Abstract
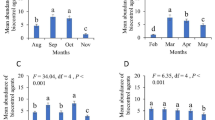
The brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stål), is a highly polyphagous invasive pest. Increased use of broad-spectrum insecticides to manage H. halys has resulted in secondary pest outbreaks and disruptions to integrated pest management (IPM) programs. We evaluated H. halys mortality, molting, and feeding after exposure to insecticides in the laboratory. Five insecticides (four active ingredients), considered less risky to natural enemies, were compared to a pyrethroid insecticide and an untreated control. Compared to the control, only azadirachtin + pyrethrins significantly reduced egg hatch, while all insecticides caused significant direct mortality to 1st and 2nd instars 5 days after hatch (DAH). Bifenthrin quickly caused complete mortality of adults, and the only insecticide to statistically match this level of mortality was sulfoxaflor at 14 days after treatment (DAT). Azadirachtin + pyrethrins and sulfoxaflor significantly reduced the proportion of 1st instars that molted compared to the control. Adults that survived sulfoxaflor exposure produced significantly fewer feeding sites than the control. However, when taking into consideration both lethal and sublethal effects, all insecticides, except pyrethrins, resulted in significant reductions in feeding sites/individual compared to the control. This more complete estimate of efficacy (i.e., reduction in injury/insect), confirms the potential of several insecticides to reduce crop injury without the necessity of high direct mortality to H. halys.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams A, Gore J, Catchot A et al (2016) Residual and systemic efficacy of chlorantraniliprole and flubendiamide against corn earworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in soybean. J Econ Entomol 109:2411–2417. doi:10.1093/jee/tow210
Aigner JD, Walgenbach JF, Kuhar TP (2015) Toxicities of neonicotinoid insecticides for systemic control of brown marmorated stink bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in fruiting vegetables. J Agric Urban Entomol 31:70–80. doi:10.3954/JAUE15-06.1
Barbour KS, Bradley JR Jr, Bacheler AS et al (1990) Reduction in yield and quality of cotton damaged by green stink bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). J Econ Entomol 83:842–845
Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B, Walker S (2015) _lme4: linear mixed-effects models using Eigen and S4_. https://cran.r-project.org/package=lme4. Accessed 1 Aug 2016
Bergmann EJ, Raupp MJ (2014) Efficacies of common ready to use insecticides against Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Fla Entomol 97:791–800. doi:10.1896/054.097.0262
Biondi A, Mommaerts V, Smagghe G et al (2012) The non-target impact of spinosyns on beneficial arthropods. Pest Manag Sci 68:1523–1536. doi:10.1002/ps.3396
Bowling CC (1979) The stylet sheath as an indicator of feeding activity of the rice stink bug. J Econ Entomol 72:259–260
Bowling CC (1980) The stylet sheath as an indicator of feeding activity by the southern green stink bug on soybeans. J Econ Entomol 73:1–3
Brown MW, Short BD (2010) Factors affecting appearance of stink bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) injury on apple. Environ Entomol 39:134–139. doi:10.1603/EN09175
Brust G, Rane K (2013) Transmission of the yeast Eremothecium coryli to fruits and vegetables by the brown marmorated stink bug. In: Univ. Maryl. Ext. https://extension.umd.edu/learn/transmission-yeast-eremothecium-coryli-fruits-and-vegetables-brown-marmorated-stink-bug. Accessed 12 Nov 2016
Bundy CS, McPherson RM, Herzog GA (2000) An examination of the external and internal signs of cotton boll damage by stink bugs (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). J Entomol Sci 35:402–410
Chapman RF (2013) Mouthparts and feeding. In: Simpson SJ, Douglas AE (eds) The insects structure and function, 5th edn. Cambridge Univeristy Press, Cambridge, pp 25–26
Chen X, Ma K, Li F et al (2016) Sublethal and transgenerational effects of sulfoxaflor on the biological traits of the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii Glover (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Ecotoxicology 25:1841–1848. doi:10.1007/s10646-016-1732-9
Cissel WJ, Mason CE, Whalen J et al (2015) Effects of brown marmorated stink bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) feeding injury on sweet corn yield and quality. J Econ Entomol 108:1065–1071. doi:10.1093/jee/tov059
Colares F, Michaud JP, Bain CL, Torres JB (2016) Relative toxicity of two aphicides to Hippodamia convergens (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae): implications for integrated management of sugarcane aphid, Melanaphis sacchari (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J Econ Entomol 110:tow265. doi:10.1093/jee/tow265
Delpuech J-M, Gareau E, Terrier O, Fouillet P (1998) Sublethal effects of the insecticide chlorpyrifos on the sex pheromonal communication of Trichogramma brassicae. Chemosphere 36:1775–1785. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(97)10071-6
Desneux N, Decourtye A, Delpuech J-M (2007) The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Annu Rev Entomol 52:81–106. doi:10.1146/annurev.ento.52.110405.091440
Dinno A (2016) dunn.test: Dunn’s test of multiple comparisons using rank sums. https://cran.r-project.org/package=dunn.test. Accessed 1 Aug 2016
Fernández MM, Medina P, Wanumen A et al (2017) Compatibility of sulfoxaflor and other modern pesticides with adults of the predatory mite Amblyseius swirskii. Residual contact and persistence studies. Biocontrol 62:197–208. doi:10.1007/s10526-017-9784-1
Frank SD (2012) Reduced risk insecticides to control scale insects and protect natural enemies in the production and maintenance of urban landscape plants. Environ Entomol 41:377–386. doi:10.1603/EN11230
Funayama K (2002) Residual effect of insecticides on Halyomorpha halys (Stål) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Annu Rep Plant Prot North Jpn 53:273–275
Funayama K (2012) Control effect on the brown-marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae), by combined spraying of pyrethroid and neonicotinoid insecticides in apple orchards in northern Japan. Appl Entomol Zool 47:75–78. doi:10.1007/s13355-011-0083-5
Galvan TL, Koch RL, Hutchison WD (2005) Toxicity of commonly used insecticides in sweet corn and soybean to multicolored Asian lady beetle (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). J Econ Entomol 98:780–789. doi:10.1603/0022-0493-98.3.780
Garzón A, Medina P, Amor F et al (2015) Toxicity and sublethal effects of six insecticides to last instar larvae and adults of the biocontrol agents Chrysoperla carnea (Stephens) (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae) and Adalia bipunctata (L.) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Chemosphere 132:87–93. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.03.016
Hardin MR, Benrey B, Coll M et al (1995) Arthropod pest resurgence: an overview of potential mechanisms. Crop Prot 14:3–18. doi:10.1016/0261-2194(95)91106-P
He Y, Zhao J, Zheng Y et al (2013) Assessment of potential sublethal effects of various insecticides on key biological traits of the tobacco whitefly, Bemisia tabaci. Int J Biol Sci 9:246–255. doi:10.7150/ijbs.5762
Hoebeke RE, Carter ME (2003) Halyomorpha halys (Stål) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae): a polyphagous plant pest from Asia newly detected in North America. Proc Entomol Soc Wash 105:225–237
Hope RM (2013) Rmisc: Rmisc: Ryan miscellaneous. https://cran.r-project.org/package=Rmisc. Accessed 1 Aug 2016
Hothorn T, Bretz F, Westfall P (2008) Simultaneous inference in general parametric models. Biometr J 50:346–363
Ioriatti C, Pasqualini E, Pasquier D, Tomasi C (2006) Efficacy baselines of seven insecticides against larvae of Pandemis heparana (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). J Pest Sci (2004) 79:163–168. doi:10.1007/s10340-006-0130-0
Iverson JM, Cira TM, Burkness EC, Hutchison WD (2016) Cannibalistic oophagy in Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) laboratory colonies. J Entomol Sci 51:122–128
Katsuda Y (1999) Development of and future prospects for pyrethroid chemistry. Pestic Sci 55:775–782
Kraiss H, Cullen EM (2008a) Efficacy and nontarget effects of reduced-risk insecticides on Aphis glycines (Hemiptera: Aphididae) and its biological control agent Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). J Econ Entomol 101:391–398. doi:10.1603/0022-0493(2008)101
Kraiss H, Cullen EM (2008b) Insect growth regulator effects of azadirachtin and neem oil on survivorship, development and fecundity of Aphis glycines (Homoptera: Aphididae) and its predator, Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Pest Manag Sci 64:660–668. doi:10.1002/ps.1541
Lee D, Wright SE, Leskey TC (2013) Impact of insecticide residue exposure on the invasive pest, Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae): analysis of adult mobility. J Econ Entomol 106:150–158. doi:10.1603/EC12265
Lee D-H, Short BD, Nielsen AL, Leskey TC (2014) Impact of organic insecticides on the survivorship and mobility of Halyomorpha halys (Stål) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in the laboratory. Florida Entomol 97:414–421. doi:10.1896/054.097.0211
Leskey TC, Lee D-H, Short BD, Wright SE (2012a) Impact of insecticides on the invasive Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae): analysis of insecticide lethality. J Econ Entomol 105:1726–1735. doi:10.1603/EC12096
Leskey TC, Short BD, Butler BR, Wright SE (2012b) Impact of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stål), in Mid-Atlantic tree fruit orchards in the United States: case studies of commercial management. Psyche (Stuttg) 2012:1–14. doi:10.1155/2012/535062
Leskey TC, Short BD, Lee DH (2014) Efficacy of insecticide residues on adult Halyomorpha halys (Stål) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) mortality and injury in apple and peach orchards. Pest Manag Sci 70:1097–1104. doi:10.1002/ps.3653
Mathews CR, Barry S (2014) Compost tea reduces egg hatch and early-stage nymphal development of Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Fla Entomol 97:1726–1732. doi:10.1653/024.097.0448
McPherson JE (1982) The Pentatomoidea (Hemiptera) of Northeastern North America with emphasis on the fauna of Illinois. Southern Illinois University Press, Carbondale
Morrison WR, Poling B, Leskey TC (2017) The consequences of sublethal exposure to insecticide on the survivorship and mobility of Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Pest Manag Sci 73:389–396. doi:10.1002/ps.4322
National Pesticide Information Center (2011) Bifenthrin. In: Tech. Fact Sheet. http://npic.orst.edu/factsheets/archive/biftech.html. Accessed 12 Sep 2016
Nielsen AL, Shearer PW, Hamilton GC (2008) Toxicity of insecticides to Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) using glass-vial bioassays. J Econ Entomol 101:1439–1442. doi:10.1603/0022-0493(2008)101
Owens DR, Herbert DA, Dively GP et al (2013) Does feeding by Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) reduce soybean seed quality and yield? J Econ Entomol 106:1317–1323. doi:10.1603/EC12488
Pan F, Lu Y, Wang L (2017) Toxicity and sublethal effects of sulfoxaflor on the red imported fire ant, Solenopsis invicta. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 139:377–383. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.02.014
Pedigo LP, Hutchins SH, Higley LG (1986) Economic injury levels in theory and practice. Annu Rev Entomol 31:341–368. doi:10.1146/annurev.en.31.010186.002013
Pezzini DT, Koch RL (2015) Compatibility of flonicamid and a formulated mixture of pyrethrins and azadirachtin with predators for soybean aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) management. Biocontrol Sci Technol 25:1024–1035. doi:10.1080/09583157.2015.1027659
Rice KB, Bergh CJ, Bergman E et al (2014) Biology, ecology, and management of brown marmorated stink bug (Halyomorpha halys </i >). J Integr Pest Manag 5:1–13. doi:10.1603/IPM14002
Ripper WE (1956) Effect of pesticides on balance of arthropod populations. Annu Rev Entomol 1:403–438. doi:10.1146/annurev.en.01.010156.002155
RStudio Team (2015) Integrated development environment for R, Version 0.99.902. http://www.rstudio.org/. Accessed 1 Aug 2016
Schmutterer H (1988) Potential of azadirachtin-containing pesticides for integrated pest control in developing and industrialized countries. J Insect Physiol 34:713–719. doi:10.1016/0022-1910(88)90082-0
Schmutterer H (1990) Properties and potential of natural pesticides from the neem tree, Azadirachta indica. Annu Rev Entomol 35:271–297
Singmann H, Bolker B, Westfall J, et al. (2016) afex: analysis of factorial experiments. https://cran.r-project.org/package=afex
Spurlock F, Lee M (2008) Synthetic pyrethroid use patterns, properties, and environmental effects. In: Gan J, Spurlock F, Hendley P, Weston DP (eds) Synthetic pyrethroids occurrence and behavior in aquatic environments. American Chemical Society, Washington, D.C., pp 3–25
Stark JD, Banks JE (2003) Population-level effects of pesticides and other toxicants on arthropods. Annu Rev Entomol 48:505–519. doi:10.1146/annurev.ento.48.091801.112621
Stern V, Smith R, Van Den Bosch R, Hagen K (1959) The integrated control concept. Hilgardia 29:81–100
Tang Q, Xiang M, Hu H et al (2015) Evaluation of sublethal effects of sulfoxaflor on the green peach aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) using life table parameters. J Econ Entomol 108:2720–2728. doi:10.1093/jee/tov221
Taylor CM, Coffey PL, DeLay BD, Dively GP (2014) The importance of gut symbionts in the development of the brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stål). PLoS ONE 9:e90312. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0090312
R Core Team (2016) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria. http://www.r-project.org/. Accessed 1 Sep 2016
Theiling KM, Croft BA (1988) Pesticide side-effects on arthropod natural enemies: a database summary. Agric Ecosyst Environ 21:191–218. doi:10.1016/0167-8809(88)90088-6
Tran AK, Alves TM, Koch RL (2016) Potential for sulfoxaflor to improve conservation biological control of Aphis glycines (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in soybean. J Econ Entomol 109:1–10. doi:10.1093/jee/tow168
United States Environmental Protection Agency (2016) Conventional reduced risk pesticide program. https://www.epa.gov/pesticide-registration/conventional-reduced-risk-pesticide-program#status. Accessed 17 Aug 2016
Viator HP, Pantoja A, Smith CM (1983) Damage to wheat seed quality and yield by the rice stink bug and Southern green stink bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). J Econ Entomol 76:1410–1413
Viñuela E, Adán A, Smagghe G et al (2000) Laboratory effects of ingestion of azadirachtin by two pests (Ceratitis capitata and Spodoptera exigua) and three natural enemies (Chrysoperla carnea, Opius concolor and Podisus maculiventris). Biocontrol Sci Technol 10:165–177. doi:10.1080/09583150029305
Wang H, Lai D, Yuan M, Xu H (2014) Growth inhibition and differences in protein profiles in azadirachtin-treated Drosophila melanogaster larvae. Electrophoresis 35:1122–1129. doi:10.1002/elps.201300318
Wickham H (2009) ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis. Springer, New York
Williams T, Valle J, Viñuela E (2003) Is the naturally derived insecticide Spinosad® compatible with insect natural enemies? Biocontrol Sci Technol 13:459–475. doi:10.1080/0958315031000140956
Xu L, Zhao C-Q, Zhang Y-N et al (2016) Lethal and sublethal effects of sulfoxaflor on the small brown planthopper Laodelphax striatellus. J Asia Pac Entomol 19:683–689. doi:10.1016/j.aspen.2016.06.013
Systat Software Inc. SigmaPlot 12.5
Zeilinger AR, Olson DM, Raygoza T, Andow DA (2015) Do counts of salivary sheath flanges predict food consumption in herbivorous stink bugs (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae)? Ann Entomol Soc Am. doi:10.1093/aesa/sau011
Zhu Y, Loso MR, Watson GB et al (2011) Discovery and characterization of sulfoxaflor, a novel insecticide targeting sap-feeding pests. J Agric Food Chem 59:2950–2957. doi:10.1021/jf102765x
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank those who assisted us in making this study possible including the labs of Dr. Galen Dively (University of Maryland), Dr. Thomas Kuhar (Virginia Polytech University), and Jaana Iverson, and Wally Rich IV (University of Minnesota). Additionally, we express gratitude to Drs. Amy Morey and Rob Venette for reviewing a previous draft, and Dr. Dan Cariveau for statistical assistance. We also thank our funding sources including a United States Department of Agriculture—Minnesota Department of Agriculture Specialty Crop Block Grant, a University of Minnesota—Department of Entomology, McLaughlin Gormley King Corp. (MGK) graduate fellowship, and a University of Minnesota MnDRIVE Global Food Ventures graduate fellowship. The research was also supported by the University of Minnesota Agricultural Experiment Station.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare they have no conflicts of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by T. Haye.
Special Issue: The brown marmorated stink bug Halyomorpha halys an emerging pest of global concern.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cira, T.M., Burkness, E.C., Koch, R.L. et al. Halyomorpha halys mortality and sublethal feeding effects following insecticide exposure. J Pest Sci 90, 1257–1268 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-017-0871-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-017-0871-y