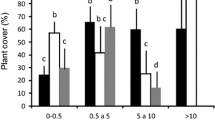
Abstract
The spatial distribution of species in forest ecosystems involves the underlying ecological processes or mechanisms of population and community structure, as well as forest dynamics. Because the relative importance of these factors can shift across life history stages, assessment of local population and community structures in the context of life history stages is essential for understanding forest dynamics. In this study, we investigated the changes in the spatial patterns of seed dispersal as well as seedling and sapling recruitment for Castanopsis fargesii, a dominant tree species in a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest in China. We found notably aggregated spatial patterns for C. fargesii seeds during the seed dispersal. A majority of seeds and newly germinated seedlings aggregated under adult tree canopies, suggesting a decreased efficiency in secondary dispersal for C. fargesii within this evergreen broad-leaved forest. During the later stages of life history (i.e., seedling and sapling stages), the spatial distribution of C. fargesii getting segregated. This is caused by a negative density dependence mechanism in seedling recruitment, rather than by spatial dispersion due to secondary dispersal. By incorporating the patterns and processes across the life history stages of dominant species of evergreen broad-leaved forests, we can add specific details in developing methods of stage-based in situ forest management and conservation frameworks.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Augspurger CK (1984) Seedling survival of tropical tree species: interactions of dispersal distance, light-gaps, and pathogens. Ecology 65:1705–1712
Baillie IC, Ashton PS, Court MN, Anderson JAR, Fitzpatrick EA, Tinsley J (1987) Site characteristics and the distribution of tree species in Mixed Dipterocarp Forest on Tertiary sediments in central Sarawak, Malaysia. J Trop Ecol 3:201–220
Baldeck CA, Harms KE, Yavitt JB, John R, Turner BL, Valencia R, Navarrete H, Bunyavejchewin S, Kiratiprayoon S, Yaacob A, Supardi MNN, Davies SJ, Hubbell SP, Chuyong GB, Kenfack D, Thomas DW, Dalling JW (2013) Habitat filtering across tree life stages in tropical forest communities. Proc R Soc Lond B 280:20130548
Barot S, Gignoux J, Menaut J-C (1999) Demography of a savanna palm tree: predictions from comprehensive spatial pattern analyses. Ecology 80:1987–2005
Beck H, Terborgh J (2002) Groves versus isolates: how spatial aggregation of Astrocaryum murumuru palms affects seed removal. J Trop Ecol 18:275–288
Bormann FH, Likens GE (1979) Pattern and process in a forested ecosystem. Springer, New York
Comita LS, Condit R, Hubbell SP (2007) Developmental changes in habitat associations of tropical trees. J Ecol 95:482–492
Condit R, Ashton PS, Baker P, Bunyavejchewin S, Gunatilleke S, Gunatilleke N, Hubbell SP, Foster RB, Itoh A, LaFrankie JV, Lee HS, Losos E, Manokaran N, Sukumar R, Yamakura T (2000) Spatial patterns in the distribution of tropical tree species. Science 288:1414–1418
Connell JH, Tracey JG, Webb LJ (1984) Compensatory recruitment, growth, and mortality as factors maintaining rain forest tree diversity. Ecol Monogr 54:142–164
Cordeiro NJ, Howe HF (2003) Forest fragmentation severs mutualism between seed dispersers and an endemic African tree. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:14052–14056
Cressie N (1993) Statistics for spatial data. Wiley, New Jersey
Dale MRT (1999) Spatial patterns analysis in plant ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Dalling JW, Muller-Landau HC, Wright SJ, Hubbell SP (2002) Role of dispersal in the recruitment limitation of neotropical pioneer species. J Ecol 90:714–727
Du X, Guo Q, Gao X, Ma K (2007) Seed rain, soil seed bank, seed loss and regeneration of Castanopsis fargesii (Fagaceae) in a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest. For Ecol Manag 238:212–219
Du Y, Mi X, Liu X, Chen L, Ma K (2009) Seed dispersal phenology and dispersal syndromes in a subtropical broad-leaved forest of China. For Ecol Manag 258:1147–1152
Forget P-M, Jansen PA (2007) Hunting increases dispersal limitation in the tree Carapa procera, a nontimber forest product. Conserv Biol 21:106–113
Frost I, Rydin H (1997) Effects of competition, grazing and cotyledon nutrient supply on growth of Quercus robur seedlings. Oikos 79:53–58
Hille Ris Lambers J, Clark JS, Beckage B (2002) Density-dependent mortality and the latitudinal gradient in species diversity. Nature 417:732–735
Holbrook KM, Loiselle BA (2009) Dispersal in a Neotropical tree, Virola flexuosa (Myristicaceae): does hunting of large vertebrates limit seed removal? Ecology 90:1449–1455
Holm S (1979) A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scand J Stat 6:65–70
Horvitz C, Schemske D, Caswell H (1997) The relative “importance” of life-history stages to population growth: prospective and retrospective analyses. In: Tuljapurkar S, Caswell H (eds) Structured-population models in marine, terrestrial, and freshwater systems. Population and community biology series, vol 18. Springer, New York, pp 247–271
Howe HF, Miriti MN (2004) When seed dispersal matters. Bioscience 54:651–660
Howe HF, Smallwood J (1982) Ecology of seed dispersal. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 13:201–228
Hu Z, Yu M (2008) Study on successions sequence of evergreen broad-leaved forest in Gutian Mountain of Zhejiang, Eastern China: species diversity. Front Biol China 3:45–49
Hubbell SP (2001) The unified neutral theory of biodiversity and biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Hyatt LA, Rosenberg MS, Howard TG, Bole G, Fang W, Anastasia J, Brown K, Grella R, Hinman K, Kurdziel JP, Gurevitch J (2003) The distance dependence prediction of the Janzen–Connell hypothesis: a meta-analysis. Oikos 103:590–602
Jansen PA, Bongers F, Hemerik L (2004) Seed mass and mast seeding enhance dispersal by a neotropical scatter-hoarding rodent. Ecol Monogr 74:569–589
Jansen PA, Hirsch BT, Emsens W-J, Zamora-Gutierrez V, Wikelski M, Kays R (2012) Thieving rodents as substitute dispersers of megafaunal seeds. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:12610–12615
Jansen PA, Visser MD, Joseph Wright S, Rutten G, Muller-Landau HC (2014) Negative density dependence of seed dispersal and seedling recruitment in a Neotropical palm. Ecol Lett 17:1111–1120
Janzen DH (1970) Herbivores and the number of tree species in tropical forests. Am Nat 104:501–528
Kneitel JM, Chase JM (2004) Trade-offs in community ecology: linking spatial scales and species coexistence. Ecol Lett 7:69–80
Kobe RK, Vriesendorp CF (2011) Conspecific density dependence in seedlings varies with species shade tolerance in a wet tropical forest. Ecol Lett 14:503–510
Kraft NJB, Ackerly DD (2014) Assembly of plant communities. In: Monson RK (ed) Ecology and the environment. The plant sciences, vol 8. Springer, New York, pp 67–88
Krannitz PG, Aarssen LW, Dow JM (1991) The effect of genetically based differences in seed size on seedling survival in Arabidopsis thaliana (Brassicaceae). Am J Bot 78:446–450
Lai J, Mi X, Ren H, Ma K (2009) Species-habitat associations change in a subtropical forest of China. J Veg Sci 20:415–423
Legendre P, Fortin M (1989) Spatial pattern and ecological analysis. Vegetatio 80:107–138
Lin L, Cao M (2009) Edge effects on soil seed banks and understory vegetation in subtropical and tropical forests in Yunnan, SW China. For Ecol Manag 257:1344–1352
Lin F, Comita L, Wang X, Bai X, Yuan Z, Xing D, Hao Z (2014) The contribution of understory light availability and biotic neighborhood to seedling survival in secondary versus old-growth temperate forest. Plant Ecol 215:795–807
Manabe T, Nishimura N, Miura M, Yamamoto S (2000) Population structure and spatial patterns for trees in a temperate old-growth evergreen broad-leaved forest in Japan. Plant Ecol 151:181–197
Manasse R, Howe H (1983) Competition for dispersal agents among tropical trees: influences of neighbors. Oecologia 59:185–190
Mantel N (1967) The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res 27:209–220
Nadeem M, Mollier A, Morel C, Vives A, Prud’homme L, Pellerin S (2011) Relative contribution of seed phosphorus reserves and exogenous phosphorus uptake to maize (Zea mays L.) nutrition during early growth stages. Plant Soil 346:231–244
Nathan R, Muller-Landau HC (2000) Spatial patterns of seed dispersal, their determinants and consequences for recruitment. Trends Ecol Evol 15:278–285
Newbery DM, Stoll P (2013) Relaxation of species-specific neighborhood effects in Bornean rain forest under climatic perturbation. Ecology 94:2838–2851
Ohsawa M (1993) Latitudinal pattern of mountain vegetation zonation in southern and eastern Asia. J Veg Sci 4:13–18
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Wagner H (2011) vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package version 2.0-10
Oliveira-Filho AT, Vilela EA, Carvalho DA, Gavilanes ML (1994) Effects of soils and topography on the distribution of tree species in a tropical riverine forest in south-eastern Brazil. J Trop Ecol 10:483–508
Oliver CD, Larson BC (1996) Forest stand dynamics. McGraw-Hill, New York
Packer A, Clay K (2000) Soil pathogens and spatial patterns of seedling mortality in a temperate tree. Nature 404:278–281
Pinheiro J, Bates D, DebRoy S, Sarkar D, R Core Team (2014) nlme: Linear and nonlinear mixed effects models. R package version 3. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Punchi-Manage R, Wiegand T, Wiegand K, Getzin S, Gunatilleke CVS, Gunatilleke IAUN (2013) Effect of spatial processes and topography on structuring species assemblages in a Sri Lankan dipterocarp forest. Ecology 95:376–386
R Core Team (2014) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Russo SE, Davies SJ, King DA, Tan S (2005) Soil-related performance variation and distributions of tree species in a Bornean rain forest. J Ecol 93:879–889
Schurman J, Baltzer J (2012) Environmental correlates of tree species distributions vary among age classes in a northern temperate forest. Plant Ecol 213:1621–1632
Shen Z-H, Tang Y-Y, Lü N, Zhao J, Li D-X, Wang G-F (2007) Community dynamics of seed rain in mixed evergreen broad-leaved and deciduous forests in a subtropical mountain of central China. J Integr Plant Biol 49:1294–1303
Silvertown J, Franco M, Pisanty I, Mendoza A (1993) Comparative plant demography—relative importance of life-cycle components to the finite rate of increase in woody and herbaceous perennials. J Ecol 81:465–476
Smouse PE, Long JC, Sokal RR (1986) Multiple regression and correlation extensions of the Mantel test of matrix correspondence. Syst Zool 35:627–632
Song Y (1988) The essential characteristics and main types of the broad-leaved evergreen forest in China. Phytocoenologia 1:105–123
Song YC, Chen XY, Wang XH (2005) Studies on evergreen broadleaved forests of China: a retrospect and prospect. J Eastchina Norm Univ (Nat Sci) 1:1–8 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Song J, Zhang H, Jiang G (2007) A study on water retention properties of soil under four types of forest communities in Jinyun Mountain Nature Reserve. J West China For Sci 36:26–33 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Tang CQ (2010) Subtropical montane evergreen broad-leaved forests of Yunnan, China: diversity, succession dynamics, human influence. Front Earth Sci China 4:22–32
Tang CQ (2015) The subtropical vegetation of southwestern China: plant distribution, diversity and ecology. Springer, New York
Taylor SL, MacLean DA (2005) Rate and causes of decline of mature and overmature balsam fir and spruce stands in New Brunswick, Canada. Can J For Res 35:2479–2490
Tokuoka Y, Ohigashi K, Nakagoshi N (2011) Limitations on tree seedling establishment across ecotones between abandoned fields and adjacent broad-leaved forests in eastern Japan. Plant Ecol 212:923–944
Tomita M, Hirabuki Y, Seiwa K (2002) Post-dispersal changes in the spatial distribution of Fagus crenata seeds. Ecology 83:1560–1565
Tsujino R, Yumoto T (2008) Seedling establishment of five evergreen tree species in relation to topography, sika deer (Cervus nippon yakushimae) and soil surface environments. J Plant Res 121:537–546
Vander Wall SB (2002) Masting in animal-dispersed pines facilitates seed dispersal. Ecology 83:3508–3516
Wang BC, Smith TB (2002) Closing the seed dispersal loop. Trends Ecol Evol 17:379–386
Wang X-H, Kent M, Fang X-F (2007) Evergreen broad-leaved forest in Eastern China: its ecology and conservation and the importance of resprouting in forest restoration. For Ecol Manag 245:76–87
Watt AS (1947) Pattern and process in the plant community. J Ecol 35:1–22
Webb CO, Peart DR (2000) Habitat associations of trees and seedlings in a Bornean rain forest. J Ecol 88:464–478
Wright JS (2002) Plant diversity in tropical forests: a review of mechanisms of species coexistence. Oecologia 130:1–14
Xiao Z, Zhang Z, Wang Y (2005) The effects of seed abundance on seed predation and dispersal by rodents in Castanopsis fargesii (Fagaceae). Plant Ecol 177:249–257
Yan E-R, Wang X-H, Huang J-J, Li G-Y, Zhou W (2008) Decline of soil nitrogen mineralization and nitrification during forest conversion of evergreen broad-leaved forest to plantations in the subtropical area of Eastern China. Biogeochemistry 89:239–251
Zhang X, Sun S, Yong S, Zhou Z, Wang R (2007) Vegetation Map of the People’s Republic of China (1: 1000000). Geological Publishing House, Beijing
Zhu Y, Comita LS, Hubbell SP, Ma K (2015) Conspecific and phylogenetic density-dependent survival differs across life stages in a tropical forest. J Ecol. doi:10.1111/1365-2745.12414
Acknowledgments
We thank Xiangyang Gao, Meng Qi, Xia Zhou, Chao Yang, Shenghe Yang and Xiaohan Li for help with field work, and Yukiko Takahashi, Kun Song, Liang Zhao and Dunmei Lin for the valuable comments. We are grateful to two anonymous reviewers for their comments to improve the manuscript. This study was supported by the Visiting Scholar Foundation of the Key Laboratory of the Three Gorges Reservoir Region’s Eco-environment (Ministry of Education) of Chongqing University, a grant from the 111 Project (No. B13041), the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars from the State Education Ministry, a grant from the Project of China Science and Technology (2015FY210200), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Project No.106112014CDJZR210007) to YY.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Rainer Matyssek.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Huang, L., Qian, S. et al. Completing the life history of Castanopsis fargesii: changes in the seed dispersal, seedling and sapling recruitment patterns. Eur J Forest Res 134, 1143–1154 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-015-0916-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-015-0916-9