Abstract
Introduction
The aim of this study was to evaluate our institution’s experience in performing laparoscopic radical nephrectomy (LRN) and partial nephrectomy (PN) in patients with small renal masses.
Methods
142 patients with cT1aN0M0 lesions were identified. 68 of these subjects were treated with LRN and 74 were treated with laparoscopic PN (LPN). The clinicopathological characteristics of the two groups of patients, including diameter-axial-polar (DAP) nephrometry and RENAL nephrometry score (RENAL-NS), operative results, and outcomes, were retrospectively analyzed.
Results
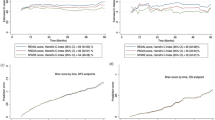
A multivariate logistic regression analysis for the selection of PN as the treatment showed that tumor size, DAP nephrometry, RENAL-NS and imperative condition were all independent factors. The area under the curve receiver operating characteristics (ROC-AUC) of DAP and RENAL-NS for performing LPN were 0.897 and 0.825, respectively.
Conclusions
Although LRN was performed in patients with a high nephrometry score in this study, open partial nephrectomy (OPN) should be considered for patients with a high nephrometry score in T1a renal cell carcinoma (RCC) because of better functional and similar oncological outcomes. Based on ROC analysis, when DAP is 6 or less, LPN should be considered and when DAP is 7 or more, OPN should be considered.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CKD:
-
Chronic kidney disease
- DAP:
-
Diameter-axial-polar nephrometry
- eGFR:
-
Estimated glomerular filtration rate
- LPN:
-
Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy
- LRN:
-
Laparoscopic radical nephrectomy
- OPN:
-
Open partial nephrectomy
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PN:
-
Partial nephrectomy
- RENAL-NS:
-
RENAL nephrometry score
- RFA:
-
Radiofrequency ablation
References
Heuer R, Gill IS, Guazzoni G et al (2010) A critical analysis of the actual role of minimally invasive surgery and active surveillance for kidney cancer. Eur Urol 57:223–232
Kunkle DA, Egleston BL, Uzzo RG (2008) Excise, ablate or observe: the small renal mass dilemma––a meta analysis and review. J Urol 179:1227–1233
Huang WC, Elkin EB, Levey AS et al (2009) Partial nephrectomy versus radical nephrectomy in patients with small renal tumors––is there a difference in mortality and cardiovascular outcomes? J Urol 181:55–61 (discussion 62)
Huang WC, Levey AS, Serio AM et al (2006) Chronic kidney disease after nephrectomy in patients with renal cortical tumors: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Oncol 7:735–740
European Association of Urology (2014) EAU Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma: The 2014 Update
National Comprehensive Cancer Network (2014) NCCN Guidelines™ Version 2. 2014 Kidney Cancer
Marszalek M, Meixl H, Polajnar M et al (2009) Laparoscopic and open partial nephrectomy: a matched-pair comparison of 200 patients. Eur Urol 55:1171–1178
Kutikov A, Uzzo RG (2009) The RENAL nephrometry score: a comprehensive standardized system for quantitating renal tumor size, location and depth. J Urol 182:844–853
Simmons MN, Hillyer SP, Lee BH et al (2012) Diameter-axial-polar nephrometry: integration and optimization of RENAL and centrality index scoring systems. J Urol 188:384–390
Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL et al (1987) A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis 40:373–383
Japanese Society of Nephrology (2009) Evidence-based practice guideline for the treatment of CKD. Clin Exp Nephrol 13:537–566
Lai FC, Kau EL, Ng CS et al (2007) Laparoscopic nephrectomy outcomes of elderly patients in the 21st century. J Endourol 21:1309–1313
Berger A, Crouzet S, Canes D et al (2008) Minimally invasive nephron-sparing surgery. Curr Opin Urol 18:462–466
Broughton GJ, Clark P, Barocas DA et al (2012) Tumour size, tumour complexity, and surgical approach are associated with nephrectomy type in small renal cortical tumours treated electively. BJU Int 109:1607–1613
Zini L, Perrotte P, Capitanio U et al (2009) Radical versus partial nephrectomy: effect on overall and noncancer mortality. Cancer 115:1465–1471
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Naya, Y., Kawauchi, A., Oishi, M. et al. Comparison of diameter-axial-polar nephrometry and RENAL nephrometry score for treatment decision-making in patients with small renal mass. Int J Clin Oncol 20, 358–361 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-014-0714-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-014-0714-2