Abstract
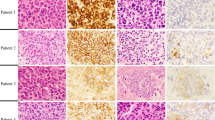
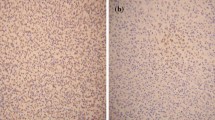
Nowadays, resistance to rituximab has become a major issue in clinical practice. And loss of CD20 may contribute to it. Here we presented a case of loss of CD20 expression in relapsed diffuse large B cell lymphoma treated with rituximab and discuss the incidence, mechanism, influence factors, specific markers, prognosis and treatment of this disease. These results suggested that a post-relapse biopsy after rituximab treatment should be performed. CD79a and Pax-5 should be used as the first-line B lineage-specific markers for these patients. Though mechanisms of CD20 decrement are not fully elucidated, the down-regulation of CD20 mRNA is the most probable hypothesis. Recently various new agents are developed, but the prognosis is still poor. Further studies for new treatments are needed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis TA, Czerwinski DK, Levy R. Therapy of B-cell lymphoma with anti-CD20 antibodies can result in the loss of CD20 antigen expression. Clin Cancer Res, 1999, 5: 611–615.
Vose JM, Link BK, Grossbard ML, et al. Phase II study of rituximab in combination with chop chemotherapy in patients with previously untreated, aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J Clin Oncol, 2001, 19: 389–397.
Coiffier B, Lepage E, Briere J, et al. CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med, 2002, 346: 235–242.
Davis TA, Grillo-Lopez AJ, White CA, et al. Rituximab anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapy in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: safety and efficacy of re-treatment. J Clin Oncol, 2000, 18: 3135–3143.
Kennedy GA, Tey SK, Cobcroft R, et al. Incidence and nature of CD20-negative relapses following rituximab therapy in aggressive Bcell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a retrospective review. Br J Haematol, 2002, 119: 412–416.
Chu PG, Chen YY, Molina A, et al. Recurrent B-cell neoplasms after Rituximab therapy: an immunophenotypic and genotypic study. Leuk Lymphoma, 2002, 43: 2335–2341.
Maeshima AM, Taniguchi H, Nomoto J, et al. Histological and immunophenotypic changes in 59 cases of B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma after rituximab therapy. Cancer Sci, 2009, 100: 54–61.
Hiraga J, Tomita A, Sugimoto T, et al. Down-regulation of CD20 expression in B-cell lymphoma cells after treatment with rituximab-containing combination chemotherapies: its prevalence and clinical significance. Blood, 2009, 113: 4885–4893.
Chu PG, Loera S, Huang Q, et al. Lineage determination of CD20-B-Cell neoplasms: an immunohistochemical study. Am J Clin Pathol, 2006, 126: 534–544.
Pijuan L, Vicioso L, Bellosillo B, et al. CD20-negative T-cell-rich B-cell lymphoma as a progression of a nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin’s lymphoma treated with rituximab: a molecular analysis using laser capture microdissection. Am J Surg Pathol, 2005, 29: 1399–1403.
Goteri G, Olivieri A, Ranaldi R, et al. Bone marrow histopathological and molecular changes of small B-cell lymphomas after rituximab therapy: comparison with clinical response and patients outcome. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol, 2006, 19: 421–431.
Jilani I, O’Brien S, Manshuri T, et al. Transient down-modulation of CD20 by rituximab in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood, 2003, 102: 3514–3520.
Rawal YB, Nuovo GJ, Frambach GE, et al. The absence of CD20 messenger RNA in recurrent cutaneous B-cell lymphomafollowing rituximab therapy. J Cutan Pathol, 2005, 32: 616–621.
Takei K, Yamazaki T, Sawada U, et al. Analysis of changes in CD20, CD55, and CD59 expression on established rituximab-resistant Blymphoma cell lines. Leuk Res, 2006, 30: 625–631.
Tomita A, Hiraga J, Kiyoi H, et al. Epigenetic regulation of CD20 protein expression in a novel B-cell lymphoma cell line, RRBL1, established from a patient treated repeatedly with rituximab-containing chemotherapy. Int J Hematol, 2007, 86: 49–57.
Sonoki T, Li Y, Miyanishi S, et al. Establishment of a novel CD20 negative mature B-cell line, WILL2, from a CD20 positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patient treated with rituximab. Int J Hematol, 2009, 89: 400–402.
Terui Y, Mishima Y, Sugimura N, et al. Identification of CD20 C-terminal deletion mutations associated with loss of CD20 expression in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res, 2009, 15: 2523–2530.
Czuczman MS, Olejniczak S, Gowda A, et al. Acquirement of rituximab resistance in lymphoma cell lines is associated with both global CD20 gene and protein down-regulation regulated at the pretranscriptional and posttranscriptional levels. Clin Cancer Res, 2008, 14: 1561–1570.
Johnson NA, Leach S, Woolcock B, et al. CD20 mutations involving the rituximab epitope are rare in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas and are not a significant cause of R-CHOP failure. Haematologica, 2009, 94: 423–427.
Foran JM, Norton AJ, Micallef IN, et al. Loss of CD20 expression following treatment with rituximab (chimaeric monoclonal anti-CD20): a retrospective cohort analysis. Br J Haematol, 2001, 114: 881–883.
Ferreri AJ, Dognini GP, Verona C, et al. Re-occurrence of the CD20 molecule expression subsequent to CD20-negative relapse in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica, 2007, 92:e1–2.
Johnson NA, Boyle M, Bashashati A, et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: reduced CD20 expression is associated with an inferior survival. Blood, 2009, 113: 3773–3780.
Molica S. A systematic review on Richter syndrome: what is the published evidence. Leuk Lymphoma, 2010, 51: 415–421.
Berinstein NL, Grillo-Lopez AJ, White CA, et al. Association of serum Rituximab (IDEC-C2B8) concentration and anti-tumor response in the treatment of recurrent low-grade or follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Ann Oncol, 1998, 9: 995–1001.
van Meerten T, Rozemuller H, Hol S, et al. HuMab-7D8, a monoclonal antibody directed against the membrane-proximal small loop epitope of CD20 can effectively eliminate CD20 low expressing tumor cells that resist rituximab-mediated lysis. Haematologica, 2010, 95: 2063–2071.
Cheson BD. Ofatumumab, a novel anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody for the treatment of B-cell malignancies. J Clin Oncol, 2010, 28: 3525–3530.
Gerber HP, Kung-Sutherland M, Stone I, et al. Potent antitumor activity of the anti-CD19 auristatin antibody drug conjugate hBU12-vcMMAE against rituximab-sensitive and -resistant lymphomas. Blood, 2009, 113: 4352–4361.
Blanc V, Bousseau A, Caron A, et al. SAR3419: an anti-CD19-Maytansinoid Immunoconjugate for the treatment of B-cell malignancies. Clin Cancer Res, 2011, 17: 6448–6458.
Cruz RI, Hernandez-Ilizaliturri FJ, Olejniczak S, et al. CD52 over-expression affects rituximab-associated complement-mediated cytotoxicity but not antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity: preclinical evidence that targeting CD52 with alemtuzumab may reverse acquired resistance to rituximab in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma, 2007, 48: 2424–2436.
Ge X, Wu L, Hu W, et al. rILYd4, a human CD59 inhibitor, enhances complement-dependent cytotoxicity of ofatumumab against rituximab-resistant B-cell lymphoma cells and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin Cancer Res, 2011, 17: 6702–6711.
Hu W, Ge X, You T, et al. Human CD59 inhibitor sensitizes rituximabresistant lymphoma cells to complement-mediated cytolysis. Cancer Res, 2011, 71: 2298–2307.
Jazirehi AR, Vega MI, Bonavida B. Development of rituximab-resistant lymphoma clones with altered cell signaling and cross-resistance to chemotherapy. Cancer Res, 2007, 67: 1270–1281.
Vega MI, Martinez-Paniagua M, Jazirehi AR, et al. The NF-kappaB inhibitors (bortezomib and DHMEQ) sensitise rituximab-resistant AIDSB-non-Hodgkin lymphoma to apoptosis by various chemotherapeutic drugs. Leuk Lymphoma, 2008, 49: 1982–1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Zhao, Y., Dong, X. et al. Loss of CD20 expression in relapsed diffuse large B cell lymphoma after rituximab therapy: a case report and review of the literature. Chin. -Ger. J. Clin. Oncol. 12, 148–151 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-012-1116-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-012-1116-4