Abstract
Background
Aberrant expression of T helper cell (Th) cytokines is believed to play a central role in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). While the glomerulus is one of the major targets of lupus inflammation, little is known about the cytokine expression in glomeruli. The current study aimed to explore the profiles of Th cytokine gene expressions in isolated glomeruli of lupus-prone mice.
Methods
Glomeruli were purified from lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice using the magnetic microbead method. Expressions of cytokine genes representing the Th subset and FoxP3 were examined using real-time polymerase chain reaction. Serum levels of these cytokines were also measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. MRL/n mice were used as controls. Histologic glomerular damages were scored semiquantitatively. To examine the role of TNF-α in glomerular damage, we administered etanercept, a TNF-α antagonist, into the subjects.
Results
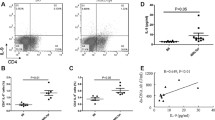
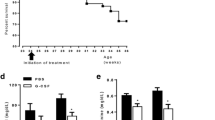
Glomerular gene expressions of TNF-α in lpr mice increased with week postpartum and reached statistically significant levels at 16 weeks compared with those of the glomeruli from control mice. Expressions of IFN-γ, IL-4 and FoxP3 also increased, but the difference was not significant. There was a significant increase in serum levels of TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-17 and decrease in those of IL-4. Among the genes examined, TNF-α significantly correlated with glomerular damage score. Administration of etanercept did not affect glomerular cytokine expressions or proteinuria and failed to ameliorate histologic glomerular damages.
Conclusion
Our data suggest that Th1 cytokines, especially TNF-α, are dominantly expressed in the glomeruli of lupus-prone mice, but its pathophysiological role remains unclear.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waldman M, Appel GB. Update on the treatment of lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 2006;70:1403–12.
Miyake K, Akahoshi M, Nakashima H. Th subset balance in lupus nephritis. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:980286.
Uhm WS, Na K, Song GW, et al. Cytokine balance in kidney tissue from lupus nephritis patients. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003;42:935–8.
Crispin JC, Oukka M, Bayliss G, et al. Expanded double negative T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus produce IL-17 and infiltrate the kidneys. J Immunol. 2008;181(12):8761–6.
Pisitkun P, Ha HL, Wang H, et al. Interleukin-17 cytokines are critical in development of fatal lupus glomerulonephritis. Immunity. 2012;37:1104–15.
Xing Q, Su H, Cui J, Wang B. Role of treg cells and TGF-beta1 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a possible relation with lupus nephritis. Immunol Invest. 2012;41:15–27.
Takemoto M, Asker N, Gerhardt H, et al. A new method for large scale isolation of kidney glomeruli from mice. Am J Pathol. 2002;161:799–805.
Kikawada E, Lenda DM, Kelley VR. IL-12 deficiency in MRL-Fas(lpr) mice delays nephritis and intrarenal IFN-gamma expression, and diminishes systemic pathology. J Immunol. 2003;170:3915–25.
Elshal MF, McCoy JP. Multiplex bead array assays: performance evaluation and comparison of sensitivity to ELISA. Methods. 2006;38:317–23.
Liu R, Bal HS, Desta T, Behl Y, Graves DT. Tumor necrosis factor-α mediates diabetes-enhanced apoptosis of matrix-producing cells and impairs diabetic healing. Am J Pathol. 2006;168:757–64.
Masutani K, Akahoshi M, Tsuruya K, et al. Predominance of Th1 immune response in diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:2097–106.
Wang Y, Ito S, Chino Y, et al. Use of laser microdissection in the analysis of renal-infiltrating T cells in MRL/lpr mice. Mod Rheumatol. 2008;18:385–93.
Wang Y, Ito S, Chino Y, et al. Laser microdissection-based analysis of cytokine balance in the kidneys of patients with lupus nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010;159:1–10.
Schmidt T, Paust HJ, Krebs CF, et al. Function of the T 17/IL-17A immune response in murine lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67:475–87.
Hondowicz BD, Fields ML, Nish SA, et al. Autoantibody production in lpr/lpr gld/gld mice reflects accumulation of CD4 + effector cells that are resistant to regulatory T cell activity. J Autoimmun. 2008;31:98–109.
Bonelli M, Goschl L, Bluml S, et al. CD4(+)CD25(−)Foxp3(+) T cells: a marker for lupus nephritis? Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16:R104.
Yazici MU, Orhan D, Kale G, et al. Studying IFN-gamma, IL-17 and FOXP3 in pediatric lupus nephritis. Pediatr Nephrol. 2014;29:853–62.
Zhu LJ, Yang X, Yu XQ. Anti-TNF-alpha therapies in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:465898.
Williams VL, Cohen PR. TNF alpha antagonist-induced lupus-like syndrome: report and review of the literature with implications for treatment with alternative TNF alpha antagonists. Int J Dermatol. 2011;50:619–25.
Almoallim H, Al-Ghamdi Y, Almaghrabi H, Alyasi O. Anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha induced systemic lupus erythematosus. Open Rheumatol J. 2012;6:315–9.
Yahya TM, Dhanyamraju S, Harrington TM, et al. Spontaneous resolution of lupus nephritis following withdrawal of etanercept. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2013;43:447–9.
Kelley VR, Wuthrich RP. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Nephrol. 1999;19:57–66.
Yokoyama H, Kreft B, Kelley VR. Biphasic increase in circulating and renal TNF-alpha in MRL-lpr mice with differing regulatory mechanisms. Kidney Int. 1995;47:122–30.
Acknowledgments
We thank Ms Rumiko Koitabashi for her excellent technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Tshilela, K.A., Ikeuchi, H., Matsumoto, T. et al. Glomerular cytokine expression in murine lupus nephritis. Clin Exp Nephrol 20, 23–29 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-015-1123-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-015-1123-1