Abstract
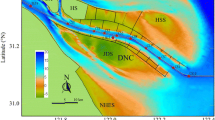
Two surveys were conducted in December, 2008, and August, 2009, in the mud depo-center off the Zhejiang-Fujian coast (MDZFC) in the inner shelf of East China Sea to depict the seasonal variation of the water column structure and analyze the factors responsible for the variation. The results were also used to discuss the sediment transport process and formation mechanism of the MDZFC. The water column structures varied significantly between the two surveys, with respect to the temperature, salinity, and turbidity. The summer water body, with relatively high temperatures and salinities, was evidently stratified with respect to the temperature, whereas the salinity remained constant throughout the water column. The stratification restricts sediment resuspension and transport. From the north to the south, the temperature in the middle-bottom water layer slightly increased, whereas the salinity remained mostly constant. In winter, the water body, with relatively low temperatures and salinities, was well mixed vertically. The temperature and salinity both increased from the surface to the bottom toward the east (deep water) and the south. A wedge-shaped water mass, which appears as a coastal upwelling, with relatively low temperature and high salinity in summer and relatively high temperature and high salinity in winter, spread landward along the sea floor, from the sea deeper than 50 m, whereas the extension was relatively stronger in winter. The water turbidity in winter was clearly higher than in summer. In the surface layer, the turbidity was generally greater than 5 FTU in winter and less than 1 FTU in summer. In the bottom layer, the turbidity was much greater than 200 FTU in winter and slightly greater than 50 FTU in summer. Moreover, the turbid water layer close to the sea floor in winter can reach into an area deeper than 50 m with a thickness of over 10 m; however, it was only limited to only 30-m-deep water with a thickness of 5 m in summer. The differences of marine sedimentary environment in the MDZFC were attributed to the seasonal variations of hydrodynamics environment, weather conditions, sediment supplies, and seasonal circulations. The results suggest that winter is the key season for particle transportation and deposition. The bottom turbid layer is the primarily channel of sediment transport, and the upwelling currents and the oceanic front systems play an important role in the sediment deposit processes and the formation of the MDZFC.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison MA, Lee MT, Ogston AS, Aller RC (2000) Origin of Amazon mudbanks along the northeastern coast of South America. Mar Geol 163(1–4):241–256. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(99)00120-6
Cattaneo A, Correggiari A, Langone L, Trincardi F (2003) The late-Holocene Gargano subaqueous delta, Adriatic shelf: sediment pathways and supply fluctuations. Mar Geol 193(1–2):61–91. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(02)00614-X
Chen CTA (2009) Chemical and physical fronts in the Bohai, Yellow and East China seas. J Marine Syst 78:394–410. doi:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2008.11.016
DeMaster DJ, McKee BA, Nittrouer CA, Qian JC, Cheng GD (1985) Rates of sediment accumulation and particle reworking based on radiochemical measurements from continental shelf deposits in the East China Sea. Cont Shelf Res 4(1–2):143–158. doi:10.1016/0278-4343(85)90026-3
DeMaster DJ, Kuehl SA, Nittrouer CA (1986) Effects of suspended sediments on geochemical processes near the mouth of the Amazon River: examination of biological silica uptake and the fate of particle-reactive elements. Cont Shelf Res 6(1–2):107–125. doi:10.1016/0278-4343(86)90056-7
Dong LX, Guan WB, Chen Q, Li XH, Liu XH, Zeng XM (2011) Sediment transport in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 93:248–258. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2011.04.003
Gong GC, Wen YH, Wang BW, Liu GJ (2003) Seasonal variation of chlorophyll a concentration, primary production and environmental conditions in the subtropical East China Sea. Deep-Sea Res II 50:1219–1236
Guo ZG, Yang ZS, Fan DJ, Pan YJ (2003) Seasonal sedimentary effect on the Changjiang estuary mud area. Acta Geogr Sin (in Chinese with English abstract) 58(4):591–597
Hoshika A, Tanimoto T, Mishima Y, Iseki K, Okamura K (2003) Variation of turbidity and particle transport in the bottom layer of the East China Sea. Deep-Sea Res II 50(2):443–455. doi:10.1016/S0967-0645(02)00462-9
Hu DX, Yang ZS (eds) (2001) The key process of marine flux in the East China Sea (in Chinese). Ocean Press, Beijing
Huh CA, Su CC (1999) Sedimentation dynamics in the East China Sea elucidated from 210Pb, 137Cs and 239,240Pu. Mar Geol 160(1–2):183–196. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(99)00020-1
Kuehl SA, DeMaster DJ, Nittrouer CA (1986) Nature of sediment accumulation on the Amazon continental shelf. Cont Shelf Res 6(1–2):209–225. doi:10.1016/0278-4343(86)90061-0
Kuehl SA, Levy BM, Moore WS, Allison MA (1997) Subaqueous delta of the Ganges–Brahmaputra river system. Mar Geol 144(1–3):81–96. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(97)00075-3
Li YH, Chen J, Huang CB, Fang JY (2010) Grain-size characteristics of the surface sediments and their seasonal variability in the mud depocenter off the Southern Zhejiang-Fujian Coast. Acta Sedimentol Sin (in Chinese with English abstract) 28(1):150–157
Liu JP, Li AC, Xu KH, Velozzi DM, Yang ZS, Milliman JD, DeMaster DJ (2006) Sedimentary features of the Yangtze River-derived along-shelf clinoform deposit in the East China Sea. Cont Shelf Res 26:2141–2156. doi:10.1016/j.csr.2006.07.013
Liu JP, Xu KH, Li AC, Milliman JD, Velozzi DM, Xiao SB, Yang ZS (2007) Flux and fate of Yangtze River sediment delivered to the East China Sea. Geomorphology 85(3–4):208–224. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.03.023
Liu JP, Xue Z, Ross K, Wang HJ, Yang ZS, Li AC, Gao S (2009) Fate of sediments delivered to the sea by Asian large rivers: long-distance transport and formation of remote alongshore clinothems. The Sedimentary Record 7(4):4–9
Liu SF, Shi XF, Liu YG, Qiao SQ, Yang G, Fang XS, Wu YH, Li CX, Li XY, Zhu AM, Gao JJ (2010) Records of the East Asian winter monsoon from the mud area on the inner shelf of the East China Sea since the mid-Holocene. Chin Sci Bull 55(21):2306–2314. doi:10.1007/s11434-010-3215-3
Liu SF, Shi XF, Liu YG, Wu YH, Qiao SQ, Yang G (2011) Recent 2000 a climatic record of mud area on the inner shelf of the East China Sea. Acta Oceanol Sin 33(3):85–93
Lv XG, Qiao FL, Xia CS, Zhu JR, Yuan YL (2006) Upwelling off Yangtze River estuary in summer. J Geohys Res 111, C11S08, doi:10.1029/2005JC003250
McKee BA, Nittrouer CA, DeMaster DJ (1983) Concepts of sediment deposition and accumulation applied to the continental shelf near the mouth of the Yangtze River. Geology 11(11):631–633
McKee BA, Aller RC, Allison MA, Bianchi TS, Kineke GC (2004) Transport and transformation of dissolved and particulate materials on continental margins influenced by major rivers: benthic boundary layer and seabed processes. Cont Shelf Res 24(7–8):899–926. doi:10.1016/j.csr.2004.02.009
Milliman JD, Shen HT, Yang ZS, Meade RH (1985) Transport and deposition of river sediment in the Changjiang estuary and adjacent continental shelf. Cont Shelf Res 4(1–2):37–45. doi:10.1016/0278-4343(85)90020-2
Qiao FL, Yang YZ, Lv XG, Xia CS, Chen XY, Wang BD, Yuan YL (2006) Coastal upwelling in the East China Sea in winter. J Geohys Res 111, C11S06, doi:10.1029/2005JC003264
Su CC, Huh CA (2002) 210Pb, 137Cs and 239,240Pu in East China Sea sediments: sources, pathways and budgets of sediments and radionuclides. Mar Geol 183(1–4):163–178. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(02)00165-2
Su JL (ed) (2005) The oceanography in the Chinese margin sea. Ocean Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Xu KH, Milliman JD (2009) Seasonal variations of sediment discharge from the Yangtze River before and after impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam. Geomorphology 104:276–283
Xu KH, Milliman JD, Li AC, Liu JP, Kao SJ, Wan SM (2009) Yangtze- and Taiwan-derived sediments on the inner shelf of East China Sea. Cont Shelf Res 29(18):2240–2256. doi:10.1016/j.csr.2009.08.017
Xu KH, Li AC, Liu JP, Milliman JD, Yang ZS, Kao SJ, Wan SM, Xu FJ (2012) Provenance, structure, and formation of the mud wedge along inner continental shelf of the East China Sea: a synthesis of the Yangtze dispersal system. Mar Geol 291–294(1):176–191. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2011.06.003
Yang ZS, Guo ZG, Wang ZX, Xu JP, Gao WB (1992) Basic pattern of transport of suspended matter from the Yellow Sea and East China Sea to the eastern deep seas. Acta Oceanol Sin (in Chinese with English abstract) 14(2):81–90
Zhu J (2003) Dynamic mechanism of the upwelling on the west side of the submerged river valley off the Changjiang mouth in summertime. Chin Sci Bull 48(24):2754–2758
Acknowledgments
The National Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 40806024, 41276059, and 40976037) and the Scientific Research Foundation of Third Institute of Oceanography, SOA (grant no. TIO2008004) provided the financial support for this work. We would like to acknowledge the assistance provided by the captain and investigators during the fieldwork. This manuscript benefited from comments and suggestions from Andrew James Manning and two anonymous reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Andrew James Manning
This article is part of the Topical Collection on the 11th International Conference on Cohesive Sediment Transport
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Qiao, L., Wang, A. et al. Seasonal variation of water column structure and sediment transport in a mud depo-center off the Zhejiang-Fujian coast in China. Ocean Dynamics 63, 679–690 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-013-0620-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-013-0620-6