Abstract
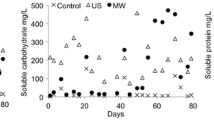
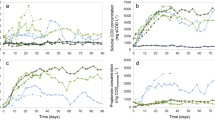
The effect of reactor design and method of heating on the efficiency of methane fermentation and composition of microbial communities, especially methanogenic Archaea, were determined. The research was carried out using submerge- and trickling-bed reactors fed with wastewater and the heat supply into the reactors included a convection heating method and microwave radiation. The polymerase chain reaction-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and relative real-time PCR were used in order to assess the biofilm communities. The best fermentation results and the highest abundance of methanogenic Archaea in biomass were observed in microwave heated trickling-bed reactors. The research proved that in reactors of identical design, the application of microwaves enabled a higher fermentation efficiency to be obtained and simultaneously increased the diversity of methanogenic Archaea communities that favors process stability. All the identified sequences of Archaea belonged to Methanosarcina sp., suggesting that species from this genera are susceptible to non-thermal effects of microwaves. There were no effects from microwaves on the bacterial communities in both types of reactors, however, the bacterial species composition varied in the reactors of different design.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn J-H, Shin SG, Hwang S (2009) Effect of microwave irradiation on the disintegration and acidogenesis of municipal secondary sludge. Chem Eng J 153:145–150
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
APHA (1992) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 18th edn. APHA, AWWA and WEF, Washington, DC
Banik S, Bandyopadhyay S, Ganguly S (2003) Bioeffects of microwave—a brief review. Bioresour Technol 87:155–159
Banik S, Bandyopadhyay S, Ganguly S, Dan D (2006) Effect of microwave-irradiated Methanosarcina barkeri DSM-804 on biomethanation. Bioresource Technol 97:819–823
Chin K-J, Lukow T, Stubner S, Conrad R (1999) Structure and function of the methanogenic archaeal community in stable cellulose-degrading enrichment cultures at two different temperatures (15 and 30 °C). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 30:313–326
Coelho MAZ, Russo C, Araujo OQF (2000) Optimization of sequencing batch reactor for biological nitrogen removal. Water Res 34:2809–2817
Cydzik-Kwiatkowska A, Zielińska M, Wojnowska-Baryła I (2012) Impact of operational parameters on bacterial community in a full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plant. Pol J Microbiol 61(1):41–49
Eskicioglu C, Terzian N, Kennedy KJ, Droste RL, Hamoda M (2007) Athermal microwave effects for enhancing digestibility of waste activated sludge. Water Res 41:2457–2466
Eskicioglu C, Kennedy KJ, Droste RL (2009) Enhanced disinfection and methane production from sewage sludge by microwave irradiation. Desalination 248:279–285
Fernàndez A, Huang S, Seston S, Xing J, Hickey R, Criddle C, Tiedje J (1999) How stable is stable? function versus community composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3697–3704
Hendrickson EL, Haydock AK, Moore BC, Whitman WB, Leigh JA (2007) Functionally distinct genes regulated by hydrogen limitation and growth rate in methanogenic Archaea. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:8930–8934
Heuer H, Krsek M, Baker P, Smalla K, Wellington EM (1997) Analysis of actinomycete communities by specific amplification of genes encoding 16S rRNA and gel-electrophoretic separation in denaturing gradients. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3233–3241
Lange M, Ahring BK (2001) A comprehensive study into the molecular methodology and molecular biology of methanogenic Archaea. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25:553–571
Lee Ch, Kim J, Hwang K, O’Flaherty V, Hwang S (2009) Quantitative analysis of methanogenic community dynamics in three anaerobic batch digesters treating different wastewaters. Water Res 43:157–165
Lettinga G (1995) Anaerobic digestion and wastewater treatment systems. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 67:3–28
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔct method. Methods 25:402–408
McHugh S, Collins G, O’Flaherty V (2006) Long-term, high-rate anaerobic biological treatment of whey wastewaters at psychrophilic temperatures. Bioresource Technol 97:1669–1678
Muyzer G, de Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microb 59:695–700
Nei M, Li WH (1979) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:5269–5273
Pakhomov AG, Akyel Y, Pakhomova ON, Stuck BE, Murphy MR (1998) Current state and implications of research on biological effects of millimeter waves: a review of the literature. Bioelectromagnetics 19:393–413
Pholchan MK, de C. Baptista J, Davenport RJ, Curtis TP (2010) Systematic study of the effect of operating variables on reactor performance and microbial diversity in laboratory-scale activated sludge reactors. Water Res 44:1341–1352
Ponne CT, Bartels P (1995) Interaction of electromagnetic energy with biological material—relation of food processing. Radiat Phys Chem 45:591–607
Rowan AK, Snape JR, Fearnside D, Barer MR, Curtis TP, Head IM (2003) Composition and diversity of ammonia-oxidising bacterial communities in wastewater treatment reactors of different design treating identical wastewater. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 43:195–206
Saikaly PE, Stroot PG, Oerther DB (2005) Use of 16S rRNA gene terminal restriction fragment analysis to assess the impact of solids retention time on the bacterial diversity of activated sludge. Appl Environ Microb 71:5814–5822
Sawayama S, Tsukahara K, Yagishita T (2006) Phylogenetic description of immobilized methanogenic community using real-time PCR in a fixed-bed anaerobic digester. Bioresource Technol 97:69–76
Sekiguchi Y, Kamagata Y, Syutsubo K, Ohashi A, Harada H, Nakamura K (1998) Phylogenetic diversity of mesophilic and thermophilic granular sludges determined by 16S rRNA gene analysis. Microbiology 144:2655–2665
Shannon CE, Weaver W (1949) The mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana
Tamura K, Nei M (1993) Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol Biol Evol 10:512–526
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739
Thauer RK, Kaster A-K, Seedorf H, Buckel W, Hedderich R (2008) Methanogenic Archaea: ecologically relevant differences in energy conservation. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:579–591
Toreci I, Kennedy KJ, Droste RL (2009) Evaluation of continuous mesophilic anaerobic sludge digestion after high temperature microwave pretreatment. Water Res 43:1273–1284
Watanabe T, Asakawa S, Nakamura A, Nagaoka K, Kimura M (2004) DGGE method for analyzing 16S rDNA of methanogenic archaeal community in paddy field soil. FEMS Microbiol Lett 232:153–163
Wiener N (1948) Cybernetics: or control and communication in the animal machine. Wiley, New York
Yang Y, Tada Ch, Tsukahara K, Sawayama S (2004) Methanogenic community and performance of fixed- and fluidized-bed reactors with reticular polyurethane foam with different pore sizes. Mater Sci Eng 24:803–813
Yu Q, Lei H, Yu G, Feng X, Li Z, Wu Z (2009) Influence of microwave irradiation on sludge dewaterability. Chem Eng J 155:88–93
Zieliński M, Ciesielski S, Cydzik-Kwiatkowska A, Turek J, Dębowski M (2007) Influence of microwave radiation on bacterial community structure in biofilm. Process Biochem 42:1250–1253
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the financial support of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education Republic of Poland (Project No. N N523 455436). All authors have agreed to submit the manuscript to ‘Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A., Zieliński, M. & Jaranowska, P. Microwave radiation and reactor design influence microbial communities during methane fermentation. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39, 1397–1405 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-012-1141-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-012-1141-x