Abstract
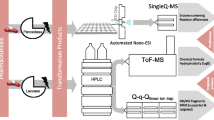
A rapid ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography coupled with hybrid triple quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS) method has been developed for the identification of degradation products and process impurities of terbutaline sulfate. Terbutaline sulfate was subjected to long-term storage and stress degradation conditions of hydrolysis (acidic, neutral and alkaline), oxidation, heat, humidity and photolysis. The separation was achieved on a phenomenex luna C18 (150 mm × 2.0 mm, 3 μm) column using a mobile phase composed of ammonium formate buffer (10 mM, pH 3.2) and methanol in gradient elution mode. A total of 17 compounds including 14 novel degradation products were characterized. Terbutaline sulfate was found to be highly susceptible to oxidative, alkaline hydrolytic and alkaline photolytic conditions. The most probable mechanisms for the formation of degradation products have been proposed for the first time. The in silico toxicity of the drug and its degradation products was assessed using toxicity prediction by computer-assisted technology (TOPKAT) software.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Müller L, Mauthe RJ, Riley CM et al (2006) A rationale for determining, testing, and controlling specific impurities in pharmaceuticals that possess potential for genotoxicity. Regul Toxicol Pharm 44:198–211
ICH (2002) Impurities in new drug substances Q3A (R1), testing of new drug substances and products Q3a (R1). In: International conference on harmonization. IFPMA, Geneva
Ahuja S, Ashman J (1990) Terbutaline sulfate. Anal Profiles Drug Subst 19:601–605
World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) The 2015 prohibited list. http://www.wada-ama.org
Faiyazuddin MD, Rauf A, Ahmad N et al (2011) A validated HPTLC method for determination of terbutaline sulfate in biological samples, Application to pharmacokinetic study. Saudi Pharm J 19:185–191
Li ST, Wang JS, Zhao SL (2009) Determination of terbutaline sulfate by capillary electrophoresis with chemiluminescence detection. J Chromatogr B 877:155–158
Rao KLN, Krishnaiah Ch, Babu KS et al (2014) Development and validation of a stability-indicating LC method for simultaneous determination of related compounds of guaifenesin, terbutaline sulfate and ambroxol HCl in cough syrup formulation. J Saudi Chem Soc 18:593–600
Henze MK, Opfermann G, Spahn-Langguth H et al (2001) Screening of β-2 agonists and confirmation of fenoterol, orciprenaline, reproterol and terbutaline with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry as tetrahydroisoquinoline derivatives. J Chromatogr B 751:93–105
Kumar A, Nanda S (2011) A validated high performance liquid chromatographic method for estimation of bromhexine and terbutaline in bulk and tablet dosage forms. Pharm Methods 2:218–222
Herring VL, Johnson JA (2000) Simple method for determination of terbutaline plasma concentration by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B 741:307–312
Zhang Y, Zhang ZR (2004) Simple determination of terbutaline in dog plasma by column-switching liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B 805:211–214
Yang WL, Abdelmelek SB, Zheng Z et al (2013) Photochemical transformation of terbutaline (pharmaceutical) in simulated natural waters, degradation kinetics and mechanisms. Water Res 47:6558–6565
European Pharmacopoeia 8.0: 3377–3378
United States Pharmacopoeia 39: 6054
Dosage forms containing terbutaline sulfate (2014) PCT/EP2013/070900
Daraghmeh N, Al-Omari MM, Sara Z et al (2002) Determination of terbutaline sulfate and its degradation products in pharmaceutical formulations using LC. J Pharm Biomed Anal 29:927–937
Vishnuvardhan C, Swain D, Borkar R et al (2016) Study of forced degradation behaviour of brinzolamide using LC-ESI-Q-TOF and in silico toxicity prediction. Chromatographia 79:1293–1308
ICH (2003) Stability testing of new drug substances and products Q1a (R2). In: International conference on harmonization. IFPMA, Geneva
ICH (1996) Guidelines on photostability testing of new drug substances and products Q1B. In: International conference on harmonization. IFPMA, Geneva
Li T, Xu XL, Fu S et al (2014) Structural elucidation of stress degradation products of ampicillin sodium by liquid chromatography/hybrid triple quadrupole linear ion trap mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography/hybrid quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 28:1929–1936
Abiramasundari A, Sudarsanam V, Vasu KK (2015) Characterization of the degradation products of bambuterol using LCMS–QTOF and NMR. Anal Methods 7:7659–7673
Domínguez-Romero JC, García-Reyes JF, Martínez-Romero R et al (2013) Detection of main urinary metabolites of β2-agonists clenbuterol, salbutamol and terbutaline by liquid chromatography high resolution mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 923–924:128–135
Chadha R, Bali A, Bansal G (2016) Characterization of stress degradation products of duloxetine hydrochloride employing LC–UV/PDA and LC–MS/TOF studies. J Pharm Biomed Anal 121:39–55
Chadha R, Bali A, Bansal G (2016) Identification and characterization of stress degradation products of dronedarone hydrochloride employing LC–UV/PDA and LC–MS/TOF and MSn studies. J Pharm Biomed Anal 118:139–148
Swain D, Patel PN, Nagaraj G et al (2016) Liquid chromatographic method development for forced degradation products of dabigatran etexilate: characterisation and in silico toxicity evaluation. Chromatographia 79:169–178
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank the No. 4 Pharmaceutical Company Limited (China) for graciously providing samples of terbutaline sulfate. The authors are also thankful for the financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81102412), the Ministry of Education Key Project of Science and Technology Foundation of China (211021), Hundreds of Innovative Talents Project of Hebei Education Department of China, and the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province of China (C2011206158, 08B031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, N., Qian, Q., Qi, P. et al. Identification of Degradation Products and Process Impurities from Terbutaline Sulfate by UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS and In Silico Toxicity Prediction. Chromatographia 80, 793–804 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-017-3259-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-017-3259-5