Abstract
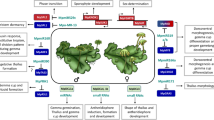
Dicer and Dicer-like (DCL) proteins are key components in small RNA biogenesis. DCLs form a small protein family in plants whose diversification time dates to the emergence of mosses (Physcomitrella patens). DCLs are ubiquitously but not evenly expressed in tissues, at different developmental stages, and in response to environmental stresses. In Arabidopsis, AtDCL1, AtDCL2, and AtDCL4 exhibit similar expression pattern during the leaf or stem development, which is distinguished from AtDCL3. However, distinct expression profiles for all DCLs are found during the development of reproductive organs flower and seed. The grape VvDCL1 and VvDCL3 may act sequentially to face the fungi challenge. Overall, the responses of DCLs to drought, cold, and salt are quite different, indicating that plants might have specialized regulatory mechanism in response to different abiotic stresses. Further analysis of the promoter regions reveals a few of cis-elements that are hormone- and stress-responsive and developmental-related. However, gain and loss of cis-elements are frequent during evolution, and not only paralogous but also orthologous DCLs have dissimilar cis-element organization. In addition to cis-elements, AtDCL1 is probably regulated by both ath-miR162 and ath-miR414. Posterior analysis has identified some critical amino acid sites that are responsible for functional divergence between DCL family members. These findings provide new insights into understanding DCL protein functions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergmann DC, Lukowitz W, Somerville CR (2004) Stomatal development and pattern controlled by a MAPKK kinase. Science 304:1494–1497
Chapman EJ, Carrington JC (2007) Specialization and evolution of endogenous small RNA pathways. Nat Rev Genet 8:884–896
Deleris A, Gallego-Bartolome J, Bao J, Kasschau KD, Carrington JC, Voinnet O (2006) Hierarchical action and inhibition of plant Dicer-like proteins in antiviral defense. Science 313:68–71
Dlakić M (2006) DUF283 domain of Dicer proteins has a double-stranded RNA-binding fold. Bioinformatics 22:2711–2714
Du Z, Lee JK, Tjhen R, Stroud RM, James TL (2008) Structural and biochemical insights into the dicing mechanism of mouse Dicer: a conserved lysine is critical for dsRNA cleavage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:2391–2396
Dunoyer P, Himber C, Voinnet O (2005) DICER-LIKE 4 is required for RNA interference and produces the 21-nucleotide small interfering RNA component of the plant cell-to-cell silencing signal. Nat Genet 37:1356–1360
Galiana-Arnoux D, Dostert C, Schneemann A, Hoffmann JA, Imler JL (2006) Essential function in vivo for Dicer-2 in host defense against RNA viruses in Drosophila. Nat Immunol 7:590–597
Groβhans H, Filipowicz W (2008) The expanding world of small RNAs. Nature 451:414–416
Gu X (1999) Statistical methods for testing functional divergence after gene duplication. Mol Biol Evol 16:1664–1674
Gu X (2003) Functional divergence in protein (family) sequence evolution. Genetica 118:133–141
Gu X, Vander Velden K (2002) DIVERGE: phylogeny-based analysis for functional-structural divergence of a protein family. Bioinformatics 18:500–501
Harfe BD, McManus MT, Mansfield JH, Hornstein E, Tabin CJ (2005) The RNase III enzyme Dicer is required for morphogenesis but not patterning of the vertebrate limb. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:10898–10903
Harris KS, Zhang Z, McManus MT, Harfe BD, Sun X (2006) Dicer function is essential for lung epithelium morphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:2208–2213
Henderson IR, Zhang X, Lu C, Johnson L, Meyers BC, Green PJ, Jacobsen SE (2006) Dissecting Arabidopsis thaliana DICER function in small RNA processing, gene silencing and DNA methylation patterning. Nat Genet 38:721–725
Jain M, Nijhawan A, Arora R, Agarwal P, Ray S, Sharma P, Kapoor S, Tyagi AK, Khurana JP (2007) Genome-wide analysis, classification, emporal and spatial gene expression during panicle and seed development, and regulation by light and abiotic stress. Plant Physiol 143:1467–1483
Jin Z, Xie T (2007) Dcr-1 maintains Drosophila ovarian stem cells. Curr Biol 17:539–544
Katiyar-Agarwal S, Morgan R, Dahlbeck D, Borsani O, Willegas A, Zhu JK, Staskawicz BJ, Jin H (2006) A pathogen-inducible endogenous siRNA in plant immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:18002–18007
Katoh K, Kuma K, Miyata T, Toh H (2005) Improvement in the accuracy of multiple sequence alignment program MAFFT. Genome Inform 16:22–33
Kidner CA, Martienssen RA (2005) The developmental role of microRNA in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:38–44
Kini HK, Walton SP (2007) In vitro binding of single-stranded RNA by human Dicer. FEBS Lett 581:5611–5616
Knight SW, Bass BL (2001) A role for the RNase III enzyme DCR-1 in RNA interference and germ line development in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 293:2269–2271
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163
Lee YS, Nakahara K, Pham JW, Kim K, He Z, Sontheimer EJ, Carthew RW (2004) Distinct roles for Drosophila Dicer-1 and Dicer-2 in the siRNA/miRNA silencing pathways. Cell 117:69–81
Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van de Peer Y, Rouzé P, Rombauts S (2002) Plant CARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30:325–327
Li M, Xu W, Yang W, Kong Z, Xue Y (2007) Genome-wide gene expression profiling reveals conserved and novel molecular functions of the stigma in rice. Plant Physiol 144:1797–1812
Liu B, Chen Z, Song X, Liu C, Cui X, Zhao X, Fang J, Xu W, Zhang H, Wang X, Chu C, Deng X, Xue Y, Cao X (2007) Oryza sativa Dicer-like4 reveals a key role for small interfering RNA silencing in plant development. Plant Cell 19:2705–2718
Llave C (2004) MicroRNAs: more than a role in plant development? Mol Plant Pathol 5:361–366
MacRae IJ, Zhou K, Li F, Repic A, Brooks AN, Cande WZ, Adams PD, Doudna JA (2006) Structural basis for double-stranded RNA processing by Dicer. Science 311:195–198
Margis R, Fusaro AF, Smith NA, Curtin SJ, Watson JM, Finnegan EJ, Waterhouse PM (2006) The evolution and diversification of Dicers in plants. FEBS Lett 580:2442–2450
Matskevich AA, Moelling K (2007) Dicer is involved in protection against influenza A virus infection. J Gen Virol 88:2627–2635
Matskevich AA, Moelling K (2008) Stimuli-dependent cleavage of Dicer during apoptosis. Biochem J 412:527–534
Millar AA, Waterhouse PM (2005) Plant and animal microRNAs: similarities and differences. Funct Integr Genomics 5:129–135
Mlotshwa S, Pruss GJ, Peragine A, Endres MW, Li J, Chen X, Poethig RS, Bowman LH, Vance V (2008) DICER-LIKE2 plays a primary role in transitive silencing of transgenes in Arabidopsis. PLOS One 3:e1755
Moissiard G, Parizotto EA, Himber C, Voinnet O (2007) Transitivity in Arabidopsis can be primed, requires the redundant action of the antiviral Dicer-like 4 and Dicer-like 2, and is compromised by viral-encoded suppressor proteins. RNA 13:1268–1278
Murakami Y, Yasuda T, Saigo K, Urashima T, Toyoda H, Okanoue T, Shimotohno K (2006) Comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression patterns in hepatocellular carcinoma and non-tumorous tissues. Oncogene 25:2537–2545
Murchison EP, Stein P, Xuan Z, Pan H, Zhang MQ, Schultz RM, Hannon GJ (2007) Critical roles for Dicer in the female germline. Genes Dev 21:682–693
Quevillon E, Silventoinen V, Pillai S, Harte N, Mulder N, Apweiler R, Lopez R (2005) InterProScan: protein domains identifier. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W116–W120
Schmid M, Davison TS, Henz SR, Pape UJ, Demar M, Vingron M, Schölkopf B, Weigel D, Lohmann JU (2005) A gene expression map of Arabidopsis thaliana development. Nat Genet 37:501–506
Schmitz RJ, Hong L, Fitzpatrick KE, Amasino RM (2007) DICER-LIKE 1 and DICER-LIKE 3 redundantly act to promote flowering via repression of FLOWERING LOCUS C in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 176:1359–1362
Singh S, Bevan SC, Patil K, Newton DC, Marsden PA (2005) Extensive variation in the 5′-UTR of Dicer mRNAs influences translational efficiency. Biochem Biophy Res Commun 33:643–650
Tahbaz N, Kolb FA, Zhang H, Jaronczyk K, Filipowicz W, Hobman TC (2004) Characterization of the interactions between mammalian PAZ PIWI domain proteins and Dicer. EMBO Rep 5:189–194
Vaucheret H (2006) Post-transcriptional small RNA pathways in plants: mechanisms and regulations. Genes Dev 20:759–771
Wang YP, Liang L, Han BC, Quan Y, Wang X, Tao T, Ji ZL (2006) GEPS: the gene expression pattern scanner. Nucleic Acids Res 34:W492–W497
Xie Z, Kasschau KD, Carrington JC (2003) Negative feedback regulation of Dicer-Like1 in Arabidopsis by microRNA-guided mRNA degradation. Curr Biol 13:784–789
Xie Z, Johansen LK, Gustafson AM, Kasschau KD, Lellis AD, Zilberman D, Jacobsen SE, Carrington JC (2004) Genetic and functional diversification of small RNA pathways in plants. PLOS Biol 2:e104
Xie Z, Allen E, Wilken A, Carrington JC (2005) DICER-LIKE 4 functions in trans-acting small interfering RNA biogenesis and vegetative phase change in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:12984–12989
Yang WJ, Yang DD, Na S, Sandusky GE, Zhang Q, Zhao G (2005) Dicer is required for embryonic angiogenesis during mouse development. J Biol Chem 280:9330–9335
Zhang Y (2005) miRU: an automated plant miRNA target prediction server. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W701–W704
Zhang H, Kolb FA, Jaskiewicz L, Westhof E, Filipowicz W (2004) Single processing center models for human Dicer and bacterial RNase III. Cell 118:57–68
Zhang JF, Yuan LJ, Shao Y, Du W, Yan DW, Lu YT (2008) The disturbance of small RNA pathways enhanced abscisic acid response and multiple stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 31:562–574
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Rudi Appels and Prof. Wujun Ma for their valuable and constructive suggestions and for careful editing of the manuscript. This work was supported by an intramural fund from Zhejiang Forestry University (to Qingpo Liu) and grants from National Basic Research Program of China (973 program; no. 2007CB109305), National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 30740011), Zijin Program from Zhejiang University (to Y. Feng), the Special Fund for Grade B Innovative Research Team from Zhejiang Forestry University (to Z. Zhu).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10142_2009_111_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Fig. S1 Functional divergence significantly related amino acid site candidates [Q k > 0.9]. A site-specific profile based on the posterior probability (Q k) was used to identify critical amino acid sites that were responsible for functional divergence between DCL family members. According to the definition, large Q k indicates a high possibility that the functional constraint (or the evolutionary rate) of a site is different between two clusters. a DCL1/DCL2; b DCL1/DCL3; c DCL1/DCL4 (PDF 17.4 KB).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Feng, Y. & Zhu, Z. Dicer-like (DCL) proteins in plants. Funct Integr Genomics 9, 277–286 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-009-0111-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-009-0111-5