Summary
Background
To evaluate the method of introduction, feasibility, and early results of a laparoscopic surgery for benign foregut disorders in a single high volume center.
Methods
A retrospective clinical study included consecutively laparoscopically operated patients due to benign foregut disorders. The study was conducted at the Department of Esophagogastric Surgery, First Surgical University Hospital, School of Medicine, University of Belgrade from March 2010 until July 2014. Complete preoperative diagnostics data, details of surgical procedures, and follow-up results are included.
Results
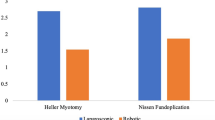
Overall, 200 consecutive patients were enrolled in the study. GERD and achalasia were the most common indications for laparoscopic surgery, with 81 and 72 patients respectively. Due to giant hiatal hernia, 37 patients were operated on, while the rest were less common indications. There were no conversions to open procedures. In three patients, pneumothorax resulted from intraoperative pleural lesion. One mucosal perforation occurred in an achalasia patient. One reoperation was conducted due to excessive port site bleeding. Short term follow-up results are highly satisfactory, and are presented in detail for every patient group.
Conclusion
Introduction of laparoscopy in a foregut surgery high volume center for the treatment of benign foregut disorders can be obtained with low incidence of complications, and satisfactory short term functional results.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bello B, Herbella FA, Allaix ME, Patti MG. Impact of minimally invasive surgery on the treatment of benign esophageal disorders. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:6764–70.
Pellegrini C, Wetter LA, Patti M, Leichter R, Mussan G, Mori T, Bernstein G, Way L. Thoracoscopic esophagomyotomy. Initial experience with a new approach for the treatment of achalasia. Ann Surg. 1992;216:291–6; discussion 296–9.
Hinder RA, Filipi CJ, Wetscher G, Neary P, DeMeester TR, Perdikis G. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication is an effective treatment for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Surg. 1994;220:472–81.
Zaninotto G, Costantini M, Rizzetto C, Zanatta L, Guirroli E, Portale G, Nicoletti L, Cavallin F, Battaglia G, Ruol A, Ancona E. Four hundred laparoscopic myotomies for esophageal achalasia: a single centre experience. Ann Surg. 2008;248:986–93.
Patti MG, Molena D, Fisichella PM, Whang K, Yamada H, Perretta S, Way LW. Laparoscopic Heller myotomy and Dor fundoplication for achalasia: analysis of successes and failures. Arch Surg. 2001;136:870–7.
Salvador R, Costantini M, Zaninotto G, Morbin T, Rizzetto C, Zanatta L, Ceolin M, Finotti E, Nicoletti L, Da Dalt G, Cavallin F, Ancona E. The preoperative manometric pattern predicts the outcome of surgical treatment for esophageal achalasia. J Gastrointest Surg. 2010;14:1635–45.
Rice T, Blackstone E. Surgical management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterol Clin N Am. 2008;37:901–19.
Salminen P, Hurme S, Ovaska J. Fifteen-year outcome of laparoscopic and open Nissen fundoplication: a randomized clinical trial. Ann Thorac Surg. 2012;93:228–33.
Davis CS, Baldea A, Johns JR, Joehl RJ, Fisichella PM. The evolution and long-term results of laparoscopic antireflux surgery for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. JSLS. 2010;14:332–41.
Schauer PR, Ikramuddin S, McLaughlin RH, Graham TO, Slivka A, Lee KK, Schraut WH, Luketich JD. Comparison of laparoscopic versus open repair of paraesophageal hernia. Am J Surg. 1998;176:659–65.
Simic´ AP, Skrobic´ OM, Radovanovic´ N, Velicˇkovic´ D, Ivanovic´ N, Peško PM. Importance of ineffective esophageal motility in patients with erosive reflux disease on the long-term outcome of Nissen fundoplication. Eur Surg. 2013;45:15–20.
Broeders JA, Sportel IG, Jamieson GG, Nijjar RS, Granchi N, Myers JC, Thompson SK. Impact of ineffective oesophageal motility and wrap type on dysphagia after laparoscopic fundoplication. Br J Surg. 2011;98:1414–21.
Horstmann R, Classen C, Röttgermann S, Langer M, Palmes D. Long-term experience of treating 185 patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) by anti-reflux surgery respecting the functional–morphological restoration of the esophagus. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2006;391:24–31.
Zehetner J, Demeester SR, Ayazi S, Kilday P, Augustin F, Hagen JA, Lipham JC, Sohn HJ, DeMeester TR. Laparoscopic versus open repair of paraesophageal hernia: the second decade. J Am Coll Surg. 2011;212:813–20.
Nason KS, Luketich JD, Qureshi I, Keeley S, Trainor S, Awais O, Shende M, Landreneau RJ, Jobe BA, Pennathur A. Laparoscopic repair of giant paraesophageal hernia results in longterm patient satisfaction and a durable repair. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008;12:2066–75.
Davis SS Jr. Current controversies in paraesophageal hernia repair. Surg Clin North Am. 2008;88:959–78.
Salminen PT, Hiekkanen HI, Rantala AP, Ovaska JT. Comparison of long-term outcome of laparoscopic and conventional Nissen fundoplication: a prospective randomized study with an 11-year follow-up. Ann Surg. 2007;246:201–6.
Rice TW, Blackstone EH. Surgical management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterol Clin N Am. 2008;37:901–19.
Simic´ AP, Radovanovic´ NS, Skrobic´ OM, Ražnatovic´ ZJ, Peško PM. Significance of limited hiatal dissection in surgery for achalasia. J Gastrointest Surg. 2010;14:587–93.
Campos G M, Vittinghoff E, Rabl C, Takata M, Gadenstatter M, Lin F, Ciovica R. Endoscopic and surgical treatments for achalasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg. 2009;249:45–57.
Rakita S, Bloomston M, Villadolid D, Thometz D, Boe B, Rosemurgy A. Age affects presenting symptoms of achalasia and outcomes after myotomy. Am Surg. 2005:71:424–9.
Ancona E, Anselmino M, Zaninotto G, Costantini M, Rossi M, Bonavina L, Boccu C, Buin F, Peracchia A. Esophageal achalasia: laparoscopic versus conventional open Heller-Dor operation. Am J Surg. 1995;170:265–70.
Douard R, Gaudric M, Chaussade S, Couturier D, Houssin D, Dousset B. Functional results after laparoscopic Heller myotomy for achalasia: a comparative study to open surgery. Surgery. 2004;136:16–24.
Stefanidis D, Richardson W, Farrell TM, Kohn GP, Augenstein V, Fanelli RD. SAGES guidelines for the surgical treatment of esophageal achalasia. Surg Endosc. 2012;26:296–311.
Fumagalli Romario U Ceolin M Porta M Rosati R. Laparoscopic repair of epiphrenic diverticulum. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2012;24:213–7.
Zaninotto G, Portale G, Costantini M, Zanatta L, Salvador R, Ruol A. Therapeutic strategies for epiphrenic diverticula: systematic review. World J Surg. 2011;35:1447–53.
Bathia L, Legner A, Tsuboi K, Mittal S. Efficasy and feasibility of laparoscopic redo fundoplication. World J Surg. 2011;35(11):2445–53.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simic´, A., Skrobić, O., Veličković, D. et al. Minimally invasive surgery for benign esophageal disorders: first 200 cases. Eur Surg 47, 25–34 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10353-015-0296-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10353-015-0296-x