Abstract
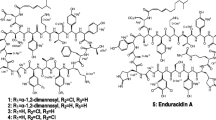
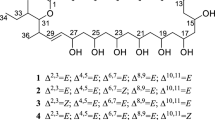
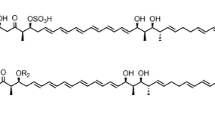
Genetic engineering of post-polyketide synthase-tailoring genes can be used to generate new macrolide analogs through manipulation of the genes involved in their biosynthesis. Rosamicin, a 16-member macrolide antibiotic produced by Micromonospora rosaria IFO13697, contains a formyl group and an epoxide at C-20 and C-12/13 positions which are formed by the cytochrome P450 enzymes RosC and RosD, respectively. The d-mycinose biosynthesis genes in mycinamicin II biosynthesis gene cluster of Micomonospora guriseorubida A11725 were introduced into the rosC and rosD disruption mutants of M. rosaria IFO13697. The resulting engineered strains, M. rosaria TPMA0054 and TPMA0069, produced mycinosyl rosamicin derivatives, IZIV and IZV, respectively. IZIV was identified as a novel mycinosyl rosamicin derivative, 23-O-mycinosyl-20-deoxo-20-dihydrorosamicin.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anzai Y, Iizaka Y, Li W, Idemoto N, Tsukada S, Koike K, Kinoshita K, Kato F (2009) Production of rosamicin derivatives in Micromonospora rosaria by introduction of D-mycinose biosynthetic gene with ϕC31-derived integration vector pSET152. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:1013–1021
Anzai Y, Li S, Chaulagain MR, Kinoshita K, Kato F, Montgomery J, Sherman DH (2008) Function analysis of MycCI and MycG, cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in biosynthesis of mycinamicin macrolide antibiotics. Chem Biol 15:950–959
Anzai Y, Sakai A, Li W, Iizaka Y, Koike K, Kinoshita K, Kato F (2010) Isolation and characterization of 23-O-mycinosyl-20-dihydro-rosamicin: a new rosamicin analogue derived from engineered Micromonospora rosaria. J Antibiot 63:325–328
Baltz RH, Seno ET, Stonesifer J, Wild GM (1983) Biosynthesis of the macrolide antibiotic tylosin. A preferred pathway from tylactone to tylosin. J Antibiot 36:131–141
Basnet DB, Park JW, Yoon YJ (2008) Combinatorial biosynthesis of 5-O-desosaminyl erythronolide A as a potent precursor of ketolide antibiotics. J Biotechnol 135:92–96
Fujiwara T, Watanabe H, Kogami Y, Shiritani Y, Sakakibara H (1989) 19-Deformyl-4′-deoxydesmycosin (TMC-016): synthesis and biological properties of a unique 16-membered macrolide antibiotic. J Antibiot 42:903–912
Iizaka Y, Higashi N, Ishida M, Oiwa R, Ichikawa Y, Takeda M, Anzai Y, Kato F (2013) Function of cytochrome P450 enzymes RosC and RosD in the biosynthesis of rosamicin macrolide antibiotic produced by Micromonospora rosaria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57:1529–1531
Inouye M, Takada Y, Muto N, Beppu T, Horinouchi S (1994) Characterization and expression of a P-450-like mycinamicin biosynthesis gene using a novel Micromonospora–Escherichia coli shuttle cosmid vector. Mol Gen Genet 245:456–464
Kinoshita K, Imura Y, Takenaka S, Hayashi M (1989) Mycinamicins, new macrolide antibiotics. XI. Isolation and structure elucidation of a key intermediate in the biosynthesis of the mycinamicins, mycinamicin VIII. J Antibiot 42:1869–1872
Nakajima S, Kojiri K, Morishima H, Okanishi M (1990) New analogs of rosaramicin isolated from a Micromonospora strain. II. Structure determination. J Antibiot 43:1006–1009
Nguyen HC, Darbon E, Thai R, Pernodet JL, Lautru S (2013) Post-PKS tailoring steps of the spiramycin macrolactone ring in Streptomyces ambofaciens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57:3836–3842
Pageni BB, Oh TJ, Sohng JK (2009) Novel desosaminyl derivatives of dihydrochalcomycin from a genetically engineered strain of Streptomyces sp. Biotechnol Lett 31:1759–1768
Park SR, Han AR, Ban YH, Yoo YJ, Kim EJ, Yoo YJ (2010) Genetic engineering of macrolide biosynthesis: past advances, current state, and future prospects. Appl Micobiol Biotechnol 85:1227–1239
Sakai A, Mitsumori A, Furukawa M, Kinoshita K, Anzai Y, Kato F (2012) Production of a hybrid 16-membered macrolide antibiotic by genetic engineering of Micromonospora sp. TPMA0041. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39:1693–1701
Salas JA, Mendez C (2007) Engineering the glycosylation of natural products in actinomycetes. Trends Microbiol 15:219–232
Tanaka A, Watanabe A, Tsuchiya T, Umezawa S, Umezawa H (1981) Syntheses of 4’-deoxy-demycarosyl tylosin and its analogues. J Antibiot 34:1381–1384
Wagman GH, Waitz JA, Marquez J, Murawski A, Oden EM, Testa RT, Weinstein MJ (1972) A new Micromonospora-produced macrolide antibiotic, rosamicin. J Antibiot 25:641–646
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Y. Iizaka and N. Higashi contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iizaka, Y., Higashi, N., Li, W. et al. A new mycinosyl rosamicin derivative produced by an engineered Micromonospora rosaria mutant with a cytochrome P450 gene disruption introducing the d-mycinose biosynthetic gene. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41, 1451–1456 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1488-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1488-2