Abstract
Background
Golimumab is a novel TNF-α inhibitor licensed to treat patients with active PsA. Although its clinical efficacy has been proven in clinical trials, its cost effectiveness is yet to be established.
Objectives
To estimate the cost effectiveness of golimumab among patients with active PsA from the UK NHS perspective.
Methods
A decision analytic model was used to simulate progression of a hypothetical cohort of active PsA patients on golimumab and other TNF-α inhibitors as well as palliative care. The clinical evidence was derived from clinical trials of TNF-α inhibitors and compared using mixed treatment models. The primary outcome measure was quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) estimated based on change in Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) and Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI) from baseline. The annual acquisition cost of golimumab was assumed to be identical to annual cost of other subcutaneous TNF-α inhibitors. The resource use costs and outcomes were discounted at 3.5% over a period of 40 years. The uncertainty surrounding important variables was further explored using probabilistic sensitivity analyses (PSA).
Results
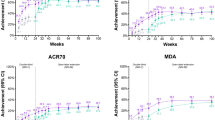
TNF-α inhibitors were significantly superior to palliative care but comparable to each other on Psoriatic Arthritis Response Criteria (PsARC), HAQ and PASI response. The incremental cost effectiveness ratio (ICERs) for golimumab compared to palliative care was £16,811 for PsA patients and £16,245 for a subgroup of PsA patients with significant psoriasis. At an acceptability threshold of £30,000 per QALY, the probability of golimumab being cost effective is 89%.
Conclusion
Once monthly, golimumab is a cost-effective treatment alternative for patients with active PsA. With its patient-focussed attributes, golimumab is likely to offer additional choice in PsA treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gladman, D.D., Antoni, C., Mease, P., Clegg, D.O., Nash, P.: Psoriatic arthritis: epidemiology, clinical features, course, and outcome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 64(II), ii14–ii17 (2006)
Krueger, G.G.: Clinical features of psoriatic arthritis. Am. J. Manag. Care 8, S160–S170 (2002)
Gottleib, A., Korman, N.J., Gordon, K.B., et al.: Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Section 2. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 58, 851–864 (2008)
Helliwell, P.S.: Therapies for dactylitis in psoriatic arthritis. A systematic review. J. Rheumatol. 33, 1439–1441 (2006)
Mease, P.J.: Assessing the impact of psoriatic arthritis on patient function and quality of life: lessons learned from other rheumatologic conditions. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 38, 320–335 (2009)
TAG 104. Etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of adults with psoriatic arthritis. NICE technology appraisal guidance 104. July 2006:18
Williams, J.P., Meyers, J.A.: Immune-mediated inflammatory disorders (I.M.I.D.s): the economic and clinical costs. Am. J. Manag. Care 8, S664–S681 (2002)
Huscher, D., Merkesdal, S., Thiele, K., Ziedler, H., Schneider, M., Zink, A.: Cost of illness in rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis and systemic lupus erythematous in Germany. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 65, 1175–1183 (2006)
Mau, W., Listing, J., Huscher, D., Zeidler, H., Zink, A.: Employment across chronic inflammatory rheumatic diseases and comparison with the general population. J. Rheumatol. 32, 721–728 (2005)
Wallenius, M., Skomsvoll, J.F., Koldingsnes, W., et al.: Work disability and health-related quality of life in males and females with psoriatic arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 68, 685–689 (2009)
Kyle, S., Chandler, D., Griffiths, C.E.M., et al.: Guideline for anti-TNF-a therapy in psoriatic arthritis. Rheumatology 44, 390–397 (2005)
Kavanaugh, A.F., Ritchlin CT, GRAPPA Treatment Guideline Committee.: Systematic review of treatments for psoriatic arthritis: an evidence based approach and basis for treatment guidelines. J. Rheumatol. 33, 1417–1421 (2006)
Kavanaugh, A., McInnes, I., Mease, P., et al.: Golimumab, a new human tumor necrosis factor-α antibody, administered every four weeks as a subcutaneous injection in psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 60, 976–986 (2009)
Cummins, E., Asseburg, C., Punekar, Y. et al.: Cost-effectiveness of infliximab for the treatment of active and progressive arthritis. Value in Health (2010)
Rogers, M., Epstein, D., Bojke, L., et al.: Etanercept, Infliximab and Adalimumab for the treatment of Psoriatic Arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Final Report 4th December 2009; Available at http://www.guidance.nice.org.uk/TA/WaveR/36
Woolacott, N., Bravo Vergel, Y., Hawkins, N., et al.: Etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol. Assess. 10, 1–265 (2006)
Wong, K., Gladman, D.D., Husted, J., et al.: Mortality studies in psoriatic arthritis: results from a single outpatient clinic. I. Causes and risk of death. Arthritis Rheum. 40, 1868–1872 (1997)
Bravo Vergel, Y., Hawkins, N.S., Claxton, K., et al.: The cost-effectiveness of etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of patients with psoriatic arthritis. Rheumatology 46, 1729–1735 (2007)
NICE TAG 199. Etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis (review of technology appraisal guidance 104 and 125). NICE 2010. Available at http://www.nice.org.uk/nicemedia/live/13110/50422/50422.pdf accessed on 18th April 2011
Antoni, C., Krueger, G., de Vlam, K., et al.: Infliximab improves signs and symptoms of psoriatic arthritis: results of the IMPACT 2 trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 64, 1150–1157 (2005)
Antoni, C.E., Kavanaugh, A., Kirkham, B.: Sustained benefits of infliximab therapy for dermatological and articular manifestations of psoriatic arthritis: results from the Infliximab Multinational Psoriatic Arthritis Controlled Trial (IMPACT). Arthritis Rheum. 4, 1227–1236 (2005)
Mease, P.J., Goffe, B.S., Metz, J., et al.: Etanercept in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis: a randomised trial. Lancet 356, 385–390 (2000)
Mease, P.J., Kivitz, A.J., Burch, F.X., et al.: Etanercept treatment of psoriatic arthritis safety, efficacy, and effect on disease progression. Arthritis Rheum. 50(7), 2264–2272 (2004)
Mease, P.J., Gladman, D.D., Ritchlin, C.T., et al.: Adalimumab for the treatment of patients with moderately to severely active psoriatic arthritis: results of a randomised placebo controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 52(10), 3279–3289 (2005)
Genovese, M.C., Mease, P.J., Thomson, G.T., et al.: Safety and efficacy of adalimumab in treatment of patients with psoriatic arthritis who had failed disease modifying antirheumatic drug therapy. J. Rheumatol. 34(6), 1439 (2007)
Acknowledgments
This study was jointly funded in full by Schering-Plough Ltd and Centocor Ortho Biotech Inc, and the writing of this paper was funded in full by Schering-Plough Ltd.
Conflict of interest
Ewen Cummins and Christian Asseburg have no conflicts of interest. Christian Asseburg was employed by Swedish Institute of Health Economics when this study was conducted. Yogesh Punekar and Manishi Prasad are employed by Schering-Plough Ltd. Jacqueline Buchanan was employed by Centocor Ortho Biotech Inc when this study was conducted.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cummins, E., Asseburg, C., Prasad, M. et al. Cost effectiveness of golimumab for the treatment of active psoriatic arthritis. Eur J Health Econ 13, 801–809 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-011-0335-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-011-0335-x