Abstract
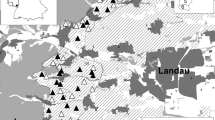
Red-legged partridges Alectoris rufa are one of the most important game species in extensively managed Mediterranean agro-forest systems. Population declines have led to management to increase their populations. This includes the creation of game crops, but their efficacy for red-legged partridges has not been tested. We developed in October 1996 an experimental introduction of 32 100 × 8 m plots in a 6.46-km2 mixed agro-forest system area in Portugal. These plots were planted with either lupin Lupinus sp., vetch Vicea sp. or triticale Triticum aestivum × Secale cereale. The main goal of this study was the evaluation of the potential effect of game crops on partridge distribution and productivity, after controlling for the effect of habitat or other management actions. Partridge abundance and distribution were assessed during spring and summer 1997 by intensive territory mapping. We compared characteristics of territory centres with those of random points in relation to land uses, game crops, and location of water points or supplementary grain sites. The most important variable explaining partridge’s location in spring was the density of supplementary water points. In summer, partridge territories were positively associated with the density of water points and lupin game crops, as well as olive trees. Productivity (number of young per territory in relation to adults observed) increased with the density of lupin game crops, but decreased with density of water points and vetch game crops and proportion of woodland within the territories. Overall, this study suggests that management for partridges in areas of agricultural abandonment, such as those in Mediterranean woodlands, would benefit from the introduction of leguminous game crops and water provision, though more studies are required for a more adequate optimization of these measures of habitat improvement, in particular about the specific cover of the crops and their spatial distribution so they provide adequate resources in summer for nestlings.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arroyo B, & Beja P (2002) Impact of hunting management practices on biodiversity. Report from EU concerted action reconciling game bird hunting and biodiversity (REGHAB) (technical report). Available at: http://digital.csic.es/bitstream/10261/8260/1/WP2-repportf.PDF
Arroyo B, Delibes-Mateos M, Díaz-Fernández S, Viñuela J (2012) Hunting management in relation to profitability aims: red-legged partridge hunting in central Spain. Eur J Wildlife Res 58:847–855
Beja P, Gordinho L, Reino L, Loureiro F, Santos–Reis M, Borralho R (2009) Predator abundance in relation to small game management in southern Portugal: conservation implications. Eur J Wildlife Res 55:227–238
Blanco-Aguiar JA (2007) Variación espacial en la biología de la perdiz roja (Alectoris rufa): una aproximación multidisciplinar. PhD thesis, Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Madrid, España
Borralho R, Rego F, Vaz Pinto P (1996) Is driven transect sampling suitable for estimating red-legged partridge Alectoris rufa densities? Wildlife Biology 2:259–268
Borralho R, Rito A, Rego F, Simões H, Vaz Pinto P (1998) Summer distribution of red-legged partridges Alectoris rufa in relation to water availability on Mediterranean farmland. Ibis 140:620–625
Borralho R, Carvalho J, Vaz Pinto P, Bugalho J, Castro Pereira D, Capelo M (2000) Gestão cinegética e evolução demográfica de duas populações de Perdiz-vermelha (Alectoris rufa) do Centro e Sul de Portugal. Silva Lusitana 8:49–59
Bro E, Deldalle B, Massot M, Reitz FO, Selmi F (2003) Density dependence of reproductive success in grey partridge Perdix perdix populations in France: management implications. Wildlife Biology 9:93–102
Bro E, Mayot P, Corda E, Reitz F (2004) Impact of habitat management on grey partridge populations: assessing wildlife cover using a multisite BACI experiment. J Appl Ecol 41:846–857
Buenestado FJ, Ferreras P, Delibes-Mateos M, Tortosa FS, Blanco-Aguiar JA, Villafuerte R (2008) Habitat selection and home range size of red-legged partridges in Spain. Agriculture Ecosystems and Environment 126:158–162
Buenestado FJ, Ferreras P, Blanco-Aguiar JA, Tortosa FS, Villafuerte R (2009) Survival and causes of mortality among wild red-legged partridges Alectoris rufa in southern Spain: implications for conservation. Ibis 151:720–730
Burnham KP, Anderson DR (2002) Model selection and multimodel inference: A practical information-theoretic approach, 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, New York
Casas F, Viñuela J (2010) Agricultural practices or game management: which is the key to improve red-legged partridge nesting success in agricultural landscapes? Environ Conserv 37:177–186
Carvalho J, Borralho R (1998) Produtividade e sucesso reprodutivo de duas populações de Perdiz-vermelha (Alectoris rufa) em diferentes habitats. Silva Lusitana 6:215–226
Díaz M, Campos P, Pulido FJ (1997) The Spanish dehesas: a diversity in land-use and wildlife. In: Pain DJ, Pienkowski MW (eds) Farming and birds in Europe. Academic, Cambridge, pp 178–209
Díaz-Fernández S (2012) Relationships between red-legged partridge hunting management, red-legged partridge populations, and human populations. PhD thesis, Universidad de Castilla- La Mancha, Ciudad Real, Spain
Díaz-Fernández S, Arroyo B, Casas F, Haro M, Viñuela J (2013) Effect of management techniques on red-legged partridge abundance. PLoS One 8(6):e66671
Joffre R, Rambal S, Ratte JP (1999) The dehesa system of southern Spain and Portugal as a natural ecosystem mimic. Agroforestry systems 45:57–79
Lucio AJ, Purroy FJ (1992) Red-legged partridge (Alectoris rufa) habitat selection in northwest Spain. Gibier Faune Sauvage 9:417–430
Meeus JH (1993) The transformation of agricultural landscapes in western Europe. Sci Total Environ 129:171–190
Meriggi A, Saino N, Montagna D, Zacchetti D (1992) Influence of habitat on density and breeding success of grey and red-legged partridges. Bolletino di Zoologia 59:289–295
Mollot B, Granval P (1996) Efficacité de la jachère faune sauvage. Bulletin Mensuel de l’Office National de la Chasse 214: 24–29.
Morris DW (1992) Scales and costs of habitat selection in heterogeneous landscapes. Evolutionary Ecology 6:412–432
Mustin K, Newey S, Irvine J, Arroyo B, Redpath S (2011) Biodiversity impacts of game bird hunting and associated management practices in Europe and North America. Contract report. James Hutton Institute, Aberdeen
Peeters A, Decamps C (1998) Choix et gestion de couverts herbacés dans les jachères et les tournières faunistiques. Gibier Faune Sauvage 15 (Hors série Tome 1): 117–129.
Peiró V, Seva E, Almiñana N (1993) Selección de hábitat en una población de perdiz roja (Alectoris rufa) en una zona de sierra del sur de la provincia de Alicante. Mediterránea Serie de Biología 14:5–22
Pépin D (1983) Utilisation et valeur de diverses méthodes d’estimation de la densité de la perdrix rouge (Alectoris rufa) au printemps. - In: J. Castroviejo (Ed.); Actas del XV Congreso Internacional de Fauna Cinegética y Silvestre, Trujillo 725–735
Pépin D, Blayac J (1990) Impacts d’un aménagement de la garrigue et de l’instauration d’un plan de chasse sur la démographie de la perdrix rouge (Alectoris rufa) en milieu méditerranéen. Gibier Faune Sauvage 7:145–158
Pinto-Correia T (1993) Threatened landscape in Alentejo, Portugal: the ‘montado’and other ‘agro-silvo-pastoral’systems. Landscape and Urban Planning 24:43–48
Pinto-Correia T, Mascarenhas J (1999) Contribution to the extensification/intensification debate: new trends in the Portuguese montado. Landscape and Urban Planning 46:125–131
PORDATA (2016). http://www.pordata.pt/en/. Accessed in Apr 2016
R Development Core Team (2014) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Available at:http://www.r-project.org. Accessed in December 2014
Reino LM, Borralho R, Bugalho JFF (2000) Revisão da utilização de culturas para a fauna na gestão de espécies cinegéticas. Revista de Ciências Agrárias 23:48–71
Ríos-Saldaña CA (2010) Los planes técnicos de caza de Castilla-La Mancha y su aplicación en la gestión y conservación de las especies cinegéticas. PhD Thesis, University of Castilla-La Mancha, Ciudad Real, Spain
Rivas-Martínez S, Lousã M, Díaz TE, Fernandez-González F, Costa JC (1990) La vegetación del sur de Portugal (Sado, Alentejo y Algarve). Itenera Geobotânica 3(5):126
Sage RB, Parish DMB, Woodburn MIA, Thompson PGL (2005) Songbirds using crops planted on farmland as cover for game birds. European Journal of Wildlife Research 51:248–253
Sá-Sousa P (2014) The Portuguese montado: conciliating ecological values with human demands within a dynamic agroforestry system. Annals of Forest Science SI:1–3
Sumozas N (2008) Estudio de la selección de hábitat y el dominio vital de la perdiz roja en pseudoestepas agrarias. Diploma de Estudios Avanzados. Universidad de Castilla-La Mancha, Ciudad Real, Spain
Stoate C, Szczur J, Aebischer NJ (2003) Winter use of wild bird cover crops by passerines on farmland in northeast England. Bird study 50:15–21
Vargas JM, Guerrero JC, Farfán MA, Barbosa AM, Real R (2006) Land use and environmental factors affecting red-legged partridge (Alectoris rufa) hunting yields in southern Spain. European Journal of Wildlife Research 52:188–195
Villanua D, Hofle U, Perez-Rodriguez L, Gortazar G (2006) Trichomonas gallinae in wintering common wood pigeons Columba palumbus in Spain. Ibis 148:641–648
Villanúa D, Torres J, Ardaiz J, Alzaga V, Ros F, Cormenzana A, Castién E (2011) Relationship between landscape heterogeneity loss and red- legged partridge (Alectoris rufa) populations survival. Abstract book of the XXXth Congress of the International Union of Game Biologist (UIGB) and PERDIX XIII. 5-9 septiembre 2011, UIGB; Barcelona, España. Pp. 176
Zuur AF, Ieno EN, Elphick CS (2010) A protocol for data exploration to avoid common statistical problems. MEE 1:3–14
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to H. Simões, S. Carvalho and A. Rito for the preparation and manipulation of the GIS, to M. Capelo, J. Carvalho, D. Castro Pereira, T. Costa, G. Vasconcelos Pessoa and P. Vaz Pinto for help in the field work, to R. Neiva Correia for allowing us to conduct this study on his land, to Joana Santana for help with Fig. 1, and to J.F. Bugalho, C. Stoate and two anonymous referees for reviewing earlier and current versions of the manuscript. We gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by ESAB and INIA through the project PAMAF-4030. This project was funded by Portuguese Foundation of Science and Technology (FCT) through the project PRAXIS/PCNA/C/BIA/105/96 and by the Portuguese Ministry of Education and Science and the European Social Fund, through FCT, under POPH - QREN - Typology 4.1, through the grant SFRH/BPD/93079/2013 (LR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reino, L., Borralho, R. & Arroyo, B. Influence of game crops on the distribution and productivity of red-legged partridges Alectoris rufa in Mediterranean woodlands. Eur J Wildl Res 62, 609–617 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10344-016-1034-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10344-016-1034-9