Abstract
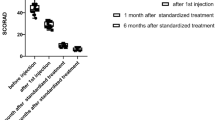
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic, inflammatory skin disease which is characterized by severe pruritus and affects patients’ quality of life. In recent years gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) has been accepted as a novel treatment for severe AD, however, its mechanism of action is not clearly identified. Present study evaluated the effect of recombinant human interferon gamma (rIFN-gamma: Gamma Immunex, Exir Pharmaceutical Company, Iran) on severity of AD (SCORAD), dermatology life quality index (DLQI) as well as serum levels of IL-4, IgE and IL-6 in AD patients. Twenty AD patients were entered in to a study in Baqiyatallah outpatient clinics and received rIFN-gamma (50 μg/m2 body area, 3 times per week, subcutaneously) for 1 month. SCORAD and DLQI were assessed at beginning and end of the treatment period. IL-4, IL-6 and IgE were measured in blood samples before and after 1 month treatment with rIFN-gamma. DLQI mean value before treatment was 20.80 ± 3.95, which decreased to 8.20 ± 2.14 after treatment (P < 0.001). SCORAD-A (percentile of the body surface involved in AD), SCORAD-B (the severity of clinical features) and SCORAD-C (patients’ scaling of itching and somnolence) significantly decreased after treatment (P < 0.001, P < 0.001 and P < 0.01). Total SCORAD at the end of treatment period was less than basal value (27.83 ± 8.48 vs. 70.04 ± 8.48; P < 0.001). Treatment with rIFN-gamma decreased serum levels of IL-4 and IL-6 (P < 0.05), but IgE remained unchanged. Results suggested the controlling effect of rIFN-gamma treatment on clinical symptoms of AD, which involves suppression of IL-4 but not IgE production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wasserbauer N, Ballow M (2010) Atopic dermatitis. Am J Med 122(2):121–125
Dou YC, Hagstromer L, Emtestam L, Johansson O (2006) Increased nerve growth factor and its receptors in atopic dermatitis: an immunohistochemical study. Arch Dermatol Res 298:31–37
Herman SM, Vender RB (2003) Antihistamines in the treatment of dermatitis. J Cutan Med Surg 7(6):467–473
Broshtilova V, Gantcheva M (2010) Therapeutic hotline: cysteinyl leukotriene receptor antagonist montelukast in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Dermatol Ther 23(1):90–93
Haw S, Shin MK, Haw CR (2010) The efficacy and safety of long-term oral cyclosporine treatment for patients with atopic dermatitis. Ann Dermatol 22(1):9–15
Hughes R, Collins P, Rogers S (2008) Further experience of using azathioprine in the treatment of severe atopic dermatitis. Clin Exp Dermatol 33(6):710–711
Murray ML, Cohen JB (2007) Mycophenolate mofetil therapy for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. Clin Exp Dermatol 32(1):23–27
Fleischer AB Jr, Boguniewicz M (2010) An approach to pruritus in atopic dermatitis: a critical systematic review of the tacrolimus ointment literature. J Drugs Dermatol 9(5):488–498
Musiał J, Milewski M, Undas A, Kopiński P, Duplaga M, Szczeklik A (1994) Human recombinant interferon gamma in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Pol Arch Med Wewn 92(6):499–506
Jang IG, Yang JK, Lee HJ, Yi JY, Kim HO, Kim CW, Kim TY (2000) Clinical improvement and immunohistochemical findings in severe atopic dermatitis treated with interferon gamma. J Am Acad Dermatol 42(6):1033–1040
Hanifin JM, Schneider LC, Leung DYM et al (1993) Recombinant interferon gamma therapy for atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol 28:189–197
Chang TT, Stevens SR (2002) Atopic dermatitis: the role of recombinant interferon-gamma therapy. Am J Clin Dermatol 3(3):175–183
Jujo K, Renz H, Abe J, Gelfand EW, Leung DY (1992) Decreased interferon gamma and increased interleukin-4 production in atopic dermatitis promotes IgE synthesis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 90(3 Pt 1):323–331
Tenda Y, Yamashita M, Kimura MY, Hasegawa A, Shimizu C, Kitajima M, Onodera A, Suzuki A, Seki N, Nakayama T (2006) Hyperresponsive TH2 cells with enhanced nuclear factor-kappa B activation induce atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in Nishiki-nezumi Cinnamon/Nagoya mice. J Allergy Clin Immunol 118(3):725–733
Punnonen J, Punnonen K, Jansén CT, Kalimo K (1993) Interferon (IFN)-alpha, IFN-gamma, interleukin (IL)-2, and arachidonic acid metabolites modulate IL-4-induced IgE synthesis similarly in healthy persons and in atopic dermatitis patients. Allergy 48(3):189–195
Gruner S, Liebenthal C, Heusser C, Brinkmann V, Zwirner A, Reinicke C, Harnack K, Sönnichsen N, Volk HD (1991) The influence of interferon-gamma and interleukin-4 on IgE production in B lymphocytes of patients with atopic dermatitis. A possible criterion for selection of patients for interferon therapy. Acta Derm Venereol 71(6):484–487
Sato A, Tsuji K, Yamamura M, Morita Y, Kanzaki H, Tada J, Makino H, Arata J (1998) Increased type 2 cytokine expression by both CD4 + CD45RO + T cells and CD8 + CD45RO + T cells in blood circulation is associated with high serum IgE but not with atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol 111(6):1079–1084
Shibata S, Maeda S, Kondo N, Inoue A, Maeda S, Chimura N, Fukata T (2011) Effect of recombinant canine interferon-γ on granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, transforming growth factor-β and CC chemokine ligand 17 mRNA transcription in a canine keratinocyte cell line (CPEK). Vet Dermatol 22(1):24–30
Hattori K, Nishikawa M, Watcharanurak K, Ikoma A, Kabashima K, Toyota H, Takahashi Y, Takahashi R, Watanabe Y, Takakura Y (2010) Sustained exogenous expression of therapeutic levels of IFN-gamma ameliorates atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice via Th1 polarization. J Immunol 184(5):2729–2735
Reinhold U, Kukel S, Brzoska J, Kreysel HW (1993) Systemic interferon gamma treatment in severe atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol 29(1):58–63
Williams HC, Burney PG, Hay RJ, Archer CB, Shipley MJ, Hunter JJ (1994) The U.K. working party´s diagnostic criteria for atopic dermatitis. I. Derivation of a minimum set of discriminators for atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol 131:383–396
Williams HC, Burney PGJ, Pembroke AC, Hay RJ (1994) The UK working party’s diagnostic criteria for atopic dermatitis III: Independent hospital validation. Br J Dermatol 131:406–416
Williams HC, Burney PGJ, Strachan D, Hay RJ (1994) The UK working party’s diagnostic criteria for atopic dermatitis II: observer variation of clinical diagnosis and signs of atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol 131:397–405
Boguniewicz M, Jaffe HS, Izu A et al (1990) Recombinant gamma interferon in treatment of patients with atopic dermatitis and elevated IgE levels. Am J Med 88:365–370
Costa C, Rilliet A, Nicolet M, Saurat JH (1989) Scoring atopic dermatitis. The simpler the better? Acta Derm Venereol(Stockh) 69:41–45
Oranje AP, Glazenburg EJ, Wolkerstorfer A, De Waard-Van Der Spek FB (2007) Practical issues on interpretation of scoring atopic dermatitis: the SCORAD index, objective SCORAD and the three-item severity score. Br J Dermatol 157:645–648
Finlay A, Khan G (1994) Dermatology life quality index (DLQI): a simple practical measure for routine clinical use. Clin Exp Dermatol 19:210–216
Schneider LC, Baz Z, Zarcone C, Zurakowski D (1998) Long term therapy with recombinant interferon-gamma for atopic dermatitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 80:263–268
Steven SR, Hanifin JM, Hamilton T, Tofte SJ, Cooper KD (1998) Long-term effectiveness and safety of recombinant human interferon gamma therapy for atopic dermatitis despite unchanged serum IgE levels. Arch Dermatol 134:799–804
Musial J, Milewski M, Undas A, Kopinski P, Duplaga M, Szczeklik A (1995) Interferon-gamma in treatment of atopic dermatitis: influence on T-cell activation. Allergy 50:520–523
Takakura M, Takeshita F, Aihara M, Xin KQ, Ichino M, Okuda K, Ikezawa Z (2005) Hyperproduction of IFN-gamma by CpG oligodeoxynucleotide-induced exacerbation of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesion in some NC/Nga mice. J Invest Dermatol 125(6):1156–1162
Simon MR, Cooper KD, Norris RB, Blok B, King CL (1995) Antigen presenting cell-independent cytokine and spontaneous in vitro IgE production in patients with atopic dermatitis: increased interferon-gamma production and lack of effects of in vivo low-dose interferon-gamma treatment. J Allergy Clin Immunol 96(1):84–91
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Department of Internal Medicine, Baqiyatallah University of Medical Sciences, for providing experimental measurements and instrumental supports.
Conflict of interest
All funds for this study were from the Chemical Injuries Research Center, Baqiyatallah University of Medical Sciences, and there was no conflict of interest to other institutes. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panahi, Y., Davoudi, S.M., Madanchi, N. et al. Recombinant human interferon gamma (Gamma Immunex) in treatment of atopic dermatitis. Clin Exp Med 12, 241–245 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-011-0164-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-011-0164-3