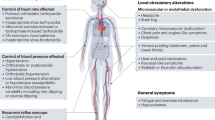
Abstract
Patients with autonomic failure are characterized by orthostatic hypotension, supine hypertension, high blood pressure variability, blunted heart rate variability, and often have a “non-dipping” or “reverse dipping” pattern on 24-h ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. These alterations may lead to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular changes, similar to the target organ damage found in hypertension. Often patients with autonomic failure are on treatment with anti-hypotensive drugs, which may worsen supine hypertension. The aim of this review is to summarize the evidence for cardiac, vascular, renal, and cerebrovascular damage in patients with autonomic failure.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Freeman R (2008) Clinical practice. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. N Engl J Med 358(6):615–624
Stuebner E, Vichayanrat E, Low DA, Mathias CJ, Isenmann S, Haensch CA (2013) Twenty-four hour non-invasive ambulatory blood pressure and heart rate monitoring in Parkinson’s disease. Front Neurol 4:49
Okamoto LE, Gamboa A, Shibao C, Black BK, Diedrich A, Raj SR et al (2009) Nocturnal blood pressure dipping in the hypertension of autonomic failure. Hypertension 53(2):363–369
Plaschke M, Trenkwalder P, Dahlheim H, Lechner C, Trenkwalder C (1998) Twenty-four-hour blood pressure profile and blood pressure responses to head-up tilt tests in Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. J Hypertens 16(10):1433–1441
Goldstein DS, Pechnik S, Holmes C, Eldadah B, Sharabi Y (2003) Association between supine hypertension and orthostatic hypotension in autonomic failure. Hypertension 42(2):136–142
Rose KM, Tyroler HA, Nardo CJ, Arnett DK, Light KC, Rosamond W et al (2000) Orthostatic hypotension and the incidence of coronary heart disease: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study. Am J Hypertens 13(6 Pt 1):571–578
Eigenbrodt ML, Rose KM, Couper DJ, Arnett DK, Smith R, Jones D (2000) Orthostatic hypotension as a risk factor for stroke: the atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study, 1987–1996. Stroke 31(10):2307–2313
Fedorowski A, Engstrom G, Hedblad B, Melander O (2010) Orthostatic hypotension predicts incidence of heart failure: the Malmo preventive project. Am J Hypertens 23(11):1209–1215
Fedorowski A, Hedblad B, Engstrom G, Gustav Smith J, Melander O (2010) Orthostatic hypotension and long-term incidence of atrial fibrillation: the malmo preventive project. J Intern Med 268(4):383–389
Fedorowski A, Stavenow L, Hedblad B, Berglund G, Nilsson PM, Melander O (2010) Orthostatic hypotension predicts all-cause mortality and coronary events in middle-aged individuals: the malmo preventive project. Eur Heart J 31(1):85–91
Parati G, Ochoa JE, Lombardi C, Bilo G (2013) Assessment and management of blood-pressure variability. Nat Rev Cardiol 10(3):143–155
Vagaonescu TD, Saadia D, Tuhrim S, Phillips RA, Kaufmann H (2000) Hypertensive cardiovascular damage in patients with primary autonomic failure. Lancet 355(9205):725–726
Maule S, Milan A, Grosso T, Veglio F (2006) Left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with autonomic failure. Am J Hypertens 19(10):1049–1054
Gambardella S, Frontoni S, Spallone V, Maiello MR, Civetta E, Lanza G et al (1993) Increased left ventricular mass in normotensive diabetic patients with autonomic neuropathy. Am J Hypertens 6(2):97–102
Pop-Busui R, Cleary PA, Braffett BH, Martin CL, Herman WH, Low PA et al (2013) Association between cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy and left ventricular dysfunction: DCCT/EDIC study (diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications). J Am Coll Cardiol 61(4):447–454
Irace L, Iarussi D, Guadagno I, Tedesco MA, Perna B, Ratti G et al (1996) Left ventricular performance and autonomic dysfunction in patients with long-term insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol 33(4):269–273
Taskiran M, Rasmussen V, Rasmussen B, Fritz-Hansen T, Larsson HB, Jensen GB et al (2004) Left ventricular dysfunction in normotensive Type 1 diabetic patients: the impact of autonomic neuropathy. Diabet Med 21(6):524–530
Karamitsos TD, Karvounis HI, Didangelos T, Parcharidis GE, Karamitsos DT (2008) Impact of autonomic neuropathy on left ventricular function in normotensive type 1 diabetic patients: a tissue Doppler echocardiographic study. Diabetes Care 31(2):325–327
Mogensen UM, Jensen T, Kober L, Kelbaek H, Mathiesen AS, Dixen U et al (2012) Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy and subclinical cardiovascular disease in normoalbuminuric type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetes 61(7):1822–1830
Willenheimer RB, Erhardt LR, Nilsson H, Lilja B, Juul-Moller S, Sundkvist G (1998) Parasympathetic neuropathy associated with left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Scand Cardiovasc J 32(1):17–22
Huijben AM, Mattace-Raso FU, Deinum J, Lenders J, van den Meiracker AH (2012) Aortic augmentation index and pulse wave velocity in response to head-up tilting: effect of autonomic failure. J Hypertens 30(2):307–314
Meyer C, Milat F, McGrath BP, Cameron J, Kotsopoulos D, Teede HJ (2004) Vascular dysfunction and autonomic neuropathy in Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med 21(7):746–751
van Ittersum FJ, Schram MT, van der Heijden-Spek JJ, Van Bortel LM, Elte JW, Biemond P et al (2004) Autonomic nervous function, arterial stiffness and blood pressure in patients with Type I diabetes mellitus and normal urinary albumin excretion. J Hum Hypertens 18(11):761–768
Prince CT, Secrest AM, Mackey RH, Arena VC, Kingsley LA, Orchard TJ (2010) Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy, HDL cholesterol, and smoking correlate with arterial stiffness markers determined 18 years later in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 33(3):652–657
Liatis S, Alexiadou K, Tsiakou A, Makrilakis K, Katsilambros N, Tentolouris N (2011) Cardiac autonomic function correlates with arterial stiffness in the early stage of type 1 diabetes. Exp Diabetes Res 2011:957901
Secrest AM, Marshall SL, Miller RG, Prince CT, Orchard TJ (2011) Pulse wave analysis and cardiac autonomic neuropathy in type 1 diabetes: a report from the Pittsburgh epidemiology of diabetes complications study. Diabetes Technol Ther 13(12):1264–1268
Theilade S, Lajer M, Persson F, Joergensen C, Rossing P (2013) Arterial stiffness is associated with cardiovascular, renal, retinal, and autonomic disease in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 36(3):715–721
Nemes A, Takacs R, Gavaller H, Varkonyi TT, Wittmann T, Forster T et al (2010) Correlations between aortic stiffness and parasympathetic autonomic function in healthy volunteers. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 88(12):1166–1171
Gottsäter A, Ryden-Ahlgren A, Szelag B, Hedblad B, Persson J, Berglund G et al (2003) Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy associated with carotid atherosclerosis in Type 2 diabetic patients. Diabet Med 20(6):495–499
Sinha PK, Santr G, De D, Sah A, Biswas K, Bhattachary P et al (2012) Carotid intima-media thickness in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with cardiac autonomic neuropathy. J Assoc Physicians India 60:14–18
Jung CH, Baek AR, Kim KJ, Kim BY, Kim CH, Kang SK et al (2013) Association between Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy, Diabetic Retinopathy and Carotid Atherosclerosis in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 28(4):309–319
Gottsäter A, Ahlgren AR, Taimour S, Sundkvist G (2006) Decreased heart rate variability may predict the progression of carotid atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes. Clin Auton Res 16(3):228–234
Canani LH, Copstein E, Pecis M, Friedman R, Leitao CB, Azevedo MJ et al (2013) Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with peripheral artery disease. Diabetol Metab Syndr 5(1):54
Garland EM, Gamboa A, Okamoto L, Raj SR, Black BK, Davis TL et al (2009) Renal impairment of pure autonomic failure. Hypertension 54(5):1057–1061
Torffvit O, Lindqvist A, Agardh CD, Pahlm O (1997) The association between diabetic nephropathy and autonomic nerve function in type 1 diabetic patients. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 57(2):183–191
Pavy-Le Traon A, Fontaine S, Tap G, Guidolin B, Senard JM, Hanaire H (2010) Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy and other complications in type 1 diabetes. Clin Auton Res 20:153–160
Kim YK, Lee JE, Kim YG, Kim DJ, Oh HY, Yang CW et al (2009) Cardiac autonomic neuropathy as a predictor of deterioration of the renal function in normoalbuminuric, normotensive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Korean Med Sci 24(Suppl):S69–S74
Bilal N, Erdogan M, Ozbek M, Cetinkalp S, Karadeniz M, Ozgen AG et al (2008) Increasing severity of cardiac autonomic neuropathy is associated with increasing prevalence of nephropathy, retinopathy, and peripheral neuropathy in Turkish type 2 diabetics. J Diabetes Complicat 22:181–185
Lim TS, Lee PH, Kim HS, Yong SW (2009) White matter hyperintensities in patients with multiple system atrophy. J Neurol 256(10):1663–1670
Umoto M, Miwa H, Ando R, Kajimoto Y, Kondo T (2012) White matter hyperintensities in patients with multiple system atrophy. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 18(1):17–20
Tha KK, Terae S, Yabe I, Miyamoto T, Soma H, Zaitsu Y et al (2010) Microstructural white matter abnormalities of multiple system atrophy: in vivo topographic illustration by using diffusion-tensor MR imaging. Radiology 255(2):563–569
Oh YS, Kim JS, Yang DW, Koo JS, Kim YI, Jung HO et al (2013) Night time blood pressure and white matter hyperintensities in patients with Parkinson disease. Chronobiol Int 30(6):811–817
Struhal W, Lahrmann H, Mathias CJ (2013) Incidence of cerebrovascular lesions in pure autonomic failure. Auton Neurosci 179(1–2):159–162
Toyry JP, Niskanen LK, Lansimies EA, Partanen KP, Uusitupa MI (1996) Autonomic neuropathy predicts the development of stroke in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Stroke 27(8):1316–1318
Cohen JA, Estacio RO, Lundgren RA, Esler AL, Schrier RW (2003) Diabetic autonomic neuropathy is associated with an increased incidence of strokes. Auton Neurosci 108(1–2):73–78
Ko SH, Song KH, Park SA, Kim SR, Cha BY, Son HY et al (2008) Cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction predicts acute ischaemic stroke in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 7-year follow-up study. Diabet Med 25(10):1171–1177
Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, Redon J, Zanchetti A, Bohm M et al (2013) 2013 ESH/ESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens 31(7):1281–1357
Leoncini G, Viazzi F, Storace G, Deferrari G, Pontremoli R (2013) Blood pressure variability and multiple organ damage in primary hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 27(11):663–670
Cuspidi C, Meani S, Salerno M, Valerio C, Fusi V, Severgnini B et al (2004) Cardiovascular target organ damage in essential hypertensives with or without reproducible nocturnal fall in blood pressure. J Hypertens 22(2):273–280
Fan XH, Wang Y, Sun K, Zhang W, Wang H, Wu H et al (2010) Disorders of orthostatic blood pressure response are associated with cardiovascular disease and target organ damage in hypertensive patients. Am J Hypertens 23(8):829–837
Franceschini N, Rose KM, Astor BC, Couper D, Vupputuri S (2010) Orthostatic hypotension and incident chronic kidney disease: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Hypertension 56(6):1054–1059
Melillo P, Izzo R, De Luca N, Pecchia L (2012) Heart rate variability and target organ damage in hypertensive patients. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 12:105
Schillaci G, Bilo G, Pucci G, Laurent S, Macquin-Mavier I, Boutouyrie P et al (2012) Relationship between short-term blood pressure variability and large-artery stiffness in human hypertension: findings from 2 large databases. Hypertension 60(2):369–377
Protogerou AD, Stergiou GS, Lourida P, Achimastos A (2008) Arterial stiffness and orthostatic blood pressure changes in untreated and treated hypertensive subjects. J Am Soc Hypertens 2:372–377
Valbusa F, Labat C, Salvi P, Vivian ME, Hanon O, Benetos A (2012) Orthostatic hypotension in very old individuals living in nursing homes: the PARTAGE study. J Hypertens 30(1):53–60
Chobanian AV, Volicer L, Tifft CP, Gavras H, Liang CS, Faxon D (1979) Mineralocorticoid-induced hypertension in patients with orthostatic hypotension. N Engl J Med 301(2):68–73
Biaggioni I, Garcia F, Inagami T, Haile V (1993) Hyporeninemic normoaldosteronism in severe autonomic failure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 76(3):580–586
Arnold AC, Okamoto LE, Gamboa A, Shibao C, Raj SR, Robertson D et al (2013) Angiotensin II, independent of plasma renin activity, contributes to the hypertension of autonomic failure. Hypertension 61(3):701–706
Pop-Busui R, Evans GW, Gerstein HC, Fonseca V, Fleg JL, Hoogwerf BJ et al (2010) Effects of cardiac autonomic dysfunction on mortality risk in the action to control cardiovascular risk in diabetes (ACCORD) trial. Diabetes Care 33(7):1578–1584
Wenning GK, Geser F, Krismer F, Seppi K, Duerr S, Boesch S et al (2013) The natural history of multiple system atrophy: a prospective European cohort study. Lancet Neurol 12(3):264–274
Papapetropoulos S, Tuchman A, Laufer D, Papatsoris AG, Papapetropoulos N, Mash DC (2007) Causes of death in multiple system atrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78(3):327–329
Shimohata T, Ozawa T, Nakayama H, Tomita M, Shinoda H, Nishizawa M (2008) Frequency of nocturnal sudden death in patients with multiple system atrophy. J Neurol 255(10):1483–1485
Maule S, Milazzo V, Maule MM, Di Stefano C, Milan A, Veglio F (2012) Mortality and prognosis in patients with neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. Funct Neurol 27:101–106
Mabuchi N, Hirayama M, Koike Y, Watanabe H, Ito H, Kobayashi R et al (2005) Progression and prognosis in pure autonomic failure (PAF): comparison with multiple system atrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76(7):947–952
Gorell JM, Johnson CC, Rybicki BA (1994) Parkinson’s disease and its comorbid disorders: an analysis of Michigan mortality data, from 1970 to 1990. Neurology 44(10):1865–1868
Driver JA, Kurth T, Buring JE, Gaziano JM, Logroscino G (2008) Parkinson disease and risk of mortality: a prospective comorbidity-matched cohort study. Neurology 70(16 Pt 2):1423–1430
Oh YS, Kim JS, Lee KS (2013) Orthostatic and supine blood pressures are associated with white matter hyperintensities in Parkinson disease. J Mov Disord 6(2):23–27
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milazzo, V., Di Stefano, C., Milan, A. et al. Cardiovascular complications in patients with autonomic failure. Clin Auton Res 25, 133–140 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-015-0275-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-015-0275-0