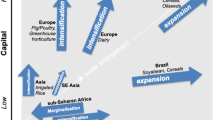
Abstract
Many societies are spoiled for choice when they purchase meat and other livestock products, and around the globe food choice has grown dramatically in the last two decades. What is more, besides the cost and obvious health concerns influencing commodity section, an increasing proportion of choices is made to contribute to the achievement of certain ideals, such as natural resource management, climate change mitigation, animal welfare concerns and personal lifestyle. At the same time, human health considerations are becoming more important for consumption choices as richer societies, and increasingly the urban poor in low- and middle-income countries, face an unprecedented epidemic of over-consumption and associated diet-related non-communicable diseases. Animal source foods are considered significant contributors to this trend. This paper reviews this complicated arena, and explores the range of considerations that influence consumers’ preferences for meat and other animal source foods. This paper also argues that deeper drivers of consumption behaviour of many foods may act in opposition to the articulated preferences for choices around animal source food consumption. We review how the returns to different causes are being valued, how emerging metrics are helping to manage and influence consumption behaviours, and draw conclusions regarding options which influence food choice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abolitionist Approach (2015). http://www.abolitionistapproach.com/animal-welfare-regulation-happy-exploitation-and-speciesism/#.Ujw4pRbhGgE. Accessed 4 July 2015
Adams J, Tyrrell R, Adamson AJ, White M. (2012). Effect of restrictions on television food advertising to children on exposure to advertisements for ‘less healthy’ foods: repeat cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 7(2):e31578.
Andreyeva T, Luedicke J, Middleton AE, Long MW, Schwartz MB. (2012). Positive influence of the revised Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children food packages on access to healthy foods. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 112(6):850-8
Anon (2005) Performance Evaluation of Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS). Programme Evaluation Organisation, Planning Commission, Government of India, New Delhi, March 2005. http://planningcommission.nic.in/reports/peoreport/peo/peo_tpds.pdf
Appelhans, B. M., Woolf, K., Pagoto, S. L., Schneider, K. L., Whited, M. C., & Liebman, R. (2011). Inhibiting food reward: delay discounting, food reward sensitivity, and palatable food intake in overweight and obese women. Obesity.19(11), 2175–2182
Bailey R, Froggatt A, Wellesley L (2014) Livestock—climate change’s forgotten sector. Global Public Opinion on Meat and Dairy Consumption. Research Paper, Chatham House, The Royal Institute of International Affairs, London. https://www.chathamhouse.org/sites/files/chathamhouse/field/field_document/20141203LivestockClimateChangeBaileyFroggattWellesley.pdf. Accessed 4 November 2015.
Baum CL, (2011). The Effects of food stamps on obesity. Southern Economic Journal 77(3):623-651.
Bernués A, De Boer IJM, Ripoll-Bosch R, Vellinga T (2011) Greenhouse gas emissions throughout the life cycle of Spanish lamb-meat: a comparison of three production systems. In: Bernués A, Boutonnet JP, Casasús I, Chentouf M, Gabiña D, Joy M, López-Francos A, Morand-Fehr P, Pacheco F (eds.). Economic, social and environmental sustainability in sheep and goat production systems Zaragoza : CIHEAM/FAO/CITA-DGA Options Méditerranéennes : Série A. Séminaires Méditerranéens; n. 100
Bonti-Ankomah S, Yiridoe E (2006). Organic and conventional food: a literature review of the economics of consumer perceptions and preferences. Final Report Submitted to Organic Agriculture Centre of Canada, Nova Scotia Agricultural College, Nova Scotia Canada. http://www.organicagcentre.ca/Docs/BONTI%20%26%20YIRIDOE%20April%2028%202006%20Final.pdf. Accessed 4 November 2015.
Borden NH (1984). The concept of the marketing mix. Harvard Business school. http://www.guillaumenicaise.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/10/Borden-1984_The-concept-of-marketing-mix.pdf. Accessed on 5th July 2015.
Brenton (2013). The political motivations of ethical consumers. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 37, 490–497
Bryant, R.L. and Goodman, M.K. (2004). Consuming narratives: the political ecology of ‘alternative’ consumption. Transactions of the Institute of British Geographers, New Series, Vol. 29, No. 3 pp. 344-366
Bryant R, Goodman M, Redclift M (2008). Spaces of intention as exclusionary practice: exploring ethical limits to ‘alternative’ sustainable consumption. http://www.kcl.ac.uk/schools/sspp/geography/research/epd/working.html
Bryant R, Goodman M (2013). Peopling the Practices of Sustainable Consumption: Eco-Chic and the Limits to the Spaces of Intention. http://www.kcl.ac.uk/sspp/departments/geography/research/epd/workingpapers.aspx
Buse, K and Hawkes, S. (2015). Health in the sustainable development goals: ready for a paradigm shift? Globalization and Health, 11:13
Campos S, Doxey J, Hammond D. (2011). Nutrition labels on pre-packaged foods: a systematic review. Public Health Nutr.14(8):1496–1506
Cawley, J (2010), “The Economics of Childhood Obesity,” Health Affairs 29(3): 364-371
CBPP (2015). Policy basics: introduction to SNAP, Center on Budget and Policy Priorities. http://www.cbpp.org/sites/default/files/atoms/files/policybasics-foodstamps.pdf. Accessed on 9th November
Cederberg, C., F Hedenus, S Wirsenius and U Sonesson (2012). Trends in greenhouse gas emissions from consumption and production of animal food products – implications for long-term climate targets. Animal, 7:2, pp 330–340.
Chamhuri, N. and Batt P.J., (2013). Exploring the factors influencing consumers’ choice of retail store when purchasing fresh meat in Malaysia International Food and Agribusiness Management Review 16(3):99-122.
Chandon P, Wansink B. (2012). Does food marketing need to make us fat? A review and solutions. Nutrition Revues, 70(10):571-93.
Christakis NA, Fowler JH. (2007). The spread of obesity in a large social network over 32 years. New England Journal of Medicine; 357(4):370-9.
Cordain, L., Eaton, S.B., Sebastian, A., Mann, N., Lindeberg, S., Watkins, B.A, O’Keefe, J.H. & Brand-Miller, J. (2005). Origins and evolution of the Western diet: health implications for the 21st century. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 81(2): 341-354.
Dallman MF. (2010). Stress-induced obesity and the emotional nervous system. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 21:159–65
de Jonge J, Frewer L, van Trijp H, Renes R, de Wit W, Timmers J (2004). Monitoring consumer confidence in food safety: an exploratory study, British Food Journal 106(10/11):837–849. http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/00070700410561423. Accessed 1 July 2015.
DEFRA (2008). Comparative life-cycle assessment of food commodities procured for UK consumption through a diversity of supply chains. Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, United Kingdom. http://randd.defra.gov.uk/Default.aspx?Module=More&Location=None&ProjectID=15001 Accessed 4 July 2015. http://randd.defra.gov.uk/Document.aspx?Document=FO0103_7898_FRP.doc
Devaux M, Sassi F, Church J, Cecchini M, Borgonovi F (2011). Exploring the Relationship Between Education and Obesity OECD Journal: Economic Studies, vol 2011/1.M. http://dx.doi.org/10.1787/eco_studies-2011-5kg5825v1k23
Drewnowski A, Specter SE. (2004). Poverty and obesity: the role of energy density and energy costs. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 79(1):6-16.
Drewnowski A, Almiron-Roig E. (2010). Human Perceptions and Preferences for Fat-Rich Foods. In: Montmayeur JP, le Coutre J (eds.) Fat detection: taste, texture, and post ingestive effects, Boca Raton: CRC Press Chapter 11. Published online 2012 Feb 14. doi: 10.4081/jphr.2012.e5
Edward-Jones, G., (2010). Does eating local food reduce the environmental impact of food production and enhance consumer health? Proceedings of the Nutrition Society, 69, 582–591
Eisenstein C (2002). The ethics of eating meat; a radical view. http://www.westonaprice.org/health-topics/the-ethics-of-eating-meat-a-radical-view/. Accessed 4 November 2015.
Environmental Leader (2013). Food LCA: the elusive quest to go beyond carbon. http://www.environmentalleader.com/2013/06/04/food-lca-the-elusive-quest-to-go-beyond-carbon/. Accessed 5th July 2015
Evers C, Adriaanse M, de Ridder DT, de Witt Huberts JC. (2013). Good mood food. Positive emotion as a neglected trigger for food intake. Appetite. 68:1-7
Fisher, A.V., Enser, M., Richardson, R.I., Wood, J.D., Nute, G.R., Kurt, E., Sinclair, L.A., Wilkinson, R.G. (2000). Fatty acid composition and eating quality of lamb types derived from four diverse breed X production systems. Meat Science 55, 141 -147.
Font-i-Furnols, M., Guerrero, L. (2014). Consumer preference, behavior and perception about meat and meat products: An overview. Meat Science 98, 361–371
Foster C, Green K, Bleda M, Dewick P, Evans B, Flynn A, Mylan J (2006) Environmental impacts of food production and consumption: a report to the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. Manchester Business School, DEFRA, London. https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/69436/pb13644-milk-envsocecon-impacts-080111.pdf
Fung, T.T., Schultz, M., Manson, J.E., Willett, W., Hu, F. (2004). Dietary Patterns, Meat Intake, and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in Women. Archives of Internal Medicine, 2004; 164, 2235-2240
Galizzi, MM. (2012). Label, Nudge or Tax? A Review of Health Policies for Risky Behaviours, J Public Health Res. 1(1): 14–21.
Gerber, P.J., Steinfeld, H., Henderson, B., Mottet, A., Opio, C., Dijkman, J., Falcucci, A. & Tempio, G. (2013). Tackling climate change through livestock. FAO, Rome
Goodman MK, Maye D, Holloway L (2010) Ethical foodscapes: premises, promises and possibilities. Environmental and Planning A 42:1782–1796
Grace D & McDermott J, (2015). Food safety: Reducing and managing food scares, 2014–2015 Global Food Policy Report, Washington, USA: International Food Policy Research Institute.
Grunert, K.G., Lone Bredahl, Karen Brunsø (2004). Consumer perception of meat quality and implications for product development in the meat sector—a review. Meat Science 66, 259–272.
Grunert, K.G. (2006). Future trends and consumer lifestyles with regard to meat consumption. Meat Science, 74, 149 – 160.
Hagger MS, Wood C, Stiff C, Chatzisarantis NL. (2010). Ego depletion and the strength model of self-control: a meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 136(4):495-525.
Herrero M, Grace D, Njuki J, Johnson N, Enahoro D, Silvestri S, Rufino M., (2013) The roles of livestock in developing countries. Animal: An International Journal of Animal Bioscience.7(s1):3–18
Hofmann W, Rauch W, Gawronski B. (2007). And deplete us not into temptation: Automatic attitudes, dietary restraint, and self-regulatory resources as determinants of eating behavior. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology. 43:497–504
International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) Monograph on Red Meat and Processed Meat. https://www.iarc.fr/en/media-centre/pr/2015/pdfs/pr240_E.pdf. Accessed 8th November 2015
ISO (International Organization for Standardization), 1997. ISO 14040. Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Principles and Framework.
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) (2006). ISO 14040:2006(E) Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Principles and Framework.
Jabbar MA, Baker D, Fadiga ML (eds). (2010). Demand for livestock products in developing countries with a focus on quality and safety attributes: Evidence from case studies. Research Report 24. Nairobi, Kenya, ILRI.
King CT (2014). Vegetarian, vegan and pescetarian consumers and their participation in the green movement. College of Business Administration and in the Burnett Honors College at the University of Central Florida. http://etd.fcla.edu/CF/CFH0004582/Cory_King_T_201404_BSBA.pdf. Accessed 4 November 2015
Koeth, R.A., Wang, Z., Levison, B., Buffa, J.A., Org, E., Sheehy, B.T., Britt, E.B., Fu, X., Wu, Y., Li, L., Smith, J.D., DiDonato, J., Chen, J., Li, H., Wu, G.D., Lewis, J.D., Warrier, M., Brown, J.M., Krauss, R.M., Tang, W.H.W., Bushman, F.D., Lusis, A.J., Hazen, S.L. (2013). Intestinal microbiota metabolism of l-carnitine, a nutrient in red meat, promotes atherosclerosis. Nature Medicine 19, 576–585.
Levine JA. (2011). Poverty and obesity in the U.S. Diabetes. 60(11):2667-8.
Lozano, R. et al. (2012). Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010, The Lancet, 380 (9859) 2095 – 2128
McMichael, A.J., Powles, J.W., Butler, C.D., Uauy, R. (2007). Food, livestock production, energy, climate change, and health. Lancet, 370: 1253–63.
Maki KC, Slavin JL, Rains TM, Kris-Etherton PM. (2014). Limitations of observational evidence: implications for evidence-based dietary recommendations. Adv Nutr. 5:7-15.
Mani A, Mullainathan S, Shafir E, and Zhao J. (2013). Poverty impedes cognitive function. Science. 341: 976-980.
Meat Free Mondays. http://www.meatfreemondays.com/. Accessed 4 July 2015
Morris S.S.; Cogill, B. and Uauy, R. Maternal and Child Undernutrition Study Group (2008) ‘Effective International Action Against Undernutrition: Why Has it Proven So Difficult and What can be Done to Accelerate Progress? Lancet 371(9608): 608–21
Nielsen (2013). Why retailers are keeping it fresh. Fresh foods not spoiled by inflationary heat. The Nielsen Company, March 2013. http://www.nielsen.com/content/dam/corporate/mx/reports/2013/Nielsen%20Global%20Fresh%20Foods%20Report.pdf. Accessed 4 July 2015.
O’Donovan, P., McCarthy, M. (2002). Irish consumer preference for organic meat. British Food Journal, 104, 353 - 370
Oliver, M.A., Nute, G.R., Font, M., Furnols, i., San Julia, R., Campo, M.M., Sanudo, C., Caneque, V., Guerrero, L., Alvarez, I., Dıaz, M.T., Branscheid, W., Wicke, M., Montossi, F., (2006). Eating quality of beef, from different production systems, assessed by German, Spanish and British consumers. Meat Science 74, 435–442.
Pandurangan, M., Kim, D.H. (2015). A novel approach for in vitro meat production. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 99, Issue 13, 5391-5395.
Rose D, Bodor JN, Hutchinson PL, Swalm CM. (2010) The importance of a multi-dimensional approach for studying the links between food access and consumption. The Journal of Nutrition 140:1170–74.
Roth DA, Herman CP, Polivy J, Pliner P. (2001). Self-presentational conflict in social eating situations: a normative perspective. Appetite. 36(2):165-71.
Roy, P., Daisuke Nei, Takahiro Orikasa, Qingyi Xu, Hiroshi Okadome, Nobutaka Nakamura, Takeo Shiina (2009). A review of life cycle assessment (LCA) on some food products. Journal of Food Engineering 90, 1–10
Schroeder, M.J. and McEachern, M.G. (2004). Consumer value conflicts surrounding ethical food purchase decisions: a focus on animal welfare. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 28, 2, 168–177.
Seufert V, Ramankutty N, Foley JA (2012) Comparing the yields of organic and conventional agriculture. Nature 485: 229–232
JL Stanton, JB Wiley, FF Wirth (2012) Who are the locavores? Journal of Consumer Marketing, 29(4):248–261
Stead M, McDermott L, Angus K, Hastings G., (2006). Marketing Review Final Report, Prepared for the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE), Institute for Social Marketing, University of Stirling & The Open University, Stirling, Scotland
Steinfeld H, Gerber P, Wassenaar T, Castel V, Rosales M, de Haan C (2006). Livestock’s long shadow: Environmental issues and options. FAO. Rome, Italy. Accessible online at: http://www.fao.org/docrep/010/a0701e/a0701e00.HTM
Solomon, M.R. (2007). Consumer Behavior. Buying, Having, and Being. 7th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Storcksdieck genannt Bonsmann, S., & Wills, J. M. (2012). Nutrition Labeling to Prevent Obesity: Reviewing the Evidence from Europe. Current Obesity Reports, 1(3), 134–140
Subak, S. (1998). Global environmental costs of beef production. Ecological Economics 30, 79–91
Sutin AR, Ferrucci L, Zonderman AB, Terracciano A. (2011). Personality and obesity across the adult life span. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 101(3):579-92.
Swinburn B, Egger G. (2002). Preventative strategies against weight gain and obesity. Obes Rev 2002; 3:289–301
Thaler RH, Sunstein CR. (2008). Nudge: improving decisions about health, wealth, and happiness. Yale University Press, New Heaven
Tilg H, Kaser A. (2011). Gut microbiome, obesity, and metabolic dysfunction. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 121(6):2126-32.
Tisdell, C., Lapar, ML, Staal, S, and Que, NN. (2010). “Natural protection from international competition in the livestock industry: analysis, examples and the Vietnam pork market as a case.” In: Lee, TH (ed.). Agricultural Economics: New Research. Nova Science Publish-ers, Inc.
Tonsor, G.T., Olynk, N., Wolf, C. (2009). Consumer Preferences for Animal Welfare Attributes: The Case of Gestation Crates. Journal of Agricultural and Applied Economics, 41:713–730
Vabø M and Hansen H. (2014). The Relationship between Food Preferences and Food Choice: A Theoretical Discussion. International Journal of Business and Social Science Vol. 5, No. 7, 145-157.
Wansink B., Chandon J. (2006). Can “low-fat” nutrition labels lead to obesity? J. Market. Res. 43, 605–617
WHO (2015). Obesity and overweight. Fact Sheet 311. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/. Accessed 5th July 2015
World Obesity Federation (2015). http://www.iaso.org/iotf/obesity/obesitytheglobalepidemic/. Accessed 5th July 2015
Ziraba AK, Fotso JC, Ochako R. (2009). Overweight and obesity in urban Africa: A problem of the rich or the poor? BMC Public Health; 9: 465
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perry, B.D., Grace, D.C. How Growing Complexity of Consumer Choices and Drivers of Consumption Behaviour Affect Demand for Animal Source Foods. EcoHealth 12, 703–712 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10393-015-1091-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10393-015-1091-7