Abstract
Purpose
A failure to control perfusion pressure due to impaired baroreflex sensitivity (BRS) could potentially cause chronic brain hypoperfusion, leading to cognitive dysfunction. The primary aim of this study was to determine whether BRS was associated with regional cerebral blood flow as measured by MRI arterial spin labeling (ASL) technique.
Methods
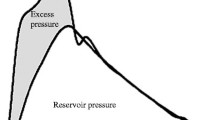
Baroreflex sensitivity was measured using the Valsalva maneuver technique in 52 middle-aged normotensive adults (49 ± 1 years), and phase IV of the Valsalva maneuver was used for analyses. Cerebral perfusion was measured using the ASL MRI technique in 10 pre-determined brain regions of interest.
Results
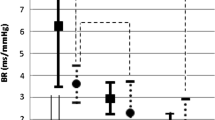
Hippocampal perfusion was correlated with BRS (R 2 = 0.17, P = 0.01). No association was observed between BRS and cerebral perfusion in the other brain regions of interest. Partial correlational analyses revealed that BRS was an important predictor of hippocampal perfusion, explaining 11 % of the variability independent of other covariates. When participants were divided into tertiles of BRS (11.8 ± 1.9 and 3.5 ± 0.1 ms/mmHg for the highest and lowest tertiles), regional cerebral perfusion of the hippocampus was significantly lower in the lowest BRS tertile than in the highest tertile (39.1 ± 4.3 and 60.5 ± 8.4 ml/100 g/min).
Conclusions
Baroreflex sensitivity in midlife is positively associated with regional cerebral perfusion of the hippocampus, and impaired BRS appears to be related to brain hypoperfusion even in apparently healthy middle-aged adults. Future longitudinal studies based on the present cross-sectional findings may help to further define the relationship between BRS to cognitive dysfunction.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hossmann KA (1994) Viability thresholds and the penumbra of focal ischemia. Ann Neurol 36:557–565
Alosco ML et al (2013) The adverse effects of reduced cerebral perfusion on cognition and brain structure in older adults with cardiovascular disease. Brain Behav 3:626–636
Launer LJ et al (1995) The association between midlife blood pressure levels and late-life cognitive function. The Honolulu-Asia Aging Study. JAMA 274:1846–1851
Skoog I et al (1996) 15-year longitudinal study of blood pressure and dementia. Lancet 347:1141–1145
Waldstein SR et al (2005) Nonlinear relations of blood pressure to cognitive function: the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Hypertension 45:374–379
Saint Martin M et al (2013) Baroreflex sensitivity, vascular risk factors, and cognitive function in a healthy elderly population: the PROOF cohort. J Am Geriatr Soc 61:2096–2102
Meel-van den Abeelen AS et al (2013) Baroreflex function is reduced in Alzheimer’s disease: a candidate biomarker? Neurobiol Aging 34:1170–1176
Poli L et al (1999) Age-related transcranial Doppler findings in the evaluation of cerebral circulation during postprandial and postural tests. Cerebrovasc Dis 9:98–101
Detre JA et al (1992) Perfusion imaging. Magn Reson Med 23:37–45
Kim SG (1995) Quantification of relative cerebral blood flow change by flow-sensitive alternating inversion recovery (FAIR) technique: application to functional mapping. Magn Reson Med 34:293–301
Liu TT, Brown GG (2007) Measurement of cerebral perfusion with arterial spin labeling: Part 1. Methods. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 13:517–525
Detre JA et al (2012) Applications of arterial spin labeled MRI in the brain. J Magn Reson Imaging 35:1026–1037
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198
Chalela JA et al (2000) Magnetic resonance perfusion imaging in acute ischemic stroke using continuous arterial spin labeling. Stroke 31:680–687
Wang J, Qiu M, Constable RT (2005) In vivo method for correcting transmit/receive nonuniformities with phased array coils. Magn Reson Med 53:666–674
De Reuck J (1971) The human periventricular arterial blood supply and the anatomy of cerebral infarctions. Eur Neurol 5:321–334
Rowbotham GF, Little E (1965) Circulations of the cerebral hemispheres. Br J Surg 52:8–21
Talairach J, Tournoux P (1988) Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the human brain. 3-Dimensional proportional system: an approach to cerebral imaging. Thieme, New York
Cox RW (1996) AFNI: software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance neuroimages. Comput Biomed Res 29:162–173
Monahan KD et al (2001) Age-associated changes in cardiovagal baroreflex sensitivity are related to central arterial compliance. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 281:H284–H289
Monahan KD et al (2000) Regular aerobic exercise modulates age-associated declines in cardiovagal baroreflex sensitivity in healthy men. J Physiol 529(Pt 1):263–271
Monahan KD et al (2001) Central arterial compliance is associated with age- and habitual exercise-related differences in cardiovagal baroreflex sensitivity. Circulation 104:1627–1632
Nualnim N et al (2011) Comparison of central artery elasticity in swimmers, runners, and the sedentary. Am J Cardiol 107:783–787
Eckberg DL, Sleight P (1992) Human baroreflexes in health and disease. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Szili-Torok T et al (2001) Depressed baroreflex sensitivity in patients with Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 22:435–438
Gupta R, Solanki RK, Pathak V (2008) Blood pressure is associated with cognitive impairment in young hypertensives. World J Biol Psychiatry 9:43–50
Skoog I et al (1998) A population-based study on blood pressure and brain atrophy in 85-year-olds. Hypertension 32:404–409
Low PA et al (1995) Prospective evaluation of clinical characteristics of orthostatic hypotension. Mayo Clin Proc 70:617–622
Roman GC (2004) Brain hypoperfusion: a critical factor in vascular dementia. Neurol Res 26:454–458
Diehl RR et al (1999) Cerebrovascular mechanisms in neurocardiogenic syncope with and without postural tachycardia syndrome. J Auton Nerv Syst 76:159–166
Ai Q et al (2014) Impact of regional white matter lesions on cognitive function in subcortical vascular cognitive impairment. Neurol Res 36:434–443
Fein G et al (2000) Hippocampal and cortical atrophy predict dementia in subcortical ischemic vascular disease. Neurology 55:1626–1635
Mungas D et al (2001) MRI predictors of cognition in subcortical ischemic vascular disease and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 57:2229–2235
Willie CK et al (2014) Integrative regulation of human brain blood flow. J Physiol 592:841–859
Gribbin B et al (1971) Effect of age and high blood pressure on baroreflex sensitivity in man. Circ Res 29:424–431
Tanaka H et al (2000) Aging, habitual exercise, and dynamic arterial compliance. Circulation 102:1270–1275
Tarumi T et al (2013) Central artery stiffness, neuropsychological function, and cerebral perfusion in sedentary and endurance-trained middle-aged adults. J Hypertens 31:2400–2409
Qiu M et al (2010) Arterial transit time effects in pulsed arterial spin labeling CBF mapping: insight from a PET and MR study in normal human subjects. Magn Reson Med 63:374–384
Smith ML et al (1996) Valsalva’s maneuver revisited: a quantitative method yielding insights into human autonomic control. Am J Physiol 271:H1240–H1249
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Thomas Liu and FBIRN for their support of the ASL analysis tools. This work was supported in part by the American Federation for Aging Research (A.P.H., 8A0024) and National Institutes of Health (A.P.H., R01 NS75565).
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laosiripisan, J., Tarumi, T., Gonzales, M.M. et al. Association between cardiovagal baroreflex sensitivity and baseline cerebral perfusion of the hippocampus. Clin Auton Res 25, 213–218 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-015-0296-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-015-0296-8