Abstract
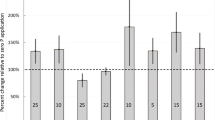
Slugs are a serious pest of cereal crops, and recent emphasis in slug pest management has shifted from solely chemical towards integrated approaches. The objective of the present research was to test if boosted silicon (Si) and calcium (Ca) levels in wheat seedlings can reduce slug grazing. Laboratory experiments were conducted in which wheat seedlings were grown firstly, with soluble Si and Ca (with and without additional mineral N) or secondly, with six levels of soluble Si, and consumption of leave sections by the field slug (Deroceras reticulatum) was measured. Boosted foliar Si concentrations reduced consumption significantly (P < 0.001) compared to an untreated control and Ca treatments in a no-choice setting; a similar trend (P < 0.10), but with a higher variability, was observed in a simultaneous choice setting. It is shown for the first time that increasing the nominal Si concentration of treatment solutions in a geometric series (from 0 to 6 g sodium metasilicate nonahydrate l−1) translated into a logarithmic increase in foliar Si concentrations (from 5.0 to 19.4 g Si kg−1 dry weight). When these leaves were offered simultaneously (choice setting), wheat leaves containing less than 10 g Si kg−1 were consumed preferentially by D. reticulatum (P < 0.001), suggesting that Si concentrations as low as 1 % leaf dry weight may be effective at reducing grazing by slugs. It is concluded that boosting Si levels in cereals has potential as a novel tool in crop protection against pest slugs and snails. Various open research questions to advance this tool are identified.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
ADAS (2010) A review of slug control in winter cereal and oilseed rape. Research Project Final Report PS2803. Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (DEFRA), London
Allan E, Crawley MJ (2011) Contrasting effects of insect and molluscan herbivores on plant diversity in a long-term field experiment. Ecol Lett 14:1246–1253
Barlow SE, Close AJ, Port GR (2013) The acceptability of meadow plants to the slug Deroceras reticulatum and implications for grassland restoration. Ann Bot 112:721–730
Bergmann W (1992) Nutritional disorders of plants. Gustav Fischer, Jena
Cid MS, Detling JK, Whicker AD, Brizuela MA (1990) Silicon uptake and distribution in Agropyron smithii as related to grazing history and defoliation. J Range Manag 43:344–346
Cotterill JV, Watkins RW, Brennon CB, Cowen DP (2007) Boosting silica levels in wheat leaves reduces grazing by rabbits. Pest Manag Sci 63:247–253
Douglas MR, Tooker JF (2012) Slug (Mollusca: Agriolimacidae, Arionidae) ecology and management in no-till field crops, with an emphasis on the mid-Atlantic region. J Integr Pest Manag 3(1):C1–C9
Eaton AD, Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE (eds) (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington DC
Epstein E (2009) Silicon: its manifold roles in plants. Ann Appl Biol 155:155–160
Franceschi VR, Nakata PA (2005) Calcium oxalate in plants: formation and function. Annu Rev Plant Biol 56:41–71
Garbuzov M, Reidinger S, Hartley SE (2011) Interactive effects of plant-available soil silicon and herbivory on competition between two grass species. Ann Bot 108:1355–1363
Glen DM, Moens R (2002) Agriolimacidae, Arionidae and Milacidae as pests in Western European cereals. In: Barker GM (ed) Molluscs as crop pests. CABI, Wallingford, pp 271–300
Gocke M, Liang W, Sommer M, Kuzyakov Y (2013) Silicon uptake by wheat: effects of Si pools and pH. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 176:551–560
Godan D (1983) Pest slugs and snails: biology and control. Springer, Berlin
Guntzer F, Keller C, Meunier JD (2012) Benefits of plant silicon for crops: a review. Agron Sustain Dev 32:201–213
Howlett SA (2012) Terrestrial slug problems: classical biological control and beyond. CAB Rev 7(article 051):1–10
Lockwood JR (1998) On the statistical analysis of multiple-choice feeding preference experiments. Oecologia 116:475–481
Massey FP, Hartley SE (2009) Physical defences wear you down: progressive and irreversible impacts of silica on insect herbivores. J Anim Ecol 78:281–291
Motheral SM, Orrock JL (2010) Gastropod herbivore preference for seedlings of two native and two exotic grass species. Am Midl Nat 163:106–114
Murray DAH, Clarke MB, and Ronning DA (2013) The current and potential costs of invertebrate pests in Australia. GRDC Project Code AEP00001. Grains Research & Development Corporation, Kingston, Australia
Park S, Doege SJ, Nakata PA, Korth KL (2009) Medicago truncatula-derived calcium oxalate crystals have a negative impact on chewing insect performance via their physical properties. Entom Exp Appl 131:208–215
Port CM, Port GR (1986) The biology and behaviour of slugs in relation to crop damage and control. Agric Zool Rev 1:255–299
Rahman MM, Kawamura O (2011) Oxalate accumulation in forage plants: some agronomic, climatic and genetic aspects. Asian-Aust J Anim Sci 24:439–448
Reynolds OL, Keeping MG, Meyer JH (2009) Silicon-augmented resistance of plants to herbivorous insects: a review. Ann Appl Biol 155:171–186
Roa R (1992) Design and analysis of multiple-choice feeding-preference experiments. Oecologia 89:509–515
Snyder GH, Matichenkov VV, Datnoff LE (2006) Silicon. In: Barker AV, Pilbeam DJ (eds) Handbook of plant nutrition. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 551–568
South A (1992) Terrestrial slugs: biology, ecology and control. Chapman & Hall, London
Speiser B (2001) Food and feeding behaviour. In: Barker GM (ed) The biology of terrestrial molluscs. CABI, Wallingford, pp 259–288
Vandevenne F, Struyf E, Clymans W, Meire P (2012) Agricultural silica harvest: have humans created a new loop in the global silica cycle? Front Ecol Environ 10:243–248
Wadham MD, Wynn Parry D (1981) The silicon content of Oryza sativa L. and its effect on the grazing behaviour of Agriolimax reticulatus Müller. Ann Bot 48:399–402
Acknowledgments
We thank Goldcrop Ltd., Cork, for donating seeds, Frank McDermott for advice on Si analysis, Aoife Smith for her help in maintaining the wheat plants, and four anonymous reviewers, one of whom provided an exceptionally detailed list of suggestions. We acknowledge an Innovation Bursary for B. Hogan, funded under the UCD Seed Funding Scheme in support of the UCD–TCD Innovation Academy, and funding provided under the National Development Plan, through COFORD, administered by the Department for Agriculture, Food and the Marine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Traugott.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Griffin, M., Hogan, B. & Schmidt, O. Silicon reduces slug feeding on wheat seedlings. J Pest Sci 88, 17–24 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-014-0579-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-014-0579-1