Abstract
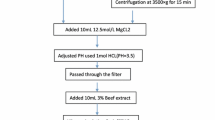
Foodborne enteroviruses such as norovirus, rotavirus and astrovirus can cause gastroenteritis in children under the age of five and infants. In this paper, a novel and ultrasensitive method, combining reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) with capillary electrophoresis laser-induced fluorescence (CE-LIF), is proposed to detect three viruses in vegetable samples. The viruses, including norovirus, rotavirus and astrovirus in vegetables, were eluted using glycine buffer (pH 9.5), and concentrated by 15 % polyethylene glycol 6000 (PEG 6000). The primers, targeting the specific and conservative sequences of nucleic acids of the viruses, were synthesized and used in RT-PCR reaction. The amplification products were labeled with highly sensitive SYBR Gold, then separated by capillary electrophoresis and detected by a laser-induced fluorescence detector within 16 min. The intraday and interday relative standard deviation of migration time for the DNA Marker was in the range of 1.09–1.30 and 1.77–2.60 %, respectively, while the detection limits of the three viruses were as low as 1.33 × 102 copies mL−1 for norovirus, 1.86 × 102 copies mL−1 for rotavirus, and 1.40 × 102 copies mL−1 for astrovirus. Meanwhile, the results of homology analysis and specificity experiments showed that the method had good specificity. A fried pickled mustard tuber tested positive for norovirus by the proposed method in an outbreak which happened recently in Chengdu. This protocol demonstrated the possibility for rapid, sensitive and specific detection of foodborne enteric viruses in vegetable samples.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jansen A, Stark K, Kunkel J, Schreier E, Ignatius R, Liesenfeld O, Werber D, Göbel UB, Zeitz M, Schneider T (2008) BMC Infect Dis 8:143–150
Naficy AB, Rao MR, Holmes JL, Abu-Elyazeed R, Savarino SJ, Wierzba TF, Frenck RW, Monroe SS, Glass RI, Clemens JD (2000) J Infect Dis 182:685–690
Dennehy PH, Nelson SM, Spangenberger S, Noel JS, Monroe SS, Glass RI (2001) J Infect Dis 184:10–15
Patel MM, Widdowson M, Glass RI, Akazawa K, Vinjé J, Parashar UD (2008) Emerg Infect Dis 14:1224–1231
Bosch A (1998) Int Microbiol 1:191–196
Koopmans M, Vennema H, Heersma H, van Strien E, van Duynhoven Y, Brown D, Reacher M, Lopman B (2003) Emerg Infect Dis 9:1136–1142
Marks PJ, Vipond IB, Regan FM, Wedgwood K, Fey RE, Caul EO (2003) Epidemiol Infect 131:727–736
Jolan E, Walter DKM (2003) Curr Opin Infect Dis 16:247–253
Santos RAT, Borges AMT, Costa PSS, Teixeira JMS, Giugliano LG, Leite JPG, Cardoso DDP (2007) Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 102:209–213
Kawai K, O Brien MA, Goveia MG, Mast TC, El Khoury AC (2012) Vaccine 30:1244–1254
Webby RJ, Carville KS, Kirk MD, Greening G, Ratcliff RM, Crerar SK, Dempsey K, Sarna M, Stafford R, Patel M, Hall G (2007) Clin Infect Dis 44:1026–1031
Anderson EJ, Katz BZ, Polin JA, Reddy S, Weinrobe MH, Noskin GA (2012) J Infect 64:89–95
Kathrin S, Reimar J, Christina S, Lüppo E, Jörg S, Günter K (2010) J Virol Methods 169:22–27
Fong TT, Lipp EK (2005) Microbiol Mol Biol R 69:357–371
Rosa M, Dalton ERRA (2002) Pediatr Infect Dis J 21:1038–1042
Hong SA, Kwon J, Kim D, Yang S (2015) Biosens Bioelectron 64:338–344
Yan Y, Wang H, Gao L, Ji J, Ge Z, Zhu X, He P, Chen Z (2013) J Virol Methods 189:277–282
Ruan J, Li M, Liu Y, Li Y, Li Y (2013) J Chromatogr B 921–922:15–20
Mao HX, Li YQ, Pei XF, He C, Lin Q (2007) Chin J Chromatogr 25:473–477
Zhang P, Ren J, Shen Z (2004) Electrophoresis 25:1823–1828
Scherer K, Mäde D, Ellerbroek L, Schulenburg J, Johne R, Klein G (2009) Food Environ Virol 1:42–49
YoungBin P, You H, Cho YJ (2008) Appl Environ Microb 74:4226–4230
Scherer K, Johne R, Schrader C, Ellerbroek L, Schulenburg J, Klein G (2010) J Virol Methods 169:22–27
Li YQ, Yang JG, Zhou Y, Zou XL, Mi JP, Zeng HY (2004) J Sichuan Univ (Med Sci Edi) 35:348–354
Li Y, White J, Stokes D, Sayler G, Sepaniak M (2001) Biotechnol Prog 17:348–354
Dubois E, Hennechart C, Merle G, Burger C, Hmila N, Ruelle S, Perelle S, Ferré V (2007) Int J Food Microbiol 117:141–149
Pang XL, Preiksaitis JK, Lee B (2005) J ClinVirol 33:168–171
Arvelo W, Sosa SM, Juliao P, López MR, Estevéz A, López B, Morales-Betoulle ME, González M, Gregoricus NA, Hall AJ, Vinje J, Parashar U, Lindblade KA (2012) J ClinVirol 55:8–11
Jan V, Marion PGK (1996) J Infect Dis 174:610–615
Vennema H, de Bruin E, Koopmans M (2002) J Clin Virol 25:233–235
Jorge F, Johnna S, Irene PS, Laura W, Dorys G, Claudio L, Albert ZK (1990) J Virol 64:4021–4024
Kou XX, Wu QP, Wang DP, Guo WP, Deng MQ (2007) Microbiology 34:401–405
Krishna NK (2005) Viral Immunol 18:17–26
Zhong JY, Zhu B, Zhou R, Wang CB, Xiao MS, Gong ST (2006) J Mod Clin Med Bioen 12:129–131
Schulz K, Wegner U, Gurtler L, Wiersbitzky S, Mentel R (2000) Eur J ClinMicrobiol Infect Dis 19:563–565
Jacqueline SN, Terry WL, John BK, Roger IG, Stephan SM (1995) J Clin Microbiol 33:797–801
Huang Y, Li JQ, Li YF, Li YZ, Chen YD (2012) Chi Trop Med 12:671–672
Marion K, Erwin D (2004) Int J Food Microbiol 90:23–41
Luciana C, Eric D, Ni gel C, Dario de M, Anna CS, Bernard C, Saskia AR, Jeffrey H, Wim HM Van der P (2008) Food Anal Methods 1:73–84
Gillian DL, Theodore GM (1998) Appl Environ Microb 54:1983–1988
Li Q, Wu X, Liu Y, Wu Y, Gao G, Yang X (2011) Chin J Heath Lab Tech 21:382–386
Tuma RS, Beaudet MP, Jin X, Jones LJ, Cheung CY, Yue S, Singer VL (1999) Anal Biochem 268:278–288
Lekanne DR, Fijnvandraat AC, Ruijter JM, Moorman AF (2002) Anal Biochem 307:63–69
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by grants from Youth Foundation of National Natural Science of China (No. 81102162).
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work and that there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in the manuscript entitled “Capillary Electrophoresis-based Detection for Foodborne Enteroviruses in Vegetable Samples”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10337_2015_2931_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 1 (TIFF 214 kb). Figure 1 SuppInfo. The sensitivity of norovirus, rotavirus and astrovirus and the electrophoretogram of Gene RulerTM Low Range DNA Ladder.The figures indicate the sizes of DNA fragments:1.25 bp 2.50 bp 3.75 bp 4.100 bp 5.150 bp 6.200 bp 7.300 bp 8.400 bp 9.500 bp 10.700 bp
10337_2015_2931_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 2 (TIFF 365 kb). Figure 2 SuppInfo. The gel electrophoresis figure of the RT-PCR products of the artificially inoculated samples
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruan, J., Sun, C.J., Chen, F. et al. Capillary Electrophoresis-Based Detection for Foodborne Enteroviruses in Vegetable Samples. Chromatographia 78, 1191–1199 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-015-2931-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-015-2931-x