Abstract
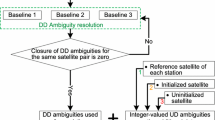
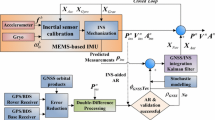
The combination of new global navigation satellite system (GNSS) has brought great benefits to reliable positioning and ambiguity resolution (AR), especially in restricted environments. However, kinematic positioning over long ranges is still a challenge due to the presence of significant atmospheric uncertainties, which contaminates the AR process. We present a tightly coupled strategy to integrate GNSS and inertial navigation system (INS) by adding ionospheric and tropospheric delay parameters and extending the stepwise AR by applying the partial ambiguity resolution (PAR) strategy. With the aid of INS predictions, the instantaneous AR can be achieved with the proposed atmospheric prediction model, along with a dual-frequency constraint ambiguity validation test. To remove the faults in both dynamic model and measurement model, a robust innovation filtering algorithm is proposed. A field vehicular test was conducted to validate the positioning performance of the proposed algorithm over long ranges. The results show that a reliable positioning solution is obtainable for the global positioning system (GPS)/BeiDou navigation satellite system (BDS)/INS integration system with baseline larger than 130 km. The average number of fixable ambiguities reaches 14.43 by applying PAR. In addition, the fixing ratio of having fixed more than three ambiguities reaches 98.57%. The results also indicate that the robust innovation filtering can efficiently detect the discrepancies in the filter.




























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bar-Itzhack IY, Berman N (1988) Control theoretic approach to inertial navigation systems. J Guid Control Dyn 11(3):237–245
Böhm J, Niell A, Tregoning P, Schuh H (2006) Global mapping function (GMF): a new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys Res Lett 33(7):1–4
Dai L, Wang J, Rizos C, Han S (2003) Predicting atmospheric biases for real-time ambiguity resolution in GPS/GLONASS reference station networks. J Geod 76(11–12):617–628
Feng Y (2008) GNSS three carrier ambiguity resolution using ionosphere-reduced virtual signals. J Geod 82(12):847–862
Feng S, Ochieng W, Moore T, Hill C, Hide C (2009) Carrier phase-based integrity monitoring for high-accuracy positioning. GPS Solut 13(1):13–22
Gelb A (1974) Applied optimal estimation. MIT press, Cambridge, pp 102–142
Godha S, Cannon M (2007) GPS/MEMS INS integrated system for navigation in urban areas. GPS Solut 11(3):193–203
Grejner-Brzezinska D, Da R, Toth C (1998) GPS error modeling and OTF ambiguity resolution for high-accuracy GPS/INS integrated system. J Geod 72(11):626–638
Han H, Wang J, Wang J, Tan X (2015) Performance analysis on carrier phase-based tightly-coupled GPS/BDS/INS integration in GNSS degraded and denied environments. Sensors 15(4):8685–8711
Han H, Xu T, Wang J (2016) Tightly coupled integration of GPS ambiguity fixed precise point positioning and MEMS-INS hrough a troposphere-constrained adaptive Kalman filter. Sensors 16(7):1057
Han H, Wang J, Wang J, Moraleda AH (2017) Reliable partial ambiguity resolution for single-frequency GPS/BDS and INS integration. GPS Solut 21(1):251–264. doi:10.1007/s10291-016-0519-z
He H, Li J, Yang Y, Xu J, Guo H, Wang A (2014) Performance assessment of single-and dual-frequency BeiDou/GPS single-epoch kinematic positioning. GPS Solut 18(3):393–403
Hewitson S, Wang J (2010) Extended receiver autonomous integrity monitoring (eRAIM) for GNSS/INS integration. J Surv Eng 136(1):13–22
Hu G, Abbey D, Castleden N, Featherstone WE, Earls C, Ovstedal O, Weihing D (2005) An approach for instantaneous ambiguity resolution for medium-to long-range multiple reference station networks. GPS Solut 9(1):1–11
Leandro RF, Langley RB, Santos MC (2008) UNB3m_pack: a neutral atmosphere delay package for radiometric space techniques. GPS Solut 12(1):65–70
Lee H, Wang J, Rizos C (2005) An integer ambiguity resolution procedure for GPS/pseudolite/INS integration. J Geod 79(4–5):242–255
Leick A, Rapoport L, Tatarnikov D (2015) GPS satellite surveying, 4th edn. Wiley, New Jersey
Li Z, Wang J, Li B, Gao J, Tan X (2014) GPS/INS/Odometer integrated system using fuzzy neural network for land vehicle navigation applications. J Navig 67(6):967–983
Niu X, Nassar S, El-Sheimy N (2007) An accurate land-vehicle MEMS IMU/GPS navigation system using 3D auxiliary velocity updates. Navigation 54(3):177–188
Odolinski R, Teunissen PJ, Odijk D (2015a) Combined BDS, Galileo, QZSS and GPS single-frequency RTK. GPS Solut 19(1):151–163
Odolinski R, Teunissen PJG, Odijk D (2015b) Combined GPS + BDS for short to long baseline RTK positioning. Meas Sci Technol 26(4):045801
Rizos C (2007) Alternatives to current GPS-RTK services and some implications for CORS infrastructure and operations. GPS Solut 11(3):151–158
Shi C, Zhao Q, Hu Z, Liu J (2013) Precise relative positioning using real tracking data from COMPASS GEO and IGSO satellites. GPS Solut 17(1):103–119
Teunissen PJ (1995) The least-squares ambiguity decorrelation adjustment: a method for fast GPS integer ambiguity estimation. J Geod 70(1–2):65–82
Teunissen P, Odolinski R, Odijk D (2014) Instantaneous BeiDou + GPS RTK positioning with high cut-off elevation angles. J Geod 88(4):335–350
Wang M, Cai H, Pan Z (2015) BDS/GPS relative positioning for long baseline with undifferenced observations. Adv Space Res 55(1):113–124
Yang Y, Song L, Xu T (2002) Robust estimator for correlated observations based on bifactor equivalent weights. J Geod 76(6–7):353–358
Zhang X, He X (2016) Performance analysis of triple-frequency ambiguity resolution with BeiDou observations. GPS Solut 20(2):269–281
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their helpful, constructive suggestions and comments that helped to improve the paper quality significantly. This research is supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0803103). Thanks for the data from iGMAS (International GNSS Monitoring and Assessment System).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, H., Wang, J. Robust GPS/BDS/INS tightly coupled integration with atmospheric constraints for long-range kinematic positioning. GPS Solut 21, 1285–1299 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-017-0612-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-017-0612-y