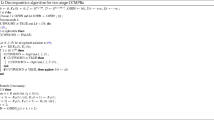
Abstract
We present a new approach for exactly solving chance-constrained mathematical programs having discrete distributions with finite support and random polyhedral constraints. Such problems have been notoriously difficult to solve due to nonconvexity of the feasible region, and most available methods are only able to find provably good solutions in certain very special cases. Our approach uses both decomposition, to enable processing subproblems corresponding to one possible outcome at a time, and integer programming techniques, to combine the results of these subproblems to yield strong valid inequalities. Computational results on a chance-constrained formulation of a resource planning problem inspired by a call center staffing application indicate the approach works significantly better than both an existing mixed-integer programming formulation and a simple decomposition approach that does not use strong valid inequalities. We also demonstrate how the approach can be used to efficiently solve for a sequence of risk levels, as would be done when solving for the efficient frontier of risk and cost.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The extension to more general discrete distributions of the form \(\mathbb P \{\omega = \omega ^k \} = p_k\), where \(p_k \ge 0\) and \(\sum _k p_k = 1\), is straightforward and is omitted to simplify exposition.
References
Luedtke, J., Ahmed, S.: A sample approximation approach for optimization with probabilistic constraints. SIAM J. Optim. 19, 674–699 (2008)
Calafiore, G., Campi, M.: Uncertain convex programs: randomized solutions and confidence levels. Math. Program. 102, 25–46 (2005)
Calafiore, G., Campi, M.: The scenario approach to robust control design. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control 51, 742–753 (2006)
Nemirovski, A., Shapiro, A.: Scenario approximation of chance constraints. In: Calafiore, G., Dabbene, F. (eds.) Probabilistic and Randomized Methods for Design Under Uncertainty, pp. 3–48. Springer, London (2005)
Campi, M., Garatti, S.: A sampling-and-discarding approach to chance-constrained optimization: feasibility and optimality. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 148, 257–280 (2011)
Jeroslow, R.: Representability in mixed integer programming, I: characterization results. Discr. Appl. Math. 17, 223–243 (1987)
Ruszczyński, A.: Probabilistic programming with discrete distributions and precedence constrained knapsack polyhedra. Math. Program. 93, 195–215 (2002)
Tanner, M., Sattenspiel, L., Ntaimo, L.: Finding optimal vaccination strategies under parameter uncertainty using stochastic programming. Math. Biosci. 215, 144–151 (2008)
Watanabe, T., Ellis, H.: Stochastic programming models for air quality management. Comput. Oper. Res. 20, 651–663 (1993)
Morgan, D., Eheart, J., Valocchi, A.: Aquifer remediation design under uncertainty using a new chance constrained programming technique. Water Resour. Res. 29, 551–561 (1993)
Andreas, A.K., Smith, J.C.: Mathematical programming algorithms for two-path routing problems with reliability considerations. INFORMS J. Comput. 20, 553–564 (2008)
Song, Y., Luedtke, J.: Branch-and-cut algorithms for chance-constrained formulations of reliable network design problems (2012). Available at http://www.optimization-online.org
Charnes, A., Cooper, W.W., Symonds, G.H.: Cost horizons and certainty equivalents: an approach to stochastic programming of heating oil. Manag. Sci. 4, 235–263 (1958)
Prékopa, A.: On probabilistic constrained programmming. In: Kuhn, H.W. (ed.) Proceedings of the Princeton Symposium on Mathematical Programming, pp. 113–138. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ (1970)
Calafiore, G., El Ghaoui, L.: On distributionally robust chance-constrained linear programs. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 130, 1–22 (2006)
Charnes, A., Cooper, W.W.: Deterministic equivalents for optimizing and satisficing under chance constraints. Oper. Res. 11, 18–39 (1963)
Beraldi, P., Ruszczyński, A.: The probabilistic set-covering problem. Oper. Res. 50, 956–967 (2002)
Dentcheva, D., Prékopa, A., Ruszczyński, A.: Concavity and efficient points of discrete distributions in probabilistic programming. Math. Program. 89, 55–77 (2000)
Küçükyavuz, S.: On mixing sets arising in chance-constrained programming. Math. Program. 132, 31–56 (2012)
Luedtke, J., Ahmed, S., Nemhauser, G.L.: An integer programming approach for linear programs with probabilistic constraints. Math. Program. 12, 247–272 (2010)
Saxena, A., Goyal, V., Lejeune, M.: MIP reformulations of the probabilistic set covering problem. Math. Program. 121, 1–31 (2009)
Dentcheva, D., Martinez, G.: Regularization methods for optimization problems with probabilistic constraints. Math. Program. 138, 223–251 (2013). doi:10.1007/s10107-012-0539-6
Henrion, R., Möller, A.: A gradient formula for linear chance constraints under gaussian distribution. Math. Oper. Res. 37, 475–488 (2012)
Hong, L., Yang, Y., Zhang, L.: Sequential convex approximations to joint chance constrained programs: A Monte Carlo approach. Oper. Res. 59, 617–630 (2011)
Prékopa, A.: Programming under probabilistic constraints with a random technology matrix. Mathematische Operationsforschung Statistik 5, 109–116 (1974)
Van Ackooij, W., Henrion, R., Möller, A., Zorgati, R.: On probabilistic constraints induced by rectangular sets and multivariate normal distributions. Math. Methods Oper. Res. 71, 535–549 (2010)
Tanner, M., Ntaimo, L.: IIS branch-and-cut for joint chance-constrained programs and application to optimal vaccine allocation. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 207, 290–296 (2010)
Beraldi, P., Bruni, M.: An exact approach for solving integer problems under probabilistic constraints with random technology matrix. Ann. Oper. Res. 177, 127–137 (2010)
Ben-Tal, A., Nemirovski, A.: Robust solutions of linear programming problems contaminated with uncertain data. Math. Program. 88, 411–424 (2000)
Bertsimas, D., Sim, M.: The price of robustness. Oper. Res. 52, 35–53 (2004)
Nemirovski, A., Shapiro, A.: Convex approximations of chance constrained programs. SIAM J. Optim. 17, 969–996 (2006)
Erdoğan, E., Iyengar, G.: Ambiguous chance constrained problems and robust optimization. Math. Program. 107, 37–61 (2006)
Erdoğan, E., Iyengar, G.: On two-stage convex chance constrained problems. Math. Meth. Oper. Res. 65, 115–140 (2007)
Luedtke, J., Ahmed, S., Nemhauser, G.: An integer programming approach for linear programs with probabilistic constraints. In: Fischetti, M., Williamson, D. (eds.) IPCO 2007, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp. 410–423. Springer, Berlin (2007)
Birge, J., Louveaux, F.: Introduction to Stochastic Programming. Springer, New York (1997)
Van Slyke, R., Wets, R.J.: L-shaped linear programs with applications to optimal control and stochastic programming. SIAM J. Appl. Math 17, 638–663 (1969)
Higle, J.L., Sen, S.: Stochastic decomposition: an algorithm for two-stage stochastic linear programs. Math. Oper. Res. 16, 650–669 (1991)
Shen, S., Smith, J., Ahmed, S.: Expectation and chance-constrained models and algorithms for insuring critical paths. Manage. Sci. 56, 1794–1814 (2010)
Sherali, H., Adams, W.: A hierarcy of relaxations between the continuous and convex hull representations for zero-one programming problems. SIAM J. Discrete Math. 3, 411–430 (1990)
Luedtke, J.: An integer programming and decomposition approach for general chance-constrained mathematical programs. In: Eisenbrand, F., Shepherd, F.B. (eds.) IPCO, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 6080, pp. 271–284. Springer, Berlin (2010)
Codato, G., Fischetti, M.: Combinatorial Benders’ cuts for mixed-integer linear programming. Oper. Res. 54, 756–766 (2006)
Atamtürk, A., Nemhauser, G.L., Savelsbergh, M.W.P.: The mixed vertex packing problem. Math. Program. 89, 35–53 (2000)
Günlük, O., Pochet, Y.: Mixing mixed-integer inequalities. Math. Program. 90, 429–457 (2001)
Linderoth, J., Savelsbergh, M.: A computational study of search strategies for mixed integer programming. INFORMS J. Comput. 11, 173–187 (1999)
Applegate, D., Bixby, R., Chvátal, V., Cook, W.: Finding cuts in the TSP. Technical Report 95–05, DIMACS (1995)
Achterberg, T., Koch, T., Martin, A.: Branching rules revisited. Oper. Res. Lett. 33, 42–54 (2004)
Gurvich, I., Luedtke, J., Tezcan, T.: Call center staffing with uncertain arrival rates: a chance-constrained optimization approach. Manag. Sci. 56, 1093–1115 (2010)
Luedtke, J.: Online supplement to: a branch-and-cut decomposition algorithm for solving chance-constrained mathematical programs (2012). Available at http://www.cae.wisc.edu/~luedtkej
Quesada, I., Grossmann, I.E.: An LP/NLP based branch-and-bound algorithm for convex MINLP optimization problems. Comput. Chem. Eng. 16, 937–947 (1992)
Qiu, F., Ahmed, S., Dey, S., Wolsey, L.: Covering linear programming with violations (2012). Available at http://www.optimization-online.org
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Shabbir Ahmed for the suggestion to compare the presented approach with a basic decomposition algorithm. The author also thanks the anonymous referees for helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research has been supported by NSF under grant CMMI-0952907.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luedtke, J. A branch-and-cut decomposition algorithm for solving chance-constrained mathematical programs with finite support. Math. Program. 146, 219–244 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-013-0684-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-013-0684-6