Abstract
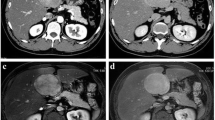
Focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) is an asymptomatic benign liver tumor that may be detected accidentally during an abdominal ultrasound examination; it is associated with unspecific complaints, sometimes painful. Diagnosis can be precise using imaging techniques like ultrasonography. The diagnostic criteria are represented by the spatial display of the tumoral vessels and their hemodynamic characteristics. Sometimes differential diagnostic issues occur with other benign or malignant liver tumors. We present the case of a young female patient without a personal pathological history, who complained of intense, diffuse, intermittent, non-systematic abdominal pain and who underwent ultrasound examination, followed by contrast-enhanced ultrasound. With this technique, we evidenced a solid extrahepatic tumor, which was mobile at the patient’s change of position and had the hemodynamic features of FNH. The article also tackles the problem of intra-abdominal pedunculated tumors.






Similar content being viewed by others

References
Kamel IR, Liapi E, Fishman EK, et al. Focal nodular hyperplasia: lesion evaluation using 16-MDCT and 3D CT angiography. Am J Roentgenol. 2006;186:1587–96.
Trotter JF, Everson GT. Benign focal lesions of the liver. Clin Liver Dis. 2001;5:17–42.
Brancatelli G, Federle MP, Grazioli L, et al. Focal nodular hyperplasia: CT findings with emphasis on multiphasic helical CT in 78 patients. Radiology. 2001;219:61–8.
Nguyen BN, Flejou JF, Terris B, et al. Focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver: a comprehensive pathologic study of 305 lesions and recognition of new histologic forms. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999;23:1441–54.
Mathieu D, Kobeiter H, Maison P, et al. Oral contraceptive use and focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver. Gastroenterology. 2000;118:560–4.
Kapp N, Curtis KM. Hormonal contraceptive use among women with liver tumors: a systematic review. Contraception. 2009;80:387–90.
Bioulac-Sage P, Balabaud C, Bedossa P, et al. Pathological diagnosis of liver cell adenoma and focal nodular hyperplasia: Bordeaux update. J Hepatol. 2007;46:521–7.
Ahn SS, Kim MJ, Lim JS, et al. Added value of gadoxetic acid-enhanced hepatobiliary phase MR imaging in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology. 2010;255:459–66.
Buell JF, Tranchart H, Cannon R, et al. Management of benign hepatic tumours. Surg Clin North Am. 2010;90:719–35.
Choi BY, Nguyen MH. The diagnosis and management of benign hepatic tumours. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2005;39:401–12.
Grazioli L, Bondioni MP, Haradome H, et al. Hepatocellular adenoma and focal nodular hyperplasia: value of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging in differential diagnosis. Radiology. 2012;262:520–9.
Purysko AS, Remer EM, Coppa CP, et al. Characteristics and distinguishing features of hepatocellular adenoma and focal nodular hyperplasia on gadoxetate disodiumenhanced MRI. Am J Roentgenol. 2012;198:115–23.
Bader TR, Braga L, Semelka RC. Exophytic benign tumors of the liver: appearance on MRI. Magn Reson Imaging. 2001;9:623–8.
Schild H, Thelen M, Paquet KJ, et al. Focal nodular hyperplasia. Fortschr Röntgenstr. 1980;133:355–64.
Sawhney S, Jain R, Safaya R, et al. Pedunculated focal nodular hyperplasia. Pediatr Radiol. 1992;22:231–2.
Ha CD, Kubomoto SM, Whetstone BM, et al. Pedunculated hepatic hemangiomas often misdiagnosed despite their typical findings. Open Surg J. 2013;7:1–5.
Brancatelli G, Federle MP, Vullierme MP, et al. CT and MR imaging evaluation of hepatic adenoma. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2006;30:745–50.
Bhatnagar A, Pathania OP, Champakam NS. Giant pedunculated haemangioma of the liver. Indian J Gastroenterol. 1987;6:51–2.
Tsai CC, Yen TC, Tzen KY. Pedunculated giant liver hemangioma mimicking a hypervascular gastric tumor on Tc-99m RBC SPECT. Clin Nucl Med. 1999;24:132–3.
Ellis JV, Salazar JE, Gavant ML. Pedunculated hepatic hemangioma: an unusual cause for anteriorly displaced retroperitoneal fat. J Ultrasound Med. 1985;4:623–4.
Akatsu T, Sakamoto M, Shimazu M, et al. Pedunculated angiomyolipoma of the liver with a predominant pelioid pattern. Virchows Arch. 2004;444:467–9.
Koh CC, Sheu JC. Hepatic lymphangioma—a case report. Pediatr Surg Int. 2000;16:515–6.
Park HS, Kim YK, Cho BH, et al. Pedunculated hepatic mass. Liver Int. 2011;31:541.
Horie Y, Katoh S, Yoshida H, et al. Pedunculated hepatocellular carcinoma. Report of three cases and review of literature. Cancer. 1983;51:746–51.
Yeh CN, Lee WC, Jeng LB, et al. Pedunculated hepatocellular carcinoma: clinicopathologic study of 18 surgically resected cases. World J Surg. 2002;26:1133–8.
Okuda K, Arakawa M, Kubo Y, et al. Right-sided pedunculated hepatocellular carcinoma: a form of adrenal metastasis. Hepatology. 1998;27:81–5.
Kim HJ, Lee DH, Lim JW, et al. Exophytic benign and malignant hepatic tumors: CT imaging features. Korean J Radiol. 2008;9:67–75.
Valls C, Guma A, Puig I, et al. Intrahepatic peripheral cholangiocarcinoma: CT evaluation. Abdom Imaging. 2000;25:490–6.
Kimura H, Yoshida T, Kinoshita S, et al. Pedunculated giant gastrointestinal stromal tumor of the stomach showing extragastric growth: report of a case. Surg Today. 2004;34:159–62.
Slim R, Smayra T, Tohme C, et al. Unusual etiology of epigastric pain. J Emerg Med. 2011;40:93–5.
Conflict of interest
Radu Badea, Magdalena Meszaros, Nadim AL Hajjar, Ioana Rusu, and Liliana Chiorean declare that they have no conflict of interest. There are no financial or other relations that could lead to a conflict of interest.
Ethical Considerations
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study. Additional informed consent was obtained from all patients for which identifying information is included in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Badea, R., Meszaros, M., AL Hajjar, N. et al. Benign nodular hyperplasia of the liver-pedunculated form: diagnostic contributions of ultrasonography and consideration of exophytic liver tumors. J Med Ultrasonics 42, 97–102 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-014-0564-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-014-0564-6