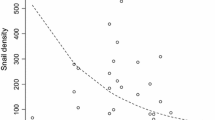
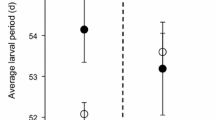
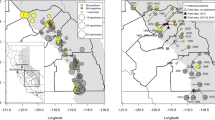
Abstract
Understanding linkages between environmental changes and disease emergence in human and wildlife populations represents one of the greatest challenges to ecologists and parasitologists. While there is considerable interest in drivers of amphibian microparasite infections and the resulting consequences, comparatively little research has addressed such questions for amphibian macroparasites. What work has been done in this area has largely focused on nematodes of the genus Rhabdias and on two genera of trematodes (Ribeiroia and Echinostoma). Here, we provide a synopsis of amphibian macroparasites, explore how macroparasites may affect amphibian hosts and populations, and evaluate the significance of these parasites in larger community and ecosystem contexts. In addition, we consider environmental influences on amphibian–macroparasite interactions by exploring contemporary ecological factors known or hypothesized to affect patterns of infection. While some macroparasites of amphibians have direct negative effects on individual hosts, no studies have explicitly examined whether such infections can affect amphibian populations. Moreover, due to their complex life cycles and varying degrees of host specificity, amphibian macroparasites have rich potential as bioindicators of environmental modifications, especially providing insights into changes in food webs. Because of their documented pathologies and value as bioindicators, we emphasize the need for broader investigation of this understudied group, noting that ecological drivers affecting these parasites may also influence disease patterns in other aquatic fauna.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albon SD, Stien A, Irvine RJ, Langvatn R, Ropstad E, Halvorsen O (2002) The role of parasites in the dynamics of a reindeer population. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series B 269:1625–1632
Anderson RC (2000) Nematode Parasites of Vertebrates: Their Development and Transmission, second edition, Wallingford: CABI Publishing
Anthony CD, Mendelson JR, Simons RR (1994) Differential parasitism by sex on plethodontid salamanders and histological evidence for structural damage to the nasolabial groove. American Midland Naturalist 132: 302–307.
Barton DP (1998) Dynamics of natural infections of Rhabdias cf. hylae (Nematoda) in Bufo marinus (Amphibia) in Australia. Parasitology 117: 505-513
Beasley VR, Faeh SA, Wikoff B, Staehle C, Eisold J, Nichols D, et al. (2005) Risk factors and the decline of the cricket frog, Acris crepitans: evidence for involvement of herbicides, parasitism, and habitat modifications. In: Amphibian Declines: The Conservation Status of United States Species, Lannoo MJ (editor), Chicago: University of Chicago Press, pp 75-87
Belden LK (2006) Impact of eutrophication on wood frog tadpoles, Rana sylvatica, infected with Echinostoma trivolvis cercariae. Canadian Journal of Zoology 84: 1315-1321
Belden LK, Kiesecker JM (2005) Glucocorticosteroid hormone treatment of larval treefrogs increases infection by Alaria sp. trematode cercariae. Journal of Parasitology 91: 686–688
Belden LK, Harris RN (2007) Infectious diseases in wildlife: the community ecology context. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 10: 533-539
Belden LK, Wojdak JM (2011) The combined influence of trematode parasites and predatory salamanders on wood frog (Rana sylvatica) tadpoles. Oecologia 166: 1077-1086
Berven KA, Boltz RS (2001) Interactive effects of Leech (Desserobdella picta) infection on Wood Frog (Rana sylvatica) tadpole fitness traits. Copeia 2001: 907-915
Blanar CA, Munkittrick KR, Houlahan J, Maclatchy DL, Marcogliese DJ (2009) Pollution and parasitism in aquatic animals: a meta-analysis of effect size. Aquatic Toxicology 93:18-28
Bolek MG, Coggins JR (2002) Observations on myiasis by the calliphorid, Bufolucilia silvarum, in the eastern American toad (Bufo americanus americanus) from southeastern Wisconsin. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 38: 598-603
Bolek MG, Janovy Jr. J (2004) Observations on myiasis by the calliphorids, Bufolucilia silvarum and Bufolucilia elongata, in wood frogs, Rana sylvatica, from southeastern Wisconsin. Journal of Parasitology 90: 1169-1171
Bolek MG, Janovy Jr. J (2008) Alternative life cycle strategies of Megalodiscus temperatus in tadpoles and metamorphosed anurans. Parasite 15: 396-401
Bolek MG, Snyder SD, Janovy Jr. J (2009) Alternative life cycle strategies and colonization of young anurans by Gorgoderina attenuata in Nebraska. Journal of Parasitology 95: 604-616
Brayton C (1992) Wasting disease associated with cutaneous and renal nematodes. Annals of the New York Academy of Science 653:197-201
Brockelman WY (1969) An analysis of density effects and predation in Bufo americanus tadpoles. Ecology 50: 632-644
Budischak SA, Belden LK, Hopkins WA (2008) Effects of Malathion on embryonic development and latent susceptibility to trematode parasites in ranid tadpoles. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 27: 2496-2500
Byers JE, Altman I, Grosse AM, Huspeni TC, Maerz JC (2011) Using parasitic trematode larvae to quantify an elusive vertebrate host. Conservation Biology 25: 85-93
Christin MS, Gendron AD, Brousseau P, Ménard L, Marcogliese DJ, Cyr D, et al. (2003) Effects of agricultural pesticides on the immune system of Rana pipiens and on its resistance to parasitic infection. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 22: 1127-1133.
Cohen N, Effrige NJ, Parsons SC, Rollins-Smith LA, Nagata S, Albright D (1984) Identification and treatment of a lethal nematode (Capillaria xenopodis) infestation in the South African frog, Xenopus laevis. Developmental and Comparative Immunology 8:739-741
Collins JP, Crump ML (2009) Extinction in Our Times: Global Amphibian Decline. New York: Oxford University Press
Cort WW, Brackett S (1938). A new strigeid cercaria which produces a bloat disease of tadpoles. Journal of Parasitology 24: 263-271
Daly EW, Johnson PTJ (2010) Beyond immunity: quantifying the effects of host anti-parasite behavior on parasite transmission. Oecologia 165: 1043-1050
Dare OK, Rutherford PL, Forbes MR (2006) Rearing density and susceptibility of Rana pipiens metamorphs to cercariae of a digenetic trematode. Journal of Parasitology 92:543-547
Daszak P, Cunningham AA, Hyatt AD (2000) Emerging infectious diseases of wildlife: threats to biodiversity and human health. Science 287:443-449
Elkan E (1960). Some interesting pathological cases in amphibians. Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London 134: 275-296
Etges FT (1961). Contributions to the life history of the brain fluke of newts and fish, Diplostomulum scheuringi Hughes 1929 (Trematoda. Diplostomatidae). Journal of Parasitology 47: 453-458
Fried B, Pane PL, Reddy A (1997) Experimental infection of Rana pipiens tadpoles with Echinostoma trivolvis cercariae. Parasitology Research 83: 666-669
Gendron AD, Marcogliese DJ, Barbeau S, Christin M-S, Brousseau P, Ruby S, et al. (2003) Exposure of leopard frogs to a pesticide mixture affects life history characteristics of the lungworm Rhabdias ranae. Oecologia 135: 469-476
Goater CP, Ward PI (1992) Negative effects of Rhabdias bufonis (Nematoda) on the growth and survival of toads (Bufo bufo). Oecologia 89: 161-165
Goater CP, Semlitsch RD, Bernasconi MV (1993) Effects of body size and parasite infection on the locomotory performance of juvenile toads Bufo bufo. Oikos 66: 129-136
Goin CJ, Ogren LH (1956) Parasitic copepods (Argulidae) on amphibians. Journal of Parasitology 42: 172
Goodman BA, Johnson PTJ (2011a) Disease and the extended phenotype: parasites control host performance and survival through induced changes in body plan. PLoS ONE 6: e20193
Goodman BA, Johnson PTJ (2011b) Ecomorphology and disease: understanding the cryptic effects of parasitism on host habitat use, thermoregulation, and predator avoidance. Ecology 92: 542-548
Gray MJ, Miller DL, Hoverman JT (2009) Ecology and pathology of amphibian ranaviruses. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 87: 243-266
Green D, Muths E (2005) Health evaluation of amphibians in and near Rocky Mountain National Park (Colorado, USA). Alytes (Paris) 22: 109-129
Griffin CT (1988) The effect of constant and changing temperatures on the development of the eggs and larvae of Oswaldocruzia filiformis (Nematoda: Trichostrongyloidea). Journal of Helminthology 62: 281-292
Griggs JL, Belden LK (2008) Effects of atrazine and metolachlor on the survivorship and infectivity of Echinostoma trivolvis trematode cercariae. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 54: 195-202
Hakalahti T, Karvonen A, Valtonen ET (2006) Climate warming and disease risks in temperate regions – Argulus coregoni and Diplostomum spathaceum as case studies. Journal of Helminthology 80: 93-98
Harvell CD, Mitchell CE, Ward JR, Altizer S, Dobson AP, Ostfield RS, et al. (2002) Ecology – Climate warming and disease risks for terrestrial and marine biota. Science 296: 2158-2162
Hatcher MJ, Dick JTA, Dunn AM (2006) How parasites affect interactions between competitors and predators. Ecology Letters 9: 1253-1271
Hechinger RF, Lafferty KD (2005) Host diversity begets parasite diversity: bird final hosts and trematodes in snail intermediate hosts. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series B 272: 1059-1066
Hendrikx WML, Van Moppes MC (1983) Oswaldocruzia filiformis (Nematoda: Trichostrongylidae): Morphology of developmental stages, parasitic development and some pathological aspects of the infection in amphibians. Parasitology Research 69: 523–537
Holland MP (2010) Echinostome-induced mortality varies across amphibian species in the field. Journal of Parasitology 96: 851-855
Holland MP, Skelly DK, Kashgarian M, Bolden SR, Harrison LM, Cappello M (2007) Echinostome infection in green frogs (Rana clamitans) is stage and age dependent. Journal of Zoology 271: 455-462
Holmstead PR, Hudson PJ, Skorping A (2005) The influence of a parasite community on the dynamics of a host population: A longitudinal study on willow ptarmigan and their parasites. Oikos 111:377-391
Holyoak MM, Leibold A, Mouquet NM, Holt RD, Hoopes MF (2005) Metacommunities: A framework for large-scale community ecology. In: Metacommunities: spatial dynamics and ecological communities, Holyoak M, Leibold MA, Holt RD (editors), Chicago: University of Chicago Press, pp 1-31
Hopkins WA (2007) Amphibians as models for studying environmental change. Institute for Laboratory Animal Research Journal 48: 270-277
Hsu CC, Carter DB, Williams DA, Besch-Williford CL (2004) Haematoloechus sp. infection in wild-caught northern leopard frogs (Rana pipiens). Contemporary Topics in Laboratory Animal Science. 43: 14-16
Hudson PJ, Dobson AP, Newborn D (1992) Do parasites make prey vulnerable to predation? Red grouse and parasites. Journal of Animal Ecology 61: 681-692
Hudson PJ, Dobson AP, Newborn D (1998) Prevention of population cycles by parasite removal. Science 282: 2256-2258
Hudson PJ, Dobson AP, Lafferty KD (2006) Is a healthy ecosystem one that is rich in parasites?. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 21: 381-385
Jayawardena UA, Rajakaruna RS, Navaratne AN, Amerasinghe PH (2010) Monostome cercariae induced malformations in amphibians: effect of infection at the pre-limb-bud stag tadpoles of Polypedates cruciger Blyth. Journal of the National Science Foundation of Sri Lanka 38: 241-248
Johnson PTJ, Chase JM (2004) Parasites in the food web: linking amphibian malformations and aquatic eutrophication. Ecology Letters 7: 521-526
Johnson PTJ, Thieltges DW (2010). Diversity, decoys and the dilution effect: how ecological communities affect disease risk. Journal of Experimental Biology 213: 961-970
Johnson PTJ, Lunde KB, Ritchie EG, Launer AE (1999) The effect of trematode infection on amphibian limb development and survivorship. Science 284: 802-804
Johnson PTJ, Lunde KB, Haight RW, Bowerman J, Blaustein AR (2001) Ribeiroia ondatrae (Trematoda: Digenea) infection induces severe limb malformations in western toads (Bufo boreas). Canadian Journal of Zoology 79: 370-379
Johnson PTJ, Lunde KB, Thurman EM, Ritchie EG, Wray SW, Sutherland DR, et al. (2002) Parasite (Ribeiroia ondatrae) infection linked to amphibian malformations in the western United States. Ecological Monographs 72: 151-168
Johnson PTJ, Lunde KB, Zelmer DA, Werner JK (2003) Limb deformities as an emerging parasitic disease in amphibians: Evidence from museum specimens and resurvey data. Conservation Biology 17: 1724-1737
Johnson PTJ, Preu ER, Sutherland DR, Romansic J, Han B, Blaustein AR (2006). Adding infection to injury: Synergistic effects of predation and parasitism on salamander limb malformations. Ecology 87: 2227-2235
Johnson PTJ, Chase JM, Dosch KL, Hartson RB, Gross JA, Larson DJ, et al. (2007) Aquatic eutrophication promotes pathogenic infection in amphibians. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 104: 15781-15786
Johnson PTJ, Hartson RB, Larson DJ, Sutherland DR (2008) Diversity and disease: community structure drives parasite transmission and host fitness. Ecology Letters 11: 1017-1026
Johnson PTJ, Lund PJ, Hartson RB, Yoshino TP (2009) Community diversity reduces Schistosoma mansoni transmission and human infection risk. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series B 276: 1657-1663
Johnson PTJ, Townsend AR, McKenzie VJ, Howarth R, Rejmankova E, Glibert P (2010a). Linking environmental nutrient enrichment and disease emergence in humans and wildlife. Ecological Applications 20: 16-29
Johnson PTJ, Dobson A, Lafferty KD, Marcogliese DJ, Memmott J, Orlofske S, et al. (2010b). When parasites become prey: ecological and epidemiological significance. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 25: 362-371
Johnson PTJ, Kellermanns E, Bowerman J (2011) Critical windows of disease risk: amphibian pathology driven by developmental changes in host resistance and tolerance. Functional Ecology 25: 726-734
Johnson PTJ, Preston DL, Hoverman JT, Henderson JS, Paull SH, Redmond MD (2012) Species diversity reduces parasite infection through cross-generational effects on host density. Ecology 93: 56-64
Jones KE, Patel N, Levy MA, Storeygard A, Balk D, Gittleman JL, Daszak P (2008) Global trends in human emerging infectious diseases. Nature 451: 990-993
Keesing F, Holt RD, Ostfeld RS (2006) Effects of species diversity on disease risk. Ecology Letters 9: 485-498
Keesing F, Belden LK, Daszak P, Dobson A, Harvell CD, Holt RD, et al. (2010) Impacts of biodiversity on the emergence and transmission of infectious diseases. Nature 468: 647- 652
Kelehear C, Jones HI (2010) Nematode larvae (Order Spirurida) in gastric tissues of Australian anurans: a comparison between the introduced cane toad and sympatric native frogs. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 46: 1126-1140
Kelehear C, Webb JK, Shine R (2009) Rhabdias pseudosphaerocephala infection in Bufo marinus: lung nematodes reduce viability of metamorph cane toads. Parasitology 136: 919-927
Kelehear C, Brown GP, Shine R (2011) Influence of lung parasites on the growth rates of free ranging and captive adult cane toads. Oecologia 165: 585-592
Kelly DW, Poulin R, Tompkins DM, Townsend CR (2009) Synergistic effects of glyphosate formulation and parasite infection on fish malformations and survival. Journal of Applied Ecology 47: 498-504
Kerby JL, Richards-Hrdlicka KL, Storfer A, Skelly DK (2010) An examination of amphibian sensitivity to environmental contaminants: are amphibians poor canaries? Ecology Letters 13: 60-67
Kiesecker JM (2002) Synergism between trematode infection and pesticide exposure: A link to amphibian limb deformities in nature? Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 99: 9900-9904
Kiesecker JM, Skelly DK (2001) Effects of disease and pond drying on gray tree frog growth, development and survival. Ecology 82: 1956-1963
Kilpatrick AM, Briggs CJ, Daszak P (2010) The ecology and impact of chytridiomycosis, an emerging disease of amphibians. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 25: 109-118
King KC, McLaughlin JD, Gendron AD, Pauli BD, Giroux I, Rondeau B, et al. (2007) Impact of agriculture on the parasite communities of northern leopard frogs (Rana pipiens) in southern Quebec, Canada. Parasitology 134: 2063-2080
King KC, Gendron AD, McLaughlin JD, Giroux I, Brousseau P, Cyr D, et al. (2008) Short-term seasonal changes in parasite community structure in northern leopard froglets (Rana pipiens) inhabiting agricultural wetlands. Journal of Parasitology 94: 13-22
King KC, Mclaughlin JD, Boily M, Marcogliese DJ (2010) Effects of agricultural landscape and pesticides on parasitism in native bullfrogs. Biological Conservation 143: 302-310
Koprivnikar J (2010) Interactions of environmental stressors impact survival and development of parasitized larval amphibians. Ecological Applications 20: 2263–2272
Koprivnikar J, Redfern JC Agricultural effects on amphibian parasitism: importance of general habitat perturbations and parasite life cycles. Journal of Wildlife Diseases (in press)
Koprivnikar J, Forbes MR, Baker RL (2006a) Effects of atrazine on cercarial longevity, activity, and infectivity. Journal of Parasitology 92: 306-311
Koprivnikar J, Forbes MR, Baker RL (2006b) On the efficacy of anti-parasite behaviour: a case study of tadpole susceptibility to cercariae of Echinostoma trivolvis. Canadian Journal of Zoology 84: 1623-1629
Koprivnikar J, Forbes MR, Baker RL (2007) Contaminant effects on host-parasite interactions: atrazine, frogs, and trematodes. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 26: 2166-2170
Koprivnikar J, Forbes MR, Baker RL (2008) Larval amphibian growth and development under varying density: are parasitized individuals poor competitors? Oecologia 155: 641-649
Koprivnikar J, Gibson CH, Redfern JC (2012) Infectious personalities: behavioural syndromes and disease risk in larval amphibiansProceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series B 279: 1544-1550
Kupferberg SJ, Catenazzi A, Lunde K, Lind AJ, Palen WJ (2009) Parasitic copepod (Lernaea cyprinacea) outbreaks in foothill yellow-legged frogs (Rana boylii) linked to unusually warm summers and amphibian malformations in northern California. Copeia 3: 529-537
Lafferty KD (2008) Ecosystem consequences of fish parasites. Journal of Fish Biology 73: 2083-2093
Lafferty KD, Holt RD (2003) How should environmental stress affect the population dynamics of disease? Ecology Letters 6: 654-664
Lafferty KD, Allesina S, Arim M, Briggs CJ, De Leo G, Dobson AP, et al. (2008) Parasites in food webs: the ultimate missing links. Ecology Letters 11: 533-546
Leibold MA, Holyoak M, Mouquet N, Amarasekare P, Chase JM, Hoopes MF, et al. (2004) The metacommunity concept: a framework for multi-scale community ecology. Ecology Letters 7: 601–613
Lips KR, Brem F, Brenes R, Reeve JD, Alford RA, Voyles J, et al. (2006) Emerging infectious disease and the loss of biodiversity in a Neotropical amphibian community. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 103: 3165-3170
Locke SA, McLaughlin JD, Lapierre AR, Johnson PTJ, Marcogliese DJ (2011) Linking larvae and adults of Apharyngostrigea cornu, Hysteromorpha triloba and Alaria mustelae (Diplostomoidea, Digenea) using molecular data. Journal of Parasitology 97: 846-851
MacKenzie K, Williams, HH, Williams B, McVicar AH, Siddall R (1995) Parasites as indicators of water quality and the potential use of helminth transmission in marine pollution studies. Advances in Parasitology 35: 85-144
Marcogliese DJ (2001) Implications of climate change for parasitism of animals in the aquatic environment. Canadian Journal of Zoology 79: 1331-1352
Marcogliese DJ (2004) Parasites: small players with crucial roles in the ecological theatre. EcoHealth 1: 151-164
Marcogliese DJ (2005) Parasites of the superorganism: are they indicators of ecosystem health? International Journal for Parasitology 35: 705-716
Marcogliese DJ (2008) The impact of climate change on the parasites and diseases of aquatic animals. Revue Scientifique et Technique de l’OIE 27: 467-484
Marcogliese DJ, Cone DK (1997) Parasite communities as indicators of ecosystem stress. Parasitologia 39: 227-232
Marcogliese DJ, Pietrock M (2011) Combined effects of parasites and contaminants on animal health: Parasites do matter. Trends in Parasitology 27: 123-130
Marcogliese DJ, King KC, Salo HM, Fournier M, Brousseau P, Spear P, et al. (2009) Combined effects of agricultural activity and parasites on biomarkers in the bullfrog, Rana catasbeiana. Aquatic Toxicology 91:126-134
Marr SR, Johnson SA, Hara AH, McGarrity ME (2010) Preliminary evaluation of the potential of the helminth parasite Rhabdias elegans as a biological control agent for invasive Puerto Rican coquis, Eleutherodactylus coqui, in Hawaii. Biological Control 54: 69-74
Martínez-Solano I, González EG (2008) Patterns of gene flow and source-sink dynamics in high altitude populations of the common toad Bufo bufo (Anura: Bufonidae). Biological Journal of the Linnean Society 95: 824-839
McKenzie VJ (2007) Human land use and patterns of parasitism in tropical amphibian hosts. Biological Conservation 137: 102-116
McKenzie VJ, Townsend AR (2007) Parasitic and infectious disease responses to a changing nitrogen cycle. EcoHealth 4: 384-396
Merilä J, Sterner M (2002) Medicinal leeches (Hirudo medicinalis) attacking and killing adult amphibians. Annales Zoologici Fennici 39: 343-346
Morley NJ, Adam ME, Lewis JW (2010) The effects of host size and temperature on the emergence of Echinoparyphium recurvatum cercariae from Lymnaea peregra under natural light conditions. Journal of Helminthology 84: 317–326
Mouritsen KN, Tompkins DM, Poulin R (2005) Climate warming may cause a parasite-induced collapse in coastal amphipod populations. Oecologia 146: 476-483
Murray DL, Cary JR, Keith LB (1997) Interactive effects of sublethal nematodes and nutritional status on showshoe hare vulnerability to predation. Journal of Animal Ecology 66: 250-264
Nigrelli RF, Maraventano LW (1944) Pericarditis in Xenopus laevis caused by Diplostomulum xenopi sp. nov., a larval strigeid. Journal of Parasitology 30: 184-190
Orlofske SA, Belden LK, Hopkins WA (2009) Moderate Echinostoma trivolvis infection has no effects on physiology and fitness-related traits of larval pickerel frogs (Rana palustris). Journal of Parasitology 95: 787-792
Orlofske SA, Jadin RC, Preston DL, Johnson PTJ (2012) Parasite transmission in complex communities: predators and alternative hosts alter pathogenic infections in amphibians. Ecology 93: 1247-1253
Ostfeld RS, Glass GE, Keesing F (2005) Spatial epidemiology: an emerging (or re-emerging) discipline. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 20: 328-336
Ostfeld RS, Keesing F, Eviner VT (2008) Infectious disease ecology: effects of ecosystems on disease and of disease on ecosystems, Princeton: Princeton University Press
Paull SH, Johnson PTJ (2011) How will climate change affect host-parasite interactions? Understanding differential responses of hosts and parasites. Freshwater Biology 56: 767-778
Paull SH, Johnson PTJ (2012) Can we predict climate-driven changes to disease dynamics? Applications for theory and management in the face of uncertainty. In: Brodie J, Post E, Doak D (eds) Wildlife conservation in a changing climate. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Pechmann JHK, Scott DE, Semlitsch RD, Caldwell JP, Vitt LJ, Gibbons JW (1991) Declining amphibian populations: the problem of separating human impacts from natural fluctuations. Science 253: 892-895
Perpinan D, Garner MM, Trupkiewicz JG, Malarchik J, Armstrong DL, Lucio-Forster A, et al. (2010) Scoliosis in a tiger salamander (Ambystoma tigrinum) associated with encysted digenetic trematodes of the genus Clinostomum. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 46: 579-584
Pfeiffer DU, Hugh-Jones M (2002) Geographical information systems as a tool in epidemiological assessment and wildlife disease management. Revue Scientifique et Technique de l’OIE 21: 91-102
Pietrock M, Marcogliese DJ (2003) Free-living endohelminth stages: at the mercy of environmental conditions. Trends in Parasitology 19: 293-299
Pizzatto L, Shine R (2011) The effects of experimentally infecting Australian tree frogs with lungworms (Rhabdias pseudosphaerocephala) from invasive cane toads. International Journal for Parasitology 41: 943-949
Pizzatto L, Shilton CM, Shine S (2010) Infection dynamics of the lungworm Rhabdias pseudosphaerocephala in its natural host, the cane toad (Bufo marinus), and in novel hosts (native Australian frogs). Journal of Wildlife Diseases 46: 1152-1164
Plasota K (1969) The effect of some ecological factors on the parasitofauna of frogs. Acta Parasitologica Polonica 16: 47-60
Poulin R (2006) Global warming and temperature-mediated increases in cercarial emergence in trematode parasites. Parasitology 132: 143-151
Poulin R (2010) Network analysis shining light on parasite ecology and diversity. Trends in Parasitology 26: 492-498
Pounds JA, Crump ML (1987) Harlequin frogs along a tropical montane stream: aggregation and the risk of predation by frog-eating flies. Biotropica 19: 306-309.
Prudhoe S, Bray RA (1982) Platyhleminth parasites of the Amphibia. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Råberg L, Graham AL, Read AF (2009) Decomposing health: tolerance and resistance to parasites in animals. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B-Biological Sciences 364: 37-49
Raffel TR, Rohr JR, Kiesecker JM, Hudson PJ (2006a) Negative effects of changing temperature on amphibian immunity under field conditions. Functional Ecology 20: 819-828
Raffel TR, LeGros RP, Love BC, Rohr JR, Hudson PJ (2006b) Parasite age-intensity relationships in red-spotted newts: Does immune memory influence salamander disease dynamics? International Journal for Parasitology 39: 231- 241
Raffel TR, Hoverman JR, Halstead NT, Michel P, Rohr JR (2010) Parasitism in a community context: Trait-mediated interactions with competition and predation. Ecology 91:1900- 1907
Raffel TR, Lloyd-Smith JO, Sessions SK, Hudson PJ, Rohr JR (2011) Does the early frog catch the worm? Disentangling potential drivers of a parasite age-intensity relationship in tadpoles. Oecologia 165: 1031-1042
Rajakaruna RS, Piyatissa PMJR, Jayawardena UA, Navaratne AN, Amerasinghe PH (2008) Trematode infection induced malformations in the common hourglass treefrogs. Journal of Zoology 275: 89–95
Read AF, Graham AL, Raberg L (2008) Animal defenses against infectious agents: is damage control more important than pathogen control? PLoS Biology 6: 2638–2641
Rohr JR, McCoy KA (2010) A quantitative meta-analysis reveals consistent effects of atrazine on freshwater fish and amphibians. Environmental Health Perspectives 118: 20-32
Rohr JR, Raffel TR (2010) Linking global climate and temperature variability to widespread amphibian declines putatively caused by disease. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 107:8269–8274
Rohr JR, Schotthoefer AM, Raffel TR, Carrick HJ, Halstead N, Hoverman JT, et al. (2008a) Agrochemicals increase trematode infections in a declining amphibian species. Nature 455: 1235-1240
Rohr JR, Raffel TR, Sessions SK, Hudson PJ (2008b) Understanding the net effects of pesticides on amphibian trematode infections. Ecological Applications 18: 1743-1753
Rohr JR, Swan A, Raffel TR, Hudson PJ (2009) Parasites, info-disruption, and the ecology of fear. Oecologia 159: 447-454
Rohr JR, Raffel TR, Hall CA (2010) Developmental variation in resistance and tolerance in a multi-host–parasite system. Functional Ecology 24: 1110–1121
Rohr JR, Dobson AP, Johnson PTJ, Kilpatrick AM, Paull SH, Raffel TR, et al. (2011) Frontiers in climate change-disease research. Trends in Ecology and Evolution. 26: 270-277
Schotthoefer AM, Koehler AV, Meteyer CU, Cole RA (2003a) Influence of Ribeiroia ondatrae (Trematoda: Digenea) infection on limb development and survival of northern leopard frogs (Rana pipiens), effects of host stage and parasite-exposure level. Canadian Journal of Zoology 81: 1144-1153
Schotthoefer AM, Cole RA, Beasley VR (2003b) Relationship of tadpole stage to location of echinostome cercariae encystment and the consequences for tadpole survival. Journal of Parasitology 89: 475-482
Schotthoefer AM, Labak KM, Beasley R (2007) Ribeiroia ondatrae cercariae are consumed by aquatic invertebrate predators. Journal of Parasitology 93: 1240–1243
Schotthoefer AM, Rohr JR, Cole RA, Koehler AV, Johnson CM, Johnson LB, et al. (2011) Effects of wetland and landscape variables on parasite communities of Rana pipiens: links to anthropogenic changes. Ecological Applications 21: 1257-1271
Sessions SK, Ruth SB (1990) Explanation for naturally-occurring supernumerary limbs in amphibians. Journal of Experimental Zoology 254: 38-47
Shields JD (1987) Pathology and mortality of the lung fluke Haematoloechus longiplexus (Trematoda) in Rana catesbeiana. Journal of Parasitology 73: 1005-1013
Shutler D, Smith TG, Robinson SR (2009) Relationship between leukocytes and Hepatozoon spp. in green frogs, Rana clamitans. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 45: 67-72
Skelly DK, Bolden SR, Holland MP, Friedenburg LK, Friedenfelds NA, Malcom TR (2006) Urbanization and disease in amphibians. In: Disease ecology: community structure and pathogen dynamics, Collinge SK, Ray C (editors), Cary, NC: Oxford University Press, pp 153-167
Skerratt LF, Berger L, Speare R, Cashins S, McDonald KR, Phillott AD, et al. (2007) Spread of chytridiomycosis has caused the rapid global decline and extinction of frogs. Ecohealth 4: 125-134
Sladky KK, Norton TM, Loomis MR (2000) Trombiculid mites (Hannemania sp.) in canyon tree frogs (Hyla arenicolor). Journal of Zoo and Wildlife Medicine 31: 570–575
Stuart SN, Chanson JS, Cox NA, Young BE, Rodrigues ASL, Fischman DL, et al. (2004) Status and trends of amphibian declines and extinctions worldwide. Science 306: 1783-1786
Stunkard HW, Cable RM (1931) Notes on a species of Lernaea parasitic on the larva of Rana clamitans. Journal of Parasitology 18: 92-97
Sutherland DR (2005) Parasites of North American Frogs. In: Amphibian declines: the conservation status of United States species, Lannoo MJ (editor), California: University of California Press, pp. 109-123
Thieltges DW, Jensen KT, Poulin, R (2008) The role of biotic factors in the transmission of free-living endohelminth stages. Parasitology 135: 407-426
Thieltges DW, Hof C, Dehling DM, Braendle M, Brandl R, Poulin R (2011) Host diversity and latitude drive trematode diversity patterns in the European freshwater fauna. Global Ecology and Biogeography 20: 675-682
Thiemann GW, Wassersug RJ (2000) Patterns and consequences of behavioural responses to predators and parasites in Rana tadpoles. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society 71: 513-528
Thomas LJ (1937) Environmental relations and life history of the tapeworm Bothriocephalus rarus Thomas. Journal of Parasitology 23: 133-152
Tinsley RC (1995) Parasitic disease in amphibians: control by the regulation of worm burdens. Parasitology 111: S153-S178
Tinsley RC, Jackson JA (2002) Host factors limiting monogenean infections: A case study. International Journal for Parasitology 32:353–365
Tinsley RC, Cable J, Porter R (2002) Pathological effects of Pseudodiplorchis americanus (Monogenea: Polystomatidae) on the lung epithelium of its host, Scaphiopus couchii. Parasitology 125: 143-53.
Tinsley RC, York JE, Everard ALE, Stott LC, Chapple SJ, Tinsley MC (2011) Environmental constraints influencing survival of an African parasite in a north temperate habitat: effects of temperature on egg development. Parasitology 138: 1029-1038
Toque K (1993) The relationship between parasite burden and host resources in the desert toad (Scaphiopus couchii), under natural conditions. Journal of Animal Ecology 62: 683-693
Tocque K, Tinsley RC (1994) The relationship between Pseudodiplorchis americanus (Monogenea) density and host resources under controlled environmental conditions. Parasitology 108:175–183
Tompkins DM, Draycott RAH, Hudson PJ (2000) Field evidence for apparent competition mediated via the shared parasites of two gamebird species. Ecology Letters 3:10–14
Westfall MC, Cecala KK, Price SJ, Dorcas ME (2008) Patterns of trombiculid mite (Hannemania dunni) parasitism among plethodontid salamanders in the western piedmont of North Carolina. Journal of Parasitology 94: 631–634
Williams RW (1960) Observations on the Life History of Rhabdias sphaerocephala Goodey, 1924 from Bufo marinus L., in the Bermuda Islands. Journal of Helminthology 34: 93-98
Acknowledgments
We thank participants in the “Causes and Consequences of Helminth Infections in Amphibians” symposium held at the 2010 meeting of the American Society of Parasitologists for stimulating discussion on these topics and Matthew Bolek for valuable suggestions on earlier drafts of this paper. We would also like to gratefully acknowledge the late Daniel Sutherland for his contributions to amphibian parasitology. Support was provided by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada to JK, the Pesticide Science Fund (Environment Canada) to DJM, Grants from the US Department of Agriculture (NRI 2006-01370 and 2009-35102-0543) and the US Environmental Protection Agency (R833835) to JRR, a NSF Graduate Research Fellowship (DGE 0707432) to SAO, and a fellowship from the David and Lucile Packard Foundation and Grant from NSF (DEB-0841758) to PTJJ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koprivnikar, J., Marcogliese, D.J., Rohr, J.R. et al. Macroparasite Infections of Amphibians: What Can They Tell Us?. EcoHealth 9, 342–360 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10393-012-0785-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10393-012-0785-3