (RES) cells is essential for the differential diagnosis of splenic hamartoma. Among the imaging techniques using contrast agents phagocytosed by RES cells, contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (CEUS) with Sonazoid is less invasive and less costly than 99mTc-labeled colloid scintigraphy. We report a case of non-symptomatic splenic hamartoma in a 40-year-old woman detected as an abdominal tumor by screening ultrasonography. The tumor was 4 cm in diameter, round, slightly hypoechoic, and associated with a cystic lesion. The tumor region was stained on enhanced computed tomography with prolonged enhancement, while the cystic lesion was not. The mass appeared as mainly isointense with partial hyperintensity on T1-weighted and as a mixed hypo- and hyperintense region on T2-weighted magnetic resonance images. 99mTc-labeled colloid scintigraphy demonstrated uptake in only the tumor region. CEUS with Sonazoid revealed that the tumor was mainly hypervascular with non-enhanced areas in the early vascular phase, but the hypervascular region appeared also as a hyperechoic area (indicating microbubble phagocytosis) in the post-vascular phase. Thus, CEUS with Sonazoid revealed all three cardinal features of splenic hamartoma: hypervascularity, presence of RES cells, and tissue heterogeneity. Splenectomy and histopathology confirmed the presence of a splenic hamartoma with associated hematoma. CEUS with Sonazoid is a promising new diagnostic tool for splenic hamartoma.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berge T. Splenoma. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;63:333–9.
Morgenstern L, McCafferty L, Rosenberg J, et al. Hamartomas of the spleen. Arch Surg. 1984;119:1291–3.
Jia HB, Li YP, Han DE, et al. Splenic hamartoma: case report and review of literature. Chin Med J (Engl). 2006;119:1403–8.
Yu RS, Zhang SZ, Hua JM. Imaging findings of splenic hamartoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10:2613–5.
Silverman ML, LiVolsi VA. Splenic hamartoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978;70:224–9.
Warnke RA, Weiss LM, Chan JK. Tumors of the lymph nodes and spleen. In: Rosai J, Sobin LH, editors. Atlas of tumor pathology. Series 3, Fascicle 14. Washington DC: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology; 1995. p. 504–6.
Zissin R, Lishner M, Rathaus V. Case report: unusual presentation of splenic hamartoma; computed tomography and ultrasonic findings. Clin Radiol. 1992;45:410–1.
Lam KY, Yip KH, Peh WC. Splenic vascular lesions: unusual features and a review of the literature. Aust N Z J Surg. 1999;69:422–5.
Ferguson ER, Sardi A, Beckman EN. Spontaneous rupture of splenic hamartoma. J La State Med Soc. 1993;145:48–52.
Okada J, Yoshikawa K, Uno K, et al. Increased activity on radiocolloid scintigraphy in splenic hamartoma. Clin Nucl Med. 1990;15:112–5.
Shimuzu K, Suga K, Matsunaga N, et al. Splenic hamartoma presenting as a “hot spot” on Tc-99m phytate SPECT imaging. Clin Nucl Med. 1998;23:370–3.
Mazurek A, Szaluś N, Stembrowicz-Nowakowska Z, et al. Detection of splenic tissue by 99mTc-labelled Sn-colloid SPECT/CT scintigraphy. Med Rev Cent East Eur. 2011;14:116–7.
Kindberg GM, Tolleshaug H, Roos N, et al. Hepatic clearance of Sonazoid perfluorobutane microbubbles by Kupffer cells does not reduce the ability of liver to phagocytose or degrade albumin microspheres. Cell Tissue Res. 2003;312:49–54.
Brinkley AA, Lee JK. Cystic hamartoma of the spleen: CT and sonographic findings. J Clin Ultrasound. 1981;9:136–8.
Caremani M, Occhini U, Caremani A, et al. Focal splenic lesions: US findings. J Ultrasound. 2013;16:65–74.
Wan YL, Cheung YC, Lui KW, et al. Ultrasonographic findings and differentiation of benign and malignant focal splenic lesions. Postgrad Med J. 2000;76:488–93.
Nakanishi S, Shiraki K, Yamamoto K, et al. Basket pattern blood flow signals discovered in a case of splenic hamartoma by power Doppler ultrasonography. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:5235–8.
Görg C, Görg K, Bert T, et al. Colour Doppler ultrasound patterns and clinical follow-up of incidentally found hypoechoic, vascular tumours of the spleen: evidence for a benign tumour. Br J Radiol. 2006;179:319–25.
Niizawa M, Ishida H, Morikawa P, et al. Color Doppler sonography in a case of splenic hemangioma: value of compressing the tumor. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991;157:965–6.
Goerg C, Schwerk WB. Color Doppler imaging of focal splenic masses. Eur J Radiol. 1994;18:214–9.
Abbott RM, Levy AD, Aguilera NS, et al. From the archives of the AFIP: primary vascular neoplasms of the spleen: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 2004;24:1137–63.
Ramani M, Reinhold C, Semelka RC, et al. Splenic hemangiomas and hamartomas: MR imaging characteristics of 28 lesions. Radiology. 1997;202:166–72.
Elsayes KM, Narra VR, Mukundan G, et al. MR imaging of the spleen: spectrum of abnormalities. Radiographics. 2005;25:967–82.
Bulakci M, Yilmaz E, Yahyayev A, et al. Superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in a case of spleen hamartoma. Med Princ Pract. 2013;22:301–3.
Tatekawa Y, Kanehiro H, Nakajima Y. Laparoscopic extirpation of splenic hamartoma. Pediatr Surg Int. 2007;23:911–4.
Yanagisawa K, Moriyasu F, Miyahara T, et al. Phagocytosis of ultrasound contrast agent microbubbles by Kupffer cells. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2007;33:318–25.
Peddu P, Shah M, Sidhu PS. Splenic abnormalities: a comparative review of ultrasound, microbubble-enhanced ultrasound and computed tomography. Clin Radiol. 2004;59:777–92.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human rights statements and informed consent
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008 (5). Informed consent was obtained from the patient for being included in this report.
About this article
Cite this article
Sugihara, T., Koda, M., Kato, J. et al. Contrast-enhanced sonography with Sonazoid as a new diagnostic tool for splenic hamartoma: a single case report. J Med Ultrasonics 43, 113–118 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-015-0660-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-015-0660-2