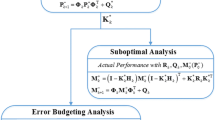
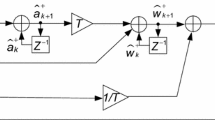
Abstract
In recent years, Kalman filter (KF)-based tracking loop architectures have gained much attention in the Global Navigation Satellite System field and have been widely investigated due to its robust and better performance compared with traditional architectures. However, less attention has been paid to the in-depth theoretical analysis of the tracking structure and to the effects of Kalman tuning. A new approach is proposed to analyze the KF-based tracking loop. A control system model is derived according to the mathematical expression of the Kalman system. Based on this model, the influence of the choice of the setting parameters on the temporal evolution of the system response is discussed from the perspective of a control system. As a result, a reasoned and complete suite of criteria to tune the initial error covariance as well as the process and measurements noise covariances is demonstrated. Furthermore, a strategy is presented to make the system more robust in higher order dynamics without degrading the accuracy of carrier phase and Doppler frequency estimates.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott AS, Lillo WE (2003) Global positioning systems and inertial measuring unit ultra-tight coupling method. U.S. Patent 6516021
Brown RG, Hwang PYC (1997) Introduction to random signals and applied Kalman filtering, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Florence M, Petovello MG (2010) Development of a one channel Galileo L1 software receiver and testing using real data. Proceedings of the US Institute of Navigation GNSS, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 25–28 September
Jaffe R, Rechtin E (1955) Design and performance of phase-lock circuits capable of near-optimum performance over a wide range of input signal and noise levels. IRE Trans Inf Theory 1:66–76
Kaplan ED, Hegarty CJ (2006) Understanding GPS. Principles and applications, 2nd edn. ARTCH HOUSE, Boston
Lashley M, Bevly DM, Hung JY (2009) Performance analysis of vector tracking algorithms for weak GPS signals in high dynamics. IEEE J Sel Top Signal Process 3(4):661–673. doi:10.1109/JSTSP.2009.2023341
Lin T, Curran JT, O’Driscoll C, Lachapelle G (2011) Implementation of a navigation domain GNSS signal tracking loop. Proceedings of ION GNSS 2011, Institute of Navigation, September, Portland, OR, pp 3644–3651
Newnes BW (1998) Control engineering pocketbook. Newnes, Oxford
O’Driscoll C, Lachapelle G (2009) Comparison of traditional and Kalman filter based tracking architecture. Proceedings of European Navigation Conference, University of Naples Parthenope, Naples, Italy, 3–6 May 2009
Parkinson BW, Spilker JJ (1996) Global positioning system: theory and application. AIAA, Washington
Patapoutian A (1999) On phase-locked loops and Kalman filters. IEEE Trans Commun 47(5):670–672. doi:10.1109/26.768758
Petovello M, Lachapelle G (2006) Comparison of vector-based software receiver implementations with application to ultra-tight GPS/INS integration. Proceedings of ION GNSS 2006, Institute of Navigation, September, Fort Worth TX, pp 1790–1799
Psiaki ML (2001) Smoother-based GPS signal tracking in a software receiver. Proceedings of ION GPS 2001, Institute of Navigation, September, Salt Lake City, UT, pp 2900–2913
Psiaki ML, Jung H (2002) Extended Kalman filter methods for tracking weak GPS signals. Proceedings of ION GPS 2002, Institute of Navigation, September, Portland, OR, pp 2539–2553
Roncagliolo PA, Garcia JG, Muravchik CH (2012) Optimized carrier tracking loop design for real-time high-dynamics GNSS receivers. Int J Navig Obs. Hindawi Publishing Corporation, 2012 (2012): 1–18. doi:10.1155/2012/651039. Article ID 651039
Salem DR, O’Driscoll C, Lachapelle G (2012) Methodology for comparing two carrier phase tracking techniques. GPS Solut 16(2):197–207. doi:10.1007/s10291-011-0222-z
Stensby J (2002) Stability of false lock states in a class of phase-lock loops. Proceedings of thirty-fourth southeastern symposium on system theory, 18–19 March, Huntsville, Alabama, pp 133–137
Stephens SA, Thomas JB (1995) Controlled-root formulation for digital phase-locked loops. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst 31(1):78–95. doi:10.1109/7.366295
Tang X, Falco G, Falletti E, Lo Presti L (2013) Practical implementation and performance assessment of an Extended Kalman Filter-based signal tracking loop. Proceedings of 2013 ICL-GNSS, Politecnico of Turin and Istituto Superiore Mario Boella (ISMB), June, Torino, Italy
Tausworthe RC (1971) A second/third-order hybrid phase locked receiver for tracking doppler rates. JPL Tech Rep 32–1526(1):42–45
Thomas JB (1989) An analysis of digital phase-locked loops, jet propulsion laboratory publication 89-2. California Institute of Technology, Pasadena
Won J-H, Eissfeller B (2013) A tuning method based on signal-to-noise power ratio for adaptive PLL and its relationship with equivalent noise bandwidth. Commun Lett IEEE 17:393–396. doi:10.1109/LCOMM.2013.01113.122503
Won J-H, Dotterbock D, Eissfeller B (2009) Performance comparison of different forms of Kalman filter approach for a vector-based GNSS signal tracking loop. Proceedings of ION GNSS 2009, Institute of Navigation, September, Savannah, GA, pp 185–199
Won J-H, Pany T, Eissfeller B (2012) Characteristics of Kalman filters for GNSS signal tracking loop. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst 48(4):3671–3681. doi:10.1109/TAES.2012.6324756
Ziedan NI, Garrison JL (2003) Bit synchronization and Doppler frequency removal at very low carrier to noise ratio using a combination of Viterbi algorithm with an extended Kalman filter. Proceedings of ION GPS/GNSS 2003, Institute of Navigation, September, Portland, OR, pp 616–627
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, X., Falco, G., Falletti, E. et al. Theoretical analysis and tuning criteria of the Kalman filter-based tracking loop. GPS Solut 19, 489–503 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-014-0408-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-014-0408-2