Abstract
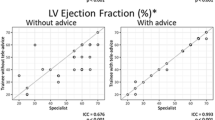
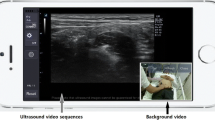
Our aim was to prove the feasibility of the remote interpretation of real-time transmitted ultrasound videos of dynamic and static organs using a smartphone with control of the image quality given a limited internet connection speed. For this study, 100 cases of echocardiography videos (dynamic organ)—50 with an ejection fraction (EF) of ≥50 s and 50 with EF <50 %—and 100 cases of suspected pediatric appendicitis (static organ)—50 with signs of acute appendicitis and 50 with no findings of appendicitis—were consecutively selected. Twelve reviewers reviewed the original videos using the liquid crystal display (LCD) monitor of an ultrasound machine and using a smartphone, to which the images were transmitted from the ultrasound machine. The resolution of the transmitted echocardiography videos was reduced by approximately 20 % to increase the frame rate of transmission given the limited internet speed. The differences in diagnostic performance between the two devices when evaluating left ventricular (LV) systolic function by measuring the EF and when evaluating the presence of acute appendicitis were investigated using a five-point Likert scale. The average areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves for each reviewer’s interpretations using the LCD monitor and smartphone were respectively 0.968 (0.949–0.986) and 0.963 (0.945–0.982) (P = 0.548) for echocardiography and 0.972 (0.954–0.989) and 0.966 (0.947–0.984) (P = 0.175) for abdominal ultrasonography. We confirmed the feasibility of remotely interpreting ultrasound images using smartphones, specifically for evaluating LV function and diagnosing pediatric acute appendicitis; the images were transferred from the ultrasound machine using image quality-controlled telesonography.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EF:
-
Ejection fraction
- DSIS:
-
Double stimulation impairment scale
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- FPS:
-
Frames per second
- OR-DBM-MRMC:
-
Obuchowski-Rockette and Dorfman-Berbaum-Metz software for diagnostic studies of multiple readers and multiple cases
- KB:
-
Kilobytes
- BPS:
-
Bits per second
References
Lee HK, Kang BS, Kim C, Choi HJ: Ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia for the pain management of elderly patients with hip fractures in the emergency department. Clin Exp Emerg Med 1(1):49–55, 2014
Ahn C, Kim C, Kang B, Choi HJ, Cho JH: Variation of availability and frequency of emergency physician-performed ultrasonography between adult and pediatric patients in the academic emergency department in Korea. Clin Exp Emerg Med 2(1):16–23, 2015
Mendlowitz AD, Young DK: A system for full-motion real-time telesonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 159(5):1123–1124, 1992
Paulus YM, Thompson NP: Inexpensive, realtime tele-ultrasound using a commercial, web-based video streaming device. J Telemed Telecare 18(4):185–188, 2012
Popov V, Popov D, Kacar I, Harris RD: The feasibility of real-time transmission of sonographic images from a remote location over low-bandwidth Internet links: a pilot study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 188(3):W219–W222, 2007
Adambounou K, Farin F, Boucher A, Adjenou KV, Gbeassor M, N’dakena K, Vincent N, Arbeille P: System of telesonography with synchronous teleconsultations and asynchronous telediagnoses (Togo). Med Sante Trop 22(1):54–60, 2012
Ogedegbe C, Morchel H, Hazelwood V, Chaplin WF, Feldman J: Development and evaluation of a novel, real time mobile telesonography system in management of patients with abdominal trauma: study protocol. BMC Emerg Med 12:19, 2012
McBeth P, Crawford I, Tiruta C, Xiao Z, Zhu GQ, Shuster M, Sewell L, Panebianco N, Lautner D, Nicolaou S, Ball CG, Blaivas M, Dente CJ, Wyrzykowski AD, Kirkpatrick AW: Help is in your pocket: The potential accuracy of smartphone- and laptop-based remotely guided resuscitative telesonography. Telemed J E Health 19(12):924–930, 2013
Biegler N, McBeth PB, Tiruta C, Hamilton DR, Xiao Z, Crawford I, Tevez-Molina M, Miletic N, Ball CG, Pian L, Kirkpatrick AW: The feasibility of nurse practitioner-performed, telementored lung telesonography with remote physician guidance—‘a remote virtual mentor’. Crit Ultrasound J 5(1):5, 2013
McBeth PB, Crawford I, Blaivas M, Hamilton T, Musselwhite K, Panebianco N, Melniker L, Ball CG, Gargani L, Gherdovich C, Kirkpatrick AW: Simple, almost anywhere, with almost anyone: remote low-cost telementored resuscitative lung ultrasound. J Trauma 71(6):1528–1535, 2011
McBeth PB, Hamilton T, Kirkpatrick AW: Cost-effective remote iPhone-teathered telementored trauma telesonography. J Trauma 69(6):1597–1599, 2010
Martinov D, Popov V, Ignjatov Z, Harris RD: Image quality in real-time teleultrasound of infant hip exam over low-bandwidth internet links: a transatlantic feasibility study. J Digit Imaging 26(2):209–216, 2013
Arbeille P, Fornage B, Boucher A, Ruiz J, Georgescu M, Blouin J, Cristea J, Carles G, Farin F, Vincent N: Telesonography: virtual 3D image processing of remotely acquired abdominal, vascular, and fetal sonograms. J Clin Ultrasound 42(2):67–73, 2014
Sable CA, Cummings SD, Pearson GD, Schratz LM, Cross RC, Quivers ES, Rudra H, Martin GR: Impact of telemedicine on the practice of pediatric cardiology in community hospitals. Pediatrics 109(1):E3, 2002
Costa C, Oliveira JL: Telecardiology through ubiquitous Internet services. Int J Med Inform 81(9):612–621, 2012
Agboma F, Liotta A: Quality of experience management in mobile content delivery system. Telecommun Syst 49(1):85–98, 2012. doi:10.1007/s11235-010-9355-6
Choi HJ, Lee JH, Kang BS: Remote CT reading using an ultramobile PC and web-based remote viewing over a wireless network. J Telemed Telecare 18(1):26–31, 2012
Park JB, Choi HJ, Lee JH, Kang BS: An assessment of the iPad 2 as a CT teleradiology tool using brain CT with subtle intracranial hemorrhage under conventional illumination. J Digit Imaging 26(4):683–690, 2013
Kim C, Kang B, Choi HJ, Park JB: A feasibility study of real-time remote CT reading for suspected acute appendicitis using an iPhone. J Digit Imaging. 2015 Feb 21
iTunes. http://www.apple.com/itunes. Accessed April 7 2015. Archived by WebCite® at http://www.webcitation.org/6XcqJOUMs
Kim C, Kang B, LEE J, Choi HJ: The feasibility and effectiveness study for clinical application of realtime emergency tele-ultrasonography using the LTE smartphone—Pilot study. Presented at: Pan-Pacific Emerg Med Congress. 2014 Oct 14
Medical Image Perception Laboratory. http://perception.radiology.uiowa.edu . Accessed April 7 2015. Archived by WebCite® at http://www.webcitation.org/6Xcs81hxF
Chawla AS, Samei E: Ambient illumination revisited: a new adaptation-based approach for optimizing medical imaging reading environments. Med Phys 34(1):81–90, 2007
Norweck JT, Seibert JA, Andriole KP, Clunie DA, Curran BH, Flynn MJ, Krupinski E, Lieto RP, Peck DJ, Mian TA: ACR-AAPM-SIIM technical standard for electronic practice of medical imaging. J Digit Imaging 26(1):38–52, 2013
Hawass NE: Comparing the sensitivities and specificities of two diagnostic procedures performed on the same group of patients. Br Radiol 70(832):360–366, 1997
Huynh-Thu Q, Ghanbari M: Temporal aspect of perceived quality in mobile video broadcasting. IEEE Tran. Broadcast. 2008 Sep;54(3)
Hillis SL, Obuchowski NA, Berbaum KS: Power estimation for multireader ROC methods an updated and unified approach. Acad Radiol 18(2):129–142, 2011
Jeffrey Jr, RB, Laing FC, Townsend RR: Acute appendicitis: sonographic criteria based on 250 cases. Radiology 167:327–329, 1988
Krishnamoorthi R, Ramarajan N, Wang NE, et al: Effectiveness of a staged US and CT protocol for the diagnosis of pediatric appendicitis: reducing radiation exposure in the age of ALARA. Radiology 259(1):231–239, 2011
Karakas SP, Guelfguat M, Leonidas JC, et al: Acute appendicitis in children: comparison of clinical diagnosis with ultrasound and CT imaging. Pediatr Radiol 30(2):94–98, 2000
Kim C, Kang B, Park JB, Ha YR: The use of clinician-performed ultrasonography to determine the treatment method for suspected paediatric appendicitis. Hong Kong J Emerg Med. 2015 Jan;22(1):31–40. Availability: http://www.hkjem.com/sites/default/files/p31-40.pdf. Accessed April 7 2015. Archived by WebCite® at http://www.webcitation.org/6XcsGbO6G
Wiersma F, Toorenvliet BR, Bloem JL, et al: US examination of the appendix in children with suspected appendicitis: the additional value of secondary signs. Eur Radiol 19(2):455–461, 2009
Trout AT, Sanchez R, Ladino-Torres MF: Reevaluating the sonographic criteria for acute appendicitis in children: a review of the literature and a retrospective analysis of 246 cases. Acad Radiol 19(11):1382–1394, 2012
The ministry of science, ICT and future planning. http://www.smartchoice.or.kr/smc/smartreport/evaluateDownload.do . Accessed April 7 2015. Archived by WebCite® at http://www.webcitation.org/6XcsNPQ1r
The State of the Internet, 4th Quarter, 2014; 7(4). http://www.akamai.com/dl/content/q4-2014-soti-report.pdf . Accessed April 7 2015. Archived by WebCite® at http://www.webcitation.org/6XcspGrey
Acknowledgments
We thank Alpinion Medical Systems, which developed the tele-ultrasonography system in collaboration with us. Author CK and HC contributed equally.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Study Approval
This study was approved by the institutional review board of our institution.
Funding Source
No external funding was secured for this study.
Financial Disclosure
The authors have no financial relationships relevant to this article to disclose.
Additional information
Trial registration: Clinical trials.gov NCT02271048
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, C., Cha, H., Kang, B.S. et al. A Feasibility Study of Smartphone-Based Telesonography for Evaluating Cardiac Dynamic Function and Diagnosing Acute Appendicitis with Control of the Image Quality of the Transmitted Videos. J Digit Imaging 29, 347–356 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-015-9849-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-015-9849-6