Abstract
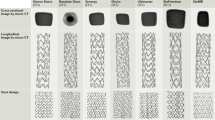
The emergence of drug-eluting stents (DES) as a viable replacement for bare metal stenting has led to a significant decrease in the incidence of clinical restenosis. This is due to the transport of anti-restenotic drugs from within the polymer coating of a DES into the artery wall which arrests the cell cycle before restenosis can occur. The efficacy of DES is still under close scrutiny in the medical field as many issues regarding the effectiveness of DES drug transport in vivo still exist. One such issue, that has received less attention, is the limiting effect that stent strut compression has on the transport of drug species in the artery wall. Once the artery wall is compressed, the stents ability to transfer drug species into the arterial wall can be reduced. This leads to a reduction in the spatial therapeutic transfer of drug species to binding sites within the arterial wall. This paper investigates the concept of idealised variable compression as a means of demonstrating how such a stent design approach could improve the spatial delivery of drug species in the arterial wall. The study focused on assessing how the trends in concentration levels changed as a result of artery wall compression. Five idealised stent designs were created with a combination of thick struts that provide the necessary compression to restore luminal patency and thin uncompressive struts that improve the transport of drugs therein. By conducting numerical simulations of diffusive mass transport, this study found that the use of uncompressive struts results in a more uniform spatial distribution of drug species in the arterial wall.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai L, Vafai K (2006) A coupling model for macromolecule transport in a stenosed arterial wall. Int J Heat Mass Transf 49(910):1568–1591
Axel DI, Kunert W, Gggelmann C, Oberhoff M, Herdeg C, Kttner A, Wild DH, Brehm BR, Riessen R, Kveker G, Karsch KR (1997) Paclitaxel inhibits arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration in vitro and in vivo using local drug delivery. Circulation 96(2):636–645
Balakrishnan B, Dooley JF, Kopia G, Edelman ER (2007) Intravascular drug release kinetics dictate arterial drug deposition, retention, and distribution. J Controlled Release 123(2):100–108
Balakrishnan B, Dooley J, Kopia G, Edelman ER (2008) Thrombus causes fluctuations in arterial drug delivery from intravascular stents. J Controlled Release 131(3):173–180
Cho HJ, Kim TY, Cho HJ, Park KW, Zhang SY, Kim JH, Kim SH, Hahn JY, Kang HJ, Park YB, Kim HS (2006) The effect of stem cell mobilization by granulocyte-colony stimulating factor on neointimal hyperplasia and endothelial healing after vascular injury with bare-metal versus paclitaxel-eluting stents. J Am Coll Cardiol 48(2):366–374
Creel CJ, Lovich MA, Edelman ER (2000) Arterial paclitaxel distribution and deposition. Circ Res 86(8):879–884
Cremers B, Speck U, Kaufels N, Mahnkopf D, Khler M, Bhm M, Scheller B (2009) Drug-eluting balloon: very short-term exposure and overlapping. Thromb Haemost 101(1):201–206
Cremers B, Milewski K, Clever YP, Aboodi MS, Biedermann M, Thim T, Kelsch B, Kaluza GL, Scheller B, Granada JF (2012) Long-term effects on vascular healing of bare metal stents delivered via paclitaxel-coated balloons in the porcine model of restenosis. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 80(4):603–610
D’Angelo C, Zunino P, Porpora A, Morlacchi S, Migliavacca F (2011) Model reduction strategies enable computational analysis of controlled drug release from cardiovascular stents. SIAM J Appl Math 71(6):2312–2333. doi:10.1137/10081695X
Denny W, OConnell B, Milroy J, Walsh M (2013) An analysis of three dimensional diffusion in a representative arterial wall mass transport model. Ann Biomed Eng 41(5):1062–1073
Dogu G, Smith JM (1975) A dynamic method for catalyst diffusivities. AIChE J 21(1):58–61
Finkelstein A, McClean D, Kar S, Takizawa K, Varghese K, Baek N, Park K, Fishbein MC, Makkar R, Litvack F, Eigler NL (2003) Local drug delivery via a coronary stent with programmable release pharmacokinetics. Circulation 107(5):777–784
Friedman MH (2008) Principles and models of biological transport. Springer Science+Business Media, Berlin
Horner M, Joshi S, Dhruva V, Sett S, Stewart S (2010) A two-species drug delivery model is required to predict deposition from drug-eluting stents. Cardiovasc Eng Technol 1(3):225–234
Hose D, Narracott A, Griffiths B, Mahmood S, Gunn J, Sweeney D, Lawford P (2004) A thermal analogy for modelling drug elution from cardiovascular stents. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng 7(5):257–264
Huang ZJ, Tarbell JM (1997) Numerical simulation of mass transfer in porous media of blood vessel walls. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 273(1):464–477
Hwang CW, Edelman ER (2002) Arterial ultrastructure influences transport of locally delivered drugs. Circ Res 90(7):826–832
Jensen LO, Maeng M, Kaltoft A, Thayssen P, Hansen HHT, Bottcher M, Lassen JF, Krussel LR, Rasmussen K, Hansen KN, Pedersen L, Johnsen SP, Soerensen HT, Thuesen L (2007) Stent thrombosis, myocardial infarction, and death after drug-eluting and bare-metal stent coronary interventions. J Am Coll Cardiol 50(5):463–470
Kastrati A, Dibra A, Spaulding C, Laarman GJ, Menichelli M, Valgimigli M, Di Lorenzo E, Kaiser C, Tierala I, Mehilli J, Seyfarth M, Varenne O, Dirksen MT, Percoco G, Varricchio A, Pittl U, Syvnne M, Suttorp MJ, Violini R, Schmig A (2007) Meta-analysis of randomized trials on drug-eluting stents vs. bare-metal stents in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J 28(22):2706–2713
Khakpour M, Vafai K (2008) A comprehensive analytical solution of macromolecular transport within an artery. Int J Heat Mass Transf 51(1112):2905–2913
Kolachalama VB, Levine EG, Edelman ER (2009) Luminal Flow Amplifies Stent-Based Drug Deposition in Arterial Bifurcations. PLoS ONE 4(12): e8105. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008105
Laarman GJ, Suttorp MJ, Dirksen MT, van Heerebeek L, Kiemeneij F, Slagboom T, van der Wieken LR, Tijssen JG, Rensing BJ, Patterson M (2006) Paclitaxel-eluting versus uncoated stents in primary percutaneous coronary intervention. N Engl J Med 355(11):1105– 1113
Levin AD, Vukmirovic N, Hwang CW, Edelman ER (2004) Specific binding to intracellular proteins determines arterial transport properties for rapamycin and paclitaxel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(25):9463–9467
Lovich M, Edelman E (1996) Tissue average binding and equilibrium distribution: an example with heparin in arterial tissues. Biophys J 70(3):1553–1559
Lovich MA, Creel C, Hong K, Hwang CW, Edelman ER (2001) Carrier proteins determine local pharmacokinetics and arterial distribution of paclitaxel. J Pharm Sci 90(9):1324–1335
McMahan CA, Gidding SS (2008) Coronary heart disease risk factors and atherosclerosis in young people. J Clin Lipidol 2(3):118–126
Members WG, Thom T, Haase N, Rosamond W, Howard VJ, Rumsfeld J, Manolio T, Zheng ZJ, Flegal K, O’Donnell C, Kittner S, Lloyd-Jones D, Goff DC, Hong Y, of the Statistics Committee M, Subcommittee SS, Adams R, Friday G, Furie K, Gorelick P, Kissela B, Marler J, Meigs J, Roger V, Sidney S, Sorlie P, Steinberger J, Wasserthiel-Smoller S, Wilson M, Wolf P (2006) Heart disease and stroke statistics 2006 update. Circulation 113(6):85–151
Mongrain Leask, Brunette Faik, Bulman-Feleming TN (2005) Numerical modeling of coronary drug eluting stents. Stud Health Technol Inform 113:443–458
Mongrain R, Faik I, Leask R, Rods-Cabau J, Larose E, Bertrand O (2007) Effects of diffusion coefficients and struts apposition using numerical simulations for drug eluting coronary stents. J Biomech Eng 129(5):733–742
Mota M, Yelshin A, Fidaleo M, Flickinger MC (2007) Modelling diffusivity in porous polymeric membranes with an intermediate layer containing microbial cells. Biochem Eng J 37(3):285–293
O’Connell B, Walsh M (2010) Demonstrating the influence of compression on artery wall mass transport. Ann Biomed Eng 38(4):1354–1366
Pan CJ, Tang JJ, Weng YJ, Wang J, Huang N (2009) Preparation and in vitro release profiles of drug-eluting controlled biodegradable polymer coating stents. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 73(2):199– 206
Pontrelli G, de Monte F (2007) Mass diffusion through two-layer porous media: an application to the drug-eluting stent. Int J Heat Mass Transf 50(1718):3658–3669
Prosi M, Zunino P, Perktold K, Quarteroni A (2005) Mathematical and numerical models for transfer of low-density lipoproteins through the arterial walls: a new methodology for the model set up with applications to the study of disturbed lumenal flow. J Biomech 38(4):903–917
Report NVS (2002) National vital statistics report
Spaulding C, Henry P, Teiger E, Beatt K, Bramucci E, Carri D, Slama MS, Merkely B, Erglis A, Margheri M, Varenne O, Cebrian A, Stoll HP, Snead DB, Bode C (2006) Sirolimus-eluting versus uncoated stents in acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 355(11):1093–1104
Sternberg K, Kramer S, Nischan C, Grabow N, Langer T, Hennighausen G, Schmitz KP (2007) In vitro study of drug-eluting stent coatings based on poly(l-lactide) incorporating cyclosporine a drug release, polymer degradation and mechanical integrity. J Mater Sci Mater Med 18(7):1423–1432
Sun N, Wood N, Hughes A, Thom S, Xu X (2006) Fluid-wall modelling of mass transfer in an axisymmetric stenosis: effects of shear-dependent transport properties. Ann Biomed Eng 34(7):1119– 1128
Sun N, Wood NB, Hughes AD, Thom SAM, Yun XuX (2007) Effects of transmural pressure and wall shear stress on ldl accumulation in the arterial wall: a numerical study using a multilayered model. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 292(6):3148–3157
Trudnowski R (1974) Specific gravity of blood and plasma at 4 and 37 degrees c. Clinical Chemistry 20(0009–9147 (Linking)):615–616
van der Hoeven BL, Pires NM, Warda HM, Oemrawsingh PV, van Vlijmen BJ, Quax PH, Schalij MJ, van der Wall EE, Jukema J (2005) Drug-eluting stents: results, promises and problems. Int J Cardiol 99(1):9–17
Waksman R (2002) Drug-eluting stents: from bench to bed. Cardiovasc Radiat Med 3(34):226–241
Weiler JM, Sparrow EM, Ramazani R (2012) Mass transfer by advection and diffusion from a drug-eluting stent. Int J Heat Mass Transf 55(13):1–7
Wootton DM, Ku DN (1999) Fluid mechanics of vascular systems, diseases, and thrombosis. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 1(1):299–329
Yang C, Burt HM (2006) Drug-eluting stents: factors governing local pharmacokinetics. Adv Drug Deliv Revi 58(3):402–411
Yang N, Vafai K (2006) Modeling of low-density lipoprotein (ldl) transport in the artery effects of hypertension. Int J Heat Mass Transf 49(56):850–867
Zhu X, Pack DW, Braatz RD (2012) Modelling intravascular delivery from drug-eluting stents with biodurable coating: investigation of anisotropic vascular drug diffusivity and arterial drug distribution. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng iFirst:1–12. doi:10.1080/10255842.2012.672815
Zunino Paolo (2004) Multidimensional pharmacokinetic models applied to the design of drug-eluting stents. Cardiovasc Eng 4:181–191
Zunino P, D’Angelo C, Petrini L, Vergara C, Capelli C, Migliavacca F (2009) Numerical simulation of drug eluting coronary stents: mechanics, fluid dynamics and drug release. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 198(4546):3633–3644
Acknowledgments
Irish Research Council for funding under the EMBARK Initiative and the Irish Government under the Programme for Research in Third Level Institutions (PRTLI) Cycle 5 and co-funded under the European Regional Development Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O’Connell, B.M., Cunnane, E.M., Denny, W.J. et al. Improving smooth muscle cell exposure to drugs from drug-eluting stents at early time points: a variable compression approach. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 13, 771–781 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-013-0533-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-013-0533-9