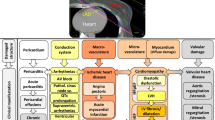
Abstract
Recently, the development of radiotherapy technology and to radiation-induced heart disease in patients with esophageal cancer. Investigations using chemotherapy has improved treatment results for esophageal cancer, and attention has been paidSEER for esophageal cancer showed that the hazard ratio of heart-related death was 1.62–1.96. Herein we review published literature regarding the mechanism of and countermeasures for radiation-induced heart disease and discuss the potential of concurrent chemotherapy, molecular-targeted agents and lifestyle for exacerbating radiation-induced heart disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ariga H, Nemoto K, Miyazaki S, et al. Prospective comparison of surgery alone and chemoradiotherapy with selective surgery in resectable squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;75(2):348–56.
Pöttgen C, Stuschke M. Radiotherapy versus surgery within multimodality protocols for esophageal cancer—a meta-analysis of the randomized trials. Cancer Treat Rev. 2012;38:599–604.
Guarneri V, Lenihan DJ, Valero V, et al. Long-term cardiac tolerability of trastuzumab in metastatic breast cancer: the M.D. Anderson Cancer Center experience. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4107.
Aleman BMP, van den Belt-Dusebout AW, Klokman WJ, et al. Long-term cause-specific mortality of patients treated for Hodgkin’s disease. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:3431–9.
Ozasa K, Takahashi I, Grant EJ. Radiation-related risks of non-cancer outcomes in the atomic bomb survivors. Ann ICRP. 2016;45(1 Suppl):253–61.
Jingu K, Matsushita H, Takeda K, et al. Results of chemoradiotherapy for stage I esophageal cancer in medically inoperable patients compared with results in operable patients. Dis Esophagus. 2013;26(5):522–7.
Jingu K, Umezawa R, Matsushita H, et al. Chemoradiotherapy for T4 and/or M1 lymph node esophageal cancer: experience since 2000 at a high-volume center in Japan. Int J Clin Oncol. 2016;21(2):276–82.
Umezawa R, Jingu K, Matsushita H, et al. Long-term results of chemoradiotherapy for stage II–III thoracic esophageal cancer in a single institution after 2000—with a focus on comparison of three protocols. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:813.
Nishimura Y, Jingu K, Itasaka S, et al. Clinical outcomes of radiotherapy for esophageal cancer between 2004 and 2008: the second survey of the Japanese Radiation Oncology Study Group (JROSG). Int J Clin Oncol. 2016;21(1):88–94.
Yamada S, Nemoto K, Takai Y, et al. Proposal for standard radiotherapy methods for superficial esophageal cancer: a multicenter retrospective evaluation. J JASTRO. 2000;12:169–76.
Ishikura S, Nihei K, Ohtsu A, et al. Long-term toxicity after definitive chemoradiotherapy for squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21(14):2697–702.
Frandsen J, Boothe D, Gaffney DK, et al. Increased risk of death due to heart disease after radiotherapy for esophageal cancer. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2015;6:516–23.
Gharzai L, Verma V, Denniston KA, et al. Radiation therapy and cardiac death in long-term survivors of esophageal cancer: an analysis of the surveillance, epidemiology, and end result database. PLoS One. 2016;11(7):e0158916.
Zamorano JL, Lancellotti P, Rodriguez Muñoz D, et al. 2016 ESC position paper on cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity developed under the auspices of the ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines: the task force for cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2016;37:2768–801.
Veinot JP, Edwards WD. Pathology of radiation-induced heart disease: a surgical and autopsy study of 27 cases. Hum Pathol. 1996;27(8):766–73.
Darby SC, Cutter DJ, Boerma M, et al. Radiation-related heart disease: current knowledge and future prospects. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;76:656–65.
Carmel RJ, Kaplan HS. Mantle irradiation in Hodgkin’s disease. An analysis of technique, tumour eradication, and complications. Cancer. 1976;37:2813–25.
Karram T, Rinkevitch D, Markiewicz W. Poor outcome in radiation-induced constrictive pericarditis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1993;25(2):329–31.
Wei X, Liu HH, Tucker SL, et al. Risk factors for pericardial effusion in inoperable esophageal cancer patients treated with definitive chemoradiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70:707–14.
Tamari K, Isohashi F, Akino Y, et al. Risk factors for pericardial effusion in patients with stage I esophageal cancer treated with chemoradiotherapy. Anticancer Res. 2014;34(12):7389–93.
Fukuda J, Shigematsu N, Takeuchi H, et al. Symptomatic pericardial effusion after chemoradiation therapy in esophageal cancer patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;87(3):487–93.
Nishizawa S, Nakamura T, Shiraishi H, et al. Successful treatment with low dose steroids for recurrent radiation pericarditis after chemoradiotherapy of lower esophageal cancer: a case report. Heart 2010;42:369–374 (Japanese).
Nishimura Y, Hiraoka M, Koike R, et al. Long-term follow-up of a randomized Phase II study of cisplatin/5-FU concurrent chemoradiotherapy for esophageal cancer (KROSG0101/JROSG021). Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2012;42(9):807–12.
Gladstone DJ, Flanagan MF, Southworth JB, et al. Radiation-induced cardiomyopathy as a function of radiation beam gating to the cardiac cycle. Phys Med Biol. 2004;49:1475–84.
Weintraub NL, Jones WK, Manka D. Understanding radiation-induced vascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55(12):1237–9.
Seddon B, Cook A, Gothard L, et al. Detection of defects in myocardial perfusion imaging in patients with early breast cancer treated with radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2002;64(1):53–63.
Umezawa R, Takase K, Jingu K, et al. Evaluation of radiation-induced myocardial damage using iodine-123 β-methyl-iodophenyl pentadecanoic acid scintigraphy. J Radiat Res. 2013;54(5):880–9.
Umezawa R, Takanami K, Kadoya N, et al. Assessment of myocardial metabolic disorder associated with mediastinal radiotherapy for esophageal cancer -a pilot study. Radiat Oncol. 2015;10(1):96.
Gyenes G, Rutqvist LE, Liedberg A, Fornander T. Long-term cardiac morbidity and mortality in a randomized trial of pre- and postoperative radiation therapy versus surgery alone in primary breast cancer. Radiother Oncol. 1998;48(2):185–90.
Ling TC, Slater JM, Nookala P, et al. Analysis of intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), proton and 3D conformal radiotherapy (3D-CRT) for reducing perioperative cardiopulmonary complications in esophageal cancer patients. Cancers (Basel). 2014;6(4):2356–68.
Jingu K, Nemoto K, Kaneta T, et al. Temporal change in brain natriuretic Peptide after radiotherapy for thoracic esophageal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;69(5):1417–23.
Palumbo I, Palumbo B, Fravolini ML, et al. Brain natriuretic peptide as a cardiac marker of transient radiotherapy-related damage in left-sided breast cancer patients: a prospective study. Breast. 2016;25:45–50.
van der Veen SJ, Ghobadi G, de Boer RA, et al. ACE inhibition attenuates radiation-induced cardiopulmonary damage. Radiother Oncol. 2015;114(1):96–103.
Brosius FC 3rd, Waller BF, Roberts WC. Radiation heart disease. Analysis of 16 young (aged 15 to 33 years) necropsy patients who received over 3,500 rads to the heart. Am J Med. 1981;70:519–30.
Heidenreich PA, Hancock SL, Lee BK, et al. Asymptomatic cardiac disease following mediastinal irradiation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;42(4):743–9.
Malanca M, Cimadevilla C, Brochet E, et al. Radiotherapy-induced mitral stenosis: a three-dimensional perspective. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2010;23:108.e1–2.
Copeland KA, Hosmane VR, Jurkovitz C, et al. Frequency of severe valvular disease caused by mediastinal radiation among patients undergoing valve surgery in a community-based, regional academic medical center. Clin Cardiol. 2013;36(4):217–21.
Baeuml H, Behrends U, Peter RU, et al. Ionizing radiation induces, via generation of reactive oxygen intermediates, intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) gene transcription and NF kappa B-like binding activity in the ICAM-1 transcriptional regulatory region. Free Radic Res. 1997;27:127–42.
Gyenes G, Fornander T, Carlens P, et al. Detection of radiation-induced myocardial damage by technetium-99m sestamibi scintigraphy. Eur J Nucl Med. 1997;24:286–92.
Küpeli S, Hazirolan T, Varan A, et al. Evaluation of coronary artery disease by computed tomography angiography in patients treated for childhood Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(6):1025–30.
Kaplan BM, Miller AJ, Bharati S, et al. Complete AV block following mediastinal radiation therapy: electrocardiographic and pathologic correlation and review of the world literature. Arch Intern Med. 1981;141:676–9.
Tötterman KJ, Pesonen E, Siltanen P. Radiation-related chronic heart disease. Chest. 1983;83(6):875–8.
Slama MS, Le Guludec D, Sebag C, et al. Complete atrioventricular block following mediastinal irradiation: a report of six cases. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1991;14(7):1112–8.
Pohjola-Sintonen S, Tötterman KJ, Kupari M. Sick sinus syndrome as a complication of mediastinal radiation therapy. Cancer. 1990;65:2494–6.
Zuppinger C, Timolati F, Suter TM. Pathophysiology and diagnosis of cancer drug induced cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2007;7(2):61–6.
Floyd JD, Nguyen DT, Lobins RL, et al. Cardiotoxicity of cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(30):7685–96.
Lieutaud T, Brain E, Golgran-Toledano D, et al. 5-Fluorouracil cardiotoxicity: a unique mechanism for ischaemic cardiopathy and cardiac failure? Eur J Cancer 1996; 32a:368–9.
Chirino J, Pedraza-Chaverri J. Role of oxidative and nitrosative stress in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Exp Toxicol Pathol 2009;61:223–42.
Suter TM, Ewer MS. Cancer drugs and the heart: importance and management. Eur Heart J. 2013;34(15):1102–11.
Zhang W, Zhao L, Liu J, et al. Cisplatin induces platelet apoptosis through the ERK signaling pathway. Thromb Res. 2012;130(1):81–91.
Saito K, Takeda K, Yoshida K, et al. Assessment of fatty acid metabolism in taxan-induced myocardial damage with iodine-123 BMIPP SPECT: comparative study with myocardial perfusion, left ventricular function, and histopathological findings. Ann Nucl Med. 2003;17(6):481–8.
Tomonari M, To H, Nishida M, Mishima T, Sasaki H, Kurose H. Mechanism of the cardioprotective effects of docetaxel pre-administration against adriamycin-induced cardiotoxicity. J Pharmacol Sci. 2011;115(3):336–45.
Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, et al. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9742):687–97.
Marinko T, Dolenc J, Bilban-Jakopin C. Cardiotoxicity of concomitant radiotherapy and trastuzumab for early breast cancer. Radiol Oncol. 2014;48(2):105–12.
Friess H, Fukuda A, Tang WH, et al. Concomitant analysis of the epidermal growth factor receptor family in esophageal cancer: overexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor mRNA but not of c-erbB-2 and c-erbB-3. World J Surg. 1999;23:1010–8.
Cellini F, Valentini V. Targeted therapies in combination with radiotherapy in oesophageal and gastroesophageal carcinoma. Curr Med Chem. 2014;21(8):990–1004.
Ikushima H, Takegawa Y, Yasuda H, et al. Radiation complications following breast conserving therapy. Breast Cancer. 1998;5(4):395–400.
Dorth JA, Patel PR, Broadwater G, et al. Incidence and risk factors of significant carotid artery stenosis in asymptomatic survivors of head and neck cancer after radiotherapy. Head Neck. 2014;36(2):215–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Statement
This article is a review. It did not involve any new clinical or laboratory work by the authors. All procedures were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation and with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki (2013).
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jingu, K., Umezawa, R. & Fukui, K. Radiation-induced heart disease after treatment for esophageal cancer. Esophagus 14, 215–220 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-017-0569-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-017-0569-5