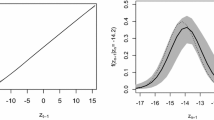
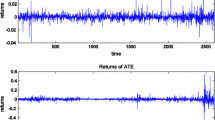
Abstract
We consider the problem of estimating the rate matrix governing a finite-state Markov jump process given a number of fragmented time series. We propose to concatenate the observed series and to employ the emerging non-Markov process for estimation. We describe the bias arising if standard methods for Markov processes are used for the concatenated process, and provide a post-processing method to correct for this bias. This method applies to discrete-time Markov chains and to more general models based on Markov jump processes where the underlying state process is not observed directly. This is demonstrated in detail for a Markov switching model. We provide applications to simulated time series and to financial market data, where estimators resulting from maximum likelihood methods and Markov chain Monte Carlo sampling are improved using the presented correction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beskos, A., Papaspiliopoulos, O., Roberts, G.O., Fearnhead, P.: Exact and efficient likelihood-based estimation for discretely observed diffusion processes. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 68(3), 333–382 (2006)
Billingsley, P.: Statistical Inference for Markov Processes. Statistical Research Monographs, vol. 2. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago (1961a)
Billingsley, P.: Statistical methods in Markov chains. Ann. Math. Stat. 32(1), 12–40 (1961b)
Bladt, M., Sørensen, M.: Statistical inference for discretely observed Markov jump processes. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 67(3), 295–410 (2005)
Brémaud, P.: Point Processes and Queues. Springer, New York (1981)
Buffington, J., Elliott, R.J.: American options with regime switching. Int. J. Theor. Appl. Finance 5, 497–514 (2002)
Deng, S.: Stochastic models of energy commodity prices and their applications: Mean-reversion with jumps and spikes. University of California Energy Institute, PWP-073 (2000)
Driffill, J., Kenc, T., Sola, M., Spagnolo, F.: On model selection and Markov switching: A empirical examination of term structure models with regime shifts. Centre for Economic Policy Research, CEPR Discussion Papers 4165 (2004)
Elliott, R.J., Krishnamurthy, V., Sass, J.: Moment based regression algorithm for drift and volatility estimation in continuous time Markov switched models. Econom. J. 11, 244–270 (2008)
Engel, C., Hamilton, J.D.: Long swings in the dollar: Are they in the data and do markets know it? Am. Econ. Rev. 80(4), 689–713 (1990)
Frühwirth-Schnatter, S.: Markov chain Monte Carlo estimation of classical and dynamic switching and mixture models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 96(453), 194–209 (2001)
Frühwirth-Schnatter, S.: Finite Mixture and Markov Switching Models. Springer, New York (2006)
Guidolin, M., Timmermann, A.: An econometric model of nonlinear dynamics in the joint distribution of stock and bond returns. J. Appl. Econom. 21(1), 1–22 (2006)
Guidolin, M., Timmermann, A.: Asset allocation under multivariate regime switching. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 31, 3503–3544 (2007)
Guo, X.: An explicit solution to an optimal stopping problem with regime switching. Stoch. Process. Appl. 38, 464–481 (2001)
Haas, M., Mittnik, S., Paolella, M.S.: A new approach to Markov-switching GARCH models. J. Financ. Econom. 2(4), 493–530 (2004)
Hahn, M., Frühwirth-Schnatter, S., Sass, J.: Markov chain Monte Carlo methods for parameter estimation in multidimensional continuous time Markov switching models. Department of Statistics, University Linz (Austria), IFAS Research Paper 2009-41 (2007)
Jarrow, R.A., Lando, D., Turnbull, S.M.: A Markov model for the term structure of credit risk spreads. Rev. Financ. Stud. 10(2), 481–523 (1997)
Liu, R.H., Zhang, Q., Yin, G.: Option pricing in a regime-switching model using the fast Fourier transform. J. Appl. Math. Stoch. Anal. 2006, 1–22 (2006)
Rydén, T., Teräsvirta, T., Åsbrink, S.: Stylized facts of daily return series and the hidden Markov model. J. Appl. Econ. 13, 217–244 (1998)
Sass, J., Haussmann, U.G.: Optimizing the terminal wealth under partial information: The drift process as a continuous time Markov chain. Finance Stoch. 8(4), 553–577 (2004)
Scott, S.L.: Bayesian methods for hidden Markov models: Recursive computing in the 21st century. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 97, 337–351 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hahn, M., Frühwirth-Schnatter, S. & Sass, J. Estimating models based on Markov jump processes given fragmented observation series. AStA Adv Stat Anal 93, 403–425 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10182-009-0116-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10182-009-0116-3