Abstract
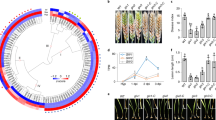
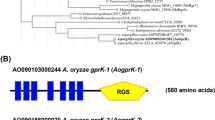
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are a large transmembrane receptor superfamily that is involved in many cellular signaling pathways. In the present study, GPCR-family genes from the toxigenic and necrotrophic plant pathogen Alternaria alternata were cloned and characterized. Three GPCR-encoding genes, AaGPR1, AaGPR2, and AaGPR3 were identified in the draft genomic data of the A. alternata tomato pathotype, which produces the host-specific AAL-toxin. AaGPR1, AaGPR2, and AaGPR3 each encodes a protein containing a seven transmembrane domain that is characteristic of GPCRs. Targeted deletion of AaGPR1, AaGPR2, or AaGPR3 in the A. alternata tomato pathotype was conducted to understand the influence of G-protein signaling mechanisms on developmental processes and virulence of this pathogen. No changes in colony morphology or AAL-toxin production were observed for the deletion strain ΔAaGPR1, 2, and 3, compared with the wild-type strain. However, one deletion strain, ΔAaGPR3, exhibited aberrant conidial morphology including decreased conidial length and beak formation. The ability to induce the formation of necrotic lesions on susceptible leaves also significantly decreased in ΔAaGPR3, indicating a reduction in virulence. These defects are similar to the phenotypes found for the Gα gene (AGA1) mutant of A. alternata. These results indicate that the G-protein signal transduction pathway appears to be involved in conidial development and virulence of A. alternata.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi Y, Akamatsu H, Otani H, Kodama M (2009a) Horizontal chromosome transfer, a mechanism for the evolution and differentiation of a plant-pathogenic fungus. Eukaryot Cell 8:1732–1738
Akagi Y, Taga M, Yamamoto M, Tsuge T, Fukumasa-Nakai Y, Otani H, Kodama M (2009b) Chromosome constitution of hybrid strains constructed by protoplast fusion between the tomato and strawberry pathotypes of Alternaria alternata. J Gen Plant Pathol 75:101–109
Akamatsu H, Itoh Y, Kodama M, Otani H, Kohmoto K (1997) AAL-toxin-deficient mutants of Alternaria alternata tomato pathotype by restriction enzyme-mediated integration. Phytopathology 87:967–972
Akamatsu H, Otani H, Kodama M (2003) Characterization of a gene cluster for host-specific AAL-toxin biosynthesis in the tomato pathotype of Alternaria alternata. Fungal Genet Newsl 50(Suppl):355
Brunner K, Omann M, Pucher ME, Delic M, Lehner SM, Domnanich P, Kratochwill K, Druzhinina I, Denk D, Zeilinger S (2008) Trichoderma G protein-coupled receptors: functional characterisation of a cAMP receptor-like protein from Trichoderma atroviride. Curr Genet 54:283–299
Fredriksson R, Lagerström MC, Lundin LG, Schiöth HB (2003) The G-protein-coupled receptors in the human genome form five main families. Phylogenetic analysis, paralogon groups, and fingerprints. Mol Pharmacol 63:1256–1272
Gao Q, Jin K, Ying SH, Zhang Y, Xiao G, Shang Y, Duan Z, Hu X, Xie XQ, Zhou G, Peng G, Luo Z, Huang W, Wang B, Fang W, Wang S, Zhong Y, Ma LJ, St.Leger RJ, Zhao GP, Pei Y, Feng MG, Xia Y, Wang C (2011) Genome sequencing and comparative transcriptomics of the model entomopathogenic fungi Metarhizium anisopliae and M. acridum. PLoS Genet 7:e1001264
Gehrke A, Heinekamp T, Jacobsen ID, Brakhage AA (2010) Heptahelical receptors GprC and GprD of Aspergillus fumigatus are essential regulators of colony growth, hyphal morphogenesis, and virulence. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:3989–3998
Gilchrist DG, Grogan RG (1976) Production and nature of a host-specific toxin from Alternaria alternata f. sp. lycopersici. Phytopathology 66:165–171
Gruber S, Omann M, Zeilinger S (2013) Comparative analysis of the repertoire of G protein-coupled receptors of three species of the fungal genus Trichoderma. BMC Microbiol 13:108
Han KH, Seo JA, Yu JH (2004) A putative G protein-coupled receptor negatively controls sexual development in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Microbiol 51:1333–1345
Howard AD, McAllister G, Feighner SD, Liu Q, Nargund RP, Van der Ploeg LHT, Patchett AA (2001) Orphan G-protein-coupled receptors and natural ligand discovery. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22:132–140
Kheder AA, Akagi Y, Akamatsu H, Yanaga K, Maekawa N, Otani H, Tsuge T, Kodama M (2012a) Functional analysis of the melanin biosynthesis genes ALM1 and BRM2-1 in the tomato pathotype of Alternaria alternata. J Gen Plant Pathol 78:30–38
Kheder AA, Akagi Y, Tsuge T, Kodama M (2012b) Functional analysis of the ceramide synthase gene ALT7, a homolog of the disease resistance gene Asc1, in the plant pathogen Alternaria alternata. J Plant Pathol Microbiol S 2:001
Kodama M, Otani H, Kohmoto K (1995) A rapid and sensitive procedure for the quantitative detection of AL-toxin by fluorescence derivatization and separation by high performance liquid chromatography. Ann Phytopathol Soc Jpn 61:477–480
Kohmoto K, Otani H, Tsuge T (1995) Alternaria alternata pathogens. In: Kohmoto K, Singh US, Singh RP (eds) Pathogenesis and host specificity in plant diseases: histopathological biochemical, genetic and molecular bases, vol 2., EukaryotesPergamon, Oxford, pp 51–63
Krishnan A, Almén MS, Fredriksson R, Schiöth HB (2012) The origin of GPCRs: identification of mammalian like Rhodopsin, Adhesion, Glutamate and Frizzled GPCRs in fungi. PLoS One 7:e29817
Kulkarni RD, Thon MR, Pan H, Dean RA (2005) Novel G-protein-coupled receptor-like proteins in the plant pathogenic fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Genome Biol 6:R24
Kuwayama H, Obara S, Morio T, Katoh M, Urushihara H, Tanaka Y (2002) PCR-mediated generation of a gene disruption construct without the use of DNA ligase and plasmid vectors. Nucleic Acids Res 30:e2
Lafon A, Han KH, Seo JA, Yu JH, d’Enfert C (2006) G-protein and cAMP-mediated signaling in aspergilli: a genomic perspective. Fungal Genet Biol 43:490–502
Lagerström MC, Schiöth HB (2008) Structural diversity of G protein-coupled receptors and significance for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:339–357
Lengeler KB, Davidson RC, D’Souza C, Harashima T, Shen WC, Wang P, Pan XW, Waugh M, Heitman J (2000) Signal transduction cascades regulating fungal development and virulence. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64:746–785
Nayak T, Szewczyk E, Oakley CE, Osmani A, Ukil L, Murray SL, Hynes MJ, Osmani SA, Oakley BR (2006) A versatile and efficient gene-targeting system for Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics 172:1557–1566
Neer EJ (1995) Heterotrimeric G-proteins: organizers of transmembrane signals. Cell 80:249–257
Ninomiya Y, Suzuki K, Ishii C, Inoue H (2004) Highly efficient gene replacements in Neurospora strains deficient for nonhomologous end-joining. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:12248–12253
Oldham WM, Hamm HE (2008) Heterotrimeric G protein activation by G-protein-coupled receptors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:60–71
Peever TL, Su G, Carpenter-Boggs L, Timmer LW (2004) Molecular systematics of citrus-associated Alternaria species. Mycologia 96:110–134
Rotem J (1994) The genus Alternaria: biology, epidemiology, and pathogenicity. APS Press, St Paul
Seo JA, Han KH, Yu JH (2004) The gprA and gprB genes encode putative G protein-coupled receptors required for self-fertilization in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Microbiol 53:1611–1623
Thomma BPHJ (2003) Alternaria spp.: from general saprophyte to specific parasite. Mol Plant Pathol 4:225–236
Tsuge T, Harimoto Y, Akimitsu K, Ohtani K, Kodama M, Akagi Y, Egusa M, Yamamoto M, Otani H (2013) Host-selective toxins produced by the plant pathogenic fungus Alternaria alternata. FEMS Microbiol Rev 37:44–66
Wang Y, Li A, Wang X, Zhang X, Zhao W, Dou D, Zheng X, Wang Y (2010) GPR11, a putative seven-transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor, controls zoospore development and virulence of Phytophthora sojae. Eukaryot Cell 9:242–250
Xue CY, Hsueh YP, Heitman J (2008) Magnificent seven: roles of G protein-coupled receptors in extracellular sensing in fungi. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:1010–1032
Yamagishi D, Akamatsu H, Otani H, Kodama M (2006a) Pathological evaluation of host-specific AAL-toxins and fumonisin mycotoxins produced by Alternaria and Fusarium species. J Gen Plant Pathol 72:323–327
Yamagishi D, Otani H, Kodama M (2006b) G protein signaling mediates developmental processes and pathogenesis of Alternaria alternata. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 19:1280–1288
Yoder OC (1980) Toxins in pathogenesis. Annu Rev Phytopathol 18:103–129
Zheng H, Zhou L, Dou T, Han X, Cai Y, Zhan X, Tang C, Huang J, Wu Q (2010) Genome-wide prediction of G protein-coupled receptors in Verticillium spp. Fungal Biol 114:359–368
Acknowledgments
We thank R. P. Oliver for providing pAN7-1. We are grateful to J. Hille, B. F. Brandwagt, D. G. Gilchrist, K. Akimitsu, and T. L. Peever for providing Alternaria strains. This work was supported by Grant-in-Aid for JSPS Fellows (Grant 24 8246), and Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (S) (19108001), (A) (23248007), (B) (23380025) and (B) (26304025) from the Japanese Society for Promotion of Sciences, and Global COE Program “Advanced Utilization of Fungus/Mushroom Resources for Sustainable Society in Harmony with Nature” by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10327_2016_647_MOESM2_ESM.tiff
Supplementary Fig. 1. Membrane topology of predicted proteins from AaGPR1, AaGPR2, and AaGPR3. Seven possible transmembrane domains of typical GPCR proteins were predicted by the SOSUI program. (TIFF 2702 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takao, K., Akagi, Y., Tsuge, T. et al. Functional characterization of putative G protein-coupled receptors in the tomato pathotype of Alternaria alternata . J Gen Plant Pathol 82, 82–88 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-016-0647-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-016-0647-x