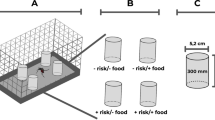
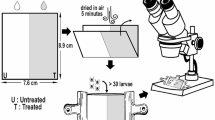
Abstract
Termites cause important economic losses worldwide and insecticides are largely used to control subterranean termites like Reticulitermes speratus Kolbe. However, few studies have documented the various effects that insecticides may have on termites, e.g., fumigation or colonial effects. Such knowledge would greatly help in optimizing termite management methods. Under laboratory conditions, we assessed toxicity of ten insecticides, i.e., chlorpyrifos, phoxim, carbofuran, propoxur, bifenthrin, cypermethrin, imidacloprid, fipronil, abamectin, and ivermectin, on R. speratus, and we documented possible insecticide transfer among termites, fumigation effect, and effect on termite colony. Abamectin, ivermectin, fipronil, and imidacloprid were effectively transferred among termite workers and induced high mortality in the receiving individuals, although the estimated LC50 values for these two insecticides were higher than those calculated for most of the others. Abamectin, ivermectin, phoxim, and chlorpyrifos showed strong fumigation effect, and ivermectin, fipronil (and to lesser extent abamectin) could lead to colony collapsing under laboratory conditions. Abamectin was the most efficient insecticide on R. speratus, being highly toxic through fumigation, highly transferable among individuals, and preventing colony to expand through abamectin-contaminated areas. Ivermectin showed similar properties but lacked the latter. Other insecticides showed various properties, either useful for preventing termite infestation or for colony suppression. The results may help in optimizing management of termites, although field experiments would need to document effects in practical situation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed S, Mustafa T, Riaz MA, Hussain A (2006) Efficacy of insecticides against subterranean termites in sugarcane. Int J Agric Biol 8:508–510
Anatra-Cordone M, Durkin P (2005) Imidacloprid. Human health assessment and ecological risk assessment, Final report. Syracuse Environmental Research Associates. Inc., New York, SERA TR, 05-43
Asogwa EU, Okelana FA, Ndubuaku TCN, Mokwunye IU (2009) The termicidal effects of Chlorpyrifos 48 EC, Endosulfan 35 EC, Dichlorvos 1000 EC and Diazinon 600 EC against termites in South-West Nigeria. Afr J Biotechnol 8:48–52
Ayre GL (1962) Problems in using the Lincoln Index for estimating the size of ant colonies (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J N Y Entomol Soc 7:159–166
Bagnères AG, Pichon A, Hope J, Davis RW, Clément JL (2009) Contact versus feeding intoxication by fipronil in Reticulitermes Reticulitermes termites (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae): laboratory evaluation of toxicity, uptake, clearance, and transfer among individuals. J Econ Entomol 102:347–356
Biondi A, Desneux N, Siscaro G, Zappalà L (2012) Using organic-certified rather than synthetic pesticides may not be safer for biological control agents: Selectivity and side effects of 14 pesticides on the predator Orius laevigatus. Chemosphere 87:803–812
Biondi A, Zappalà L, Stark JD, Desneux N (2013) Do biopesticides affect the demographic traits of a parasitoid wasp and its biocontrol services through sublethal effects? PLoS ONE 8:e76548
Biondi A, Zappala L, Desneux N, Aparo A, Siscaro G, Rapisarda C, Martin T, Tropea-Garzia G (2015) Potential toxicity of α-cypermethrin-treated net on Tuta absoluta (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). J Econ Entomol. doi:10.1093/jee/tov045
Cresswell JE, Desneux N, vanEngelsdorp D (2012) Dietary traces of neonicotinoid pesticides as a cause of population declines in honey bees: an evaluation by Hill’s epidemiological criteria. Pest Manag Sci 68:819–827
Desneux N, Rafalimanana H, Kaiser L (2004) Dose-response relationship in lethal and behavioural effects of different insecticides on the parasitic wasp Aphidius ervi. Chemosphere 54:619–627
Desneux N, Ramirez-Romero R, Kaiser L (2006) Multi step bioassay to predict recolonization potential of emerging parasitoids after a pesticide treatment. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2675–2682
Desneux N, Decourtye A, Delpuech JM (2007) The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Annu Rev Entomol 52:81–106
Finney DJ (1971) Probit Analysis, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Fry DM (1995) Reproductive effects in birds exposed to pesticides and industrial chemicals. Environ Health Perspect 103:165–171
Gautam BK, Henderson G, Davis RW (2012) Toxicity and horizontal transfer of 0.5 % fipronil dust against Formosan subterranean termites. J Econ Entomol 105:1766–1772
Guo JQ, Gong YG, Jin SQ (2008) Control efficacy of 0.3 % ivermectin EC to termite. Chin J Vector Biol Control 19:540–543
Haagsma KA, Rust MK (2005) Effect of hexaflumuron on mortality of the western subterranean termite (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) during and following exposure and movement of hexaflumuron in termite groups. Pest Manag Sci 61:517–531
Haagsma KA, Rust MK (2007) The effect of imidacloprid on mortality, activity, and horizontal transfer in the western subterranean termite (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). Sociobiology 50:1127–1148
Halley BA, VandenHeuvel WJ, Wislocki PG (1993) Environmental effects of the usage of avermectins in livestock. Vet Parasitol 48:109–125
Han P, Niu CY, Lei CL, Cui JJ, Desneux N (2010a) Use of an innovative T-tube maze assay and the proboscis extension response assay to assess sublethal effects of GM products and pesticides on learning capacity of the honey bee Apis mellifera L. Ecotoxicology 19:1612–1619
Han P, Niu CY, Lei CL, Ciu JJ, Desneux N (2010b) Quantification of toxins in a Cry1Ac + CpTI cotton cultivar and its potential effects on the honeybee Apis mellifera L. Ecotoxicology 19:1452–1459
He Y, Zhao J, Zheng Y, Weng Q, Biondi A, Desneux N, Wu K (2013) Assessment of potential sublethal effects of various insecticides on key biological traits of the tobacco whitefly Bemisia tabaci. Int J Biol Sci 9:246
Hu XP, Song DL, Scherer CW (2005) Transfer of indoxacarb among workers of Coptotermes formosanus (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae): effects of dose, donor: recipient ratio and post-exposure time. Pest Manag Sci 61:1209–1214
Huang YD, Zhou ZB, Hu YY (2001) An introduction to Chinese termites. Systematics: Reticulitermes. In: Zeng S, Dai W (eds) Hubei Science and Technology Press, Wuhan, China, pp 324–433
Isman MB (2000) Plant essential oils for pest and disease management. Crop Prot 19:603–608
Lewis VR, Haverty MI (1996) Evaluation of six techniques for control of the western drywood termite (Isoptera: Kalotermitidae) in structures. J Econ Entomol 89:922–934
Li GX, Zhao JM (2012) Control effect of 3 % ivermectin dust against termites. Chin J HygInsectic Equip 18:189–190
Lin AS, Feng LH, Hu YY, Yi AJ, Wu DF, Chen L, Mo JC (2011) Application of fipronil dust to control Coptotermes formosanus Shiraki (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) in trees. Sociobiology 57:519–525
Lin Y, Guo H, Zhang Y (2012) Advance and summaries in abamectin analogues and termites biological control research. Chin J Hyg Insectic Equip 18:465–470
Liu TX, Stansly PA (1995) Toxicity and repellency of some biorational insecticides to Bemisia argentifolii on tomato plants. Entomol Exp Appl 74:137–143
Mo JC, Teng L, Yang TC, Cheng JA, Guo JQ (2002) Toxicity of abamectin against Reticulitermes speratus (Kolbe). Chin J Pestic Sci 4:86–89
Mo JC, Wang ZY, Song XG, Guo JQ, Gong YG, Lu WL, Nei AG, Cheng JA (2006) Combination of ivermectin and a monitoring device for the control of Coptotermes formosanus (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) in the field. Sociobiology 47:915–925
Mulrooney JE, Davis MK, Wagner TL, Ingram RL (2006) Persistence and efficacy of termiticides used in preconstruction treatments to soil in Mississippi. J Econ Entomol 99:469–475
Neoh KB, Hu J, Yeoh BH, Lee CY (2012a) Toxicity and horizontal transfer of chlorantraniliprole against the Asian subterranean termite Coptotermes gestroi (Wasmann): effects of donor: recipient ratio, exposure duration and soil type. Pest Manag Sci 68:749–756
Neoh KB, Yeap BK, Tsunoda K, Yoshimura T, Lee CY (2012b) Do termites avoid carcasses? Behavioral responses depend on the nature of the carcasses. PLoS ONE 7:e36375
Park IK, Shin SC (2005) Fumigant activity of plant essential oils and components from garlic (Allium sativum) and clove bud (Eugenia caryophyllata) oils against the Japanese termite (Reticulitermes speratus Kolbe). J Agric Food Chem 53:4388–4392
Park YC, Kitade O, Schwarz M, Kim JP, Kim W (2006) Intraspecific molecular phylogeny, genetic variation and phylogeography of Reticulitermes speratus (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). Mol Cells 21:89–103
Parman V, Vargo EL (2010) Colony-level effects of imidacloprid in subterranean termites (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). J Econ Entomol 103:791–798
Qureshi NA, Qureshi MZ, Athar M, Malik A, Ullah A (2012) Fumigant toxicity of Mentha arviensis leaves extracts on Coptotermes heimi, Heterotermes indicola and their gut flagellates. Sociobiology 59:1509–1519
Ragnarsdottir KV (2000) Environmental fate and toxicology of organophosphate pesticides. J Geol Soc (Lond, UK) 157:859–876
Ramirez-Romero R, Desneux N, Decourtye A, Chaffiol A, Pham-Delègue MH (2008) Does Cry1Ab protein affect learning performances of the honey bee Apis mellifera L. (Hymenoptera, Apidae)? Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 70:327–333
Rust MK, Kennedy JM (1993) The feasibility of using modified atmospheres to control insect pests in museums. Getty Publications, Los Angeles, pp 111–115
Saran RK, Rust MK (2007) Toxicity, uptake, and transfer efficiency of fipronil in western subterranean termite (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). J Econ Entomol 100:495–508
Scheffrahn RH, Wheeler GS, Su NY (1995) Synergism of methyl bromide and sulfuryl fluoride toxicity against termites (Isoptera: Kalotermitidae, Rhinotermitidae) by admixture with carbon dioxide. J Econ Entomol 88:649–653
Shelton TG (2012) Assessment of donor/recipient ratios in permethrin transfer studies with Reticulitermes virginicus Banks. J Entomol Sci 472:139–149
Shelton TG, Grace JK (2003) Effects of exposure duration on transfer of nonrepellent termiticides among workers of Coptotermes formosanus Shiraki (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). J Econ Entomol 96:456–460
Soeprono AM, Rust MK (2004) Effect of horizontal transfer of barrier insecticides to control Argentine ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J Econ Entomol 97:1675–1681
Song DL, Hu XP (2006) Effects of dose, donor-recipient interaction time and ratio on fipronil transmission among the Formosan subterranean termite nestmates (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). Sociobiology 48:237–246
Spomer NA, Kamble ST, Warriner RA, Davis RW (2008) Influence of temperature on rate of uptake and subsequent horizontal transfer of [14C] fipronil by eastern subterranean termites (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). J Econ Entomol 101:902–908
Spomer NA, Kamble ST, Siegfried BD (2009) Bioavailability of chlorantraniliprole and indoxacarb to eastern subterranean termites (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) in various soils. J Econ Entomol 102:1922–1927
Su NY, Scheffrahn RH (1990) Comparison of eleven soil termiticides against the Formosan subterranean termite and eastern subterranean termite (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). J Econ Entomol 83:1918–1924
Su NY, Ban PM, Scheffrahn RH (1993a) Foraging populations and territories of the eastern subterranean termite (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) in southeastern Florida. Environ Entomol 22:1113–1117
Su NY, Scheffrahn RH, Ban PM (1993b) Barrier efficacy of pyrethroid and organophosphate formulations against subterranean termites (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). J Econ Entomol 86:772–776
Sultatos LG (1994) Mammalian toxicology of organophosphorus pesticides. J Toxicol Environ Health A 43:271–289
Thorne B, Breisch N, Hu XP, Song D, Presley W (2006) Less may be more: how concentration impacts efficacy of transfer. In: National conference on urban entomology, May 21–24 2006, Embassy Suites Hotel Raleigh-Durham, North Carolina, pp 1888
Tomalski M, Vargo EL (2005) Acquisition, transfer and metabolism of [14c] imidacloprid among workers of the subterranean termite, Reticulitermes flavipes (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). In: Proceedings of the 5th international conference on urban pests, pp 10–13
Tsunoda K (1991) Termite bioassays for evaluation of wood preservatives. Sociobiology 19:245–255
Valles SM, Woodson WD (2002) Group effects on insecticide toxicity in workers of the Formosan subterranean termite, Coptotermes formosanus Shiraki. Pest Manag Sci 58:769–774
Vanaclocha P, Vidal-Quist C, Oheix S, Montón H, Planes L, Catalán J, Tena A, Verdú MJ, Urbaneja A (2013) Acute toxicity in laboratory tests of fresh and aged residues of pesticides used in citrus on the parasitoid Aphytis melinus. J Pest Sci 86:329–336
Vargo EL, Parman V (2012) Effect of fipronil on subterranean termite colonies (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) in the field. J Econ Entomol 105:523–532
Verma M, Sharma S, Prasad R (2009) Biological alternatives for termite control: a review. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 63:959–972
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Zhengtang Zhou, Dong Lin, and Jinjin Dong (China Agricultural University) for their help in collecting termite specimens. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31071718). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Biondi.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Qu, Y., Xiao, D. et al. Lethal and social-mediated effects of ten insecticides on the subterranean termite Reticulitermes speratus . J Pest Sci 88, 741–751 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-015-0656-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-015-0656-0