Abstract
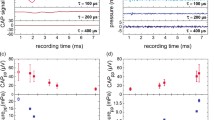
Optical neural stimulation in the cochlea has been presented as an alternative technique to the electrical stimulation due to its potential in spatially selectivity enhancement. So far, few studies have selected the near-infrared (NIR) laser in cochlear neural stimulation and limited optical parameter space has been examined. This paper focused on investigating the optical parameter effect on NIR stimulation of auditory neurons, especially under shorter pulse durations. The spiral ganglion neurons in the cochlea of deafened guinea pigs were stimulated with a pulsed 810-nm NIR laser in vivo. The laser radiation was delivered by an optical fiber and irradiated towards the modiolus. Optically evoked auditory brainstem responses (OABRs) with various optical parameters were recorded and investigated. The OABRs could be elicited with the cochlear deafened animals by using the 810-nm laser in a wide pulse duration ranged from 20 to 1000 μs. Results showed that the OABR intensity increased along with the increasing laser radiant exposure of limited range at each specific pulse duration. In addition, for the pulse durations from 20 to 300 μs, the OABR intensity increased monotonically along with the pulse duration broadening. While for pulse durations above 300 μs, the OABR intensity basically kept stable with the increasing pulse duration. The 810-nm NIR laser could be an effective stimulus in evoking the cochlear neuron response. Our experimental data provided evidence to optimize the pulse duration range, and the results suggested that the pulse durations from 20 to 300 μs could be the optimized range in cochlear neural activation with the 810-nm-wavelength laser.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clark GM (2015) The multi-channel cochlear implant: multi-disciplinary development of electrical stimulation of the cochlea and the resulting clinical benefit. Hear Res 322:4–13
Duke AR, Cayce JM, Malphrus JD, Konrad P, Mahadevan-Jansen A, Jansen ED (2009) Combined optical and electrical stimulation of neural tissue in vivo. J Biomed Opt 14(6):60501
Bareket-Keren L, Hanein Y (2014) Novel interfaces for light directed neuronal stimulation: advances and challenges. Int J Nanomedicine 9(Suppl 1):65–83
Shoham S, Deisseroth K (2010) Special issue on optical neural engineering: advances in optical stimulation technology. J Neural Eng 7(4):40201
Richter CP, Matic AI, Wells JD, Jansen ED, Walsh JJ (2011) Neural stimulation with optical radiation. Laser Photon Rev 5(1):68–80
Izzo AD, Suh E, Pathria J, Walsh JT, Whitlon DS, Richter CP (2007) Selectivity of neural stimulation in the auditory system: a comparison of optic and electric stimuli. J Biomed Opt 12(2):21008
Wells J, Kao C, Mariappan K, Albea J, Jansen ED, Konrad P, Mahadevan-Jansen A (2005) Optical stimulation of neural tissue in vivo. Opt Lett 30(5):504–506
Fried NM, Lagoda GA, Scott NJ, Su LM, Burnett AL (2008) Noncontact stimulation of the cavernous nerves in the rat prostate using a tunable-wavelength thulium fiber laser. J Endourol 22(3):409–413
Bec J, Albert ES, Marc I, Desmadryl G, Travo CEC, Muller AES, Chabbert C, Bardin F, Dumas M (2012) Characteristics of laser stimulation by near infrared pulses of retinal and vestibular primary neurons. Laser Surg Med 44(9):736–745
Cayce JM, Friedman RM, Chen G, Jansen ED, Mahadevan-Jansen A, Roe AW (2014) Infrared neural stimulation of primary visual cortex in non-human primates. Neuroimage 84:181–190
Izzo AD, Richter CP, Jansen ED, Walsh JJ (2006) Laser stimulation of the auditory nerve. Lasers Surg Med 38(8):745–753
Richter C, Bayon R, Izzo AD, Otting M, Suh E, Goyal S, Hotaling J, Walsh JT (2008) Optical stimulation of auditory neurons: effects of acute and chronic deafening. Hearing Res 242(1):42–51
Littlefield PD, Vujanovic I, Mundi J, Matic AI, Richter CP (2010) Laser stimulation of single auditory nerve fibers. Laryngoscope 120(10):2071–2082
Wells J, Kao C, Konrad P, Milner T, Kim J, Mahadevan-Jansen A, Jansen ED (2007) Biophysical mechanisms of transient optical stimulation of peripheral nerve. Biophys J 93(7):2567–2580
Rajguru SM, Richter CP, Matic AI, Holstein GR, Highstein SM, Dittami GM, Rabbitt RD (2011) Infrared photostimulation of the crista ampullaris. J Physiol 589(Pt 6):1283–1294
Albert ES, Bec JM, Desmadryl G, Chekroud K, Travo CEC, Gaboyard S, Bardin F, Marc I, Dumas M, Lenaers G et al (2012) TRPV4 channels mediate the infrared laser-evoked response in sensory neurons. J Neurophysiol 107(12):3227–3234
Dittami GM, Rajguru SM, Lasher RA, Hitchcock RW, Rabbitt RD (2011) Intracellular calcium transients evoked by pulsed infrared radiation in neonatal cardiomyocytes. J Physiol 589(Pt 6):1295–1306
Richter C, Tan X (2014) Photons and neurons. Hearing Res 311:72–88
Izzo AD, Walsh JT, Ralph H, Webb J, Bendett M, Wells J, Richter C (2008) Laser stimulation of auditory neurons: effect of shorter pulse duration and penetration depth. Biophys J 94(8):3159–3166
Xia N, Wu XY, Wang X, Mou ZX, Wang MQ, Gu X, Zheng XL, Hou WS (2014) Pulsed 808-nm infrared laser stimulation of the auditory nerve in guinea pig cochlea. Lasers Med Sci 29(1):343–349
Wang J, Lu J, Li C, Xu L, Li X, Tian L (2015) Pulsed 980 nm short wavelength infrared neural stimulation in cochlea and laser parameter effects on auditory response characteristics. Biomed Eng Online 14(1):1–11
Tan X, Rajguru S, Young H, Xia N, Stock SR, Xiao X, Richter CP (2015) Radiant energy required for infrared neural stimulation. Sci Rep 5:13273
Young HK, Tan X, Xia N, Richter CP (2015) Target structures for cochlear infrared neural stimulation. Neurophotonics 2(2):25002
Thompson AC, Fallon JB, Wise AK, Wade SA, Shepherd RK, Stoddart PR (2015) Infrared neural stimulation fails to evoke neural activity in the deaf guinea pig cochlea. Hear Res 324:46–53
Teudt IU, Maier H, Richter C, Kral A (2011) Acoustic events and “optophonic” cochlear responses induced by pulsed near-infrared laser. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 58(6):1648–1655
Izzo AD, Walsh JT Jr, Jansen ED, Bendett M, Webb J, Ralph H, Richter C (2007) Optical parameter variability in laser nerve stimulation: a study of pulse duration, repetition rate, and wavelength. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 54(6):1108–1114
Guan T, Zhu K, Chen F, He Y, Wang J, Wu M, Nie G (2015) Auditory nerve impulses induced by 980 nm laser. J Biomed Opt 20(8):88004
Keller MD, Stafford JW, Stafford RC (2013) Laser source development for infrared neural stimulation. Electronics, Communications and Photonics Conference 2013:1–4
Mccaughey RG, Cara C, Wong BJF (2010) Novel wavelengths for laser nerve stimulation. Laser Surg Med 42(1):69–75
Zhang KY, Wenzel GI, Balster S, Lim HH, Lubatschowski H, Lenarz T, Ertmer W, Reuter G (2009) Optoacoustic induced vibrations within the inner ear. Opt Express 17(25):23037–23043
Ren T, He W, Li Y, Grosh K, Fridberger A (2014) Light-induced vibration in the hearing organ. Sci Rep 4:5941
Liljemalm R, Nyberg T, von Holst H (2013) Heating during infrared neural stimulation. Laser Surg Med 45(7):469–481
Zhang K, Ma Y, Zhou Y (2015) Effects of heat conduction on the spatial selectivity of infrared stimulation in the cochlea. Biomed Eng Online 14(1):1–12
Wells J, Konrad P, Kao C (2007) Pulsed laser versus electrical energy for peripheral nerve stimulation. J Neurosci Methods 163(2):326–37
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding source
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11474185, 61271453, and 61671277), the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2013JQE27056), the Fundamental Cross-discipline Research Foundation of Shandong University (2015JC029), and the Shandong Provincial Key Research and Development Program of China (2016GGX101028).
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Informed consent
Informed consent is not applicable for the nature of this study.
Additional information
English check statement
This manuscript has been checked by a native English speaker for English grammar and syntax. The spelling and formal style of this manuscript have also been checked carefully by a professional editor. We have made our best effort to edit the manuscript to achieve a clear and concise language expression.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Tian, L., Lu, J. et al. Effect of shorter pulse duration in cochlear neural activation with an 810-nm near-infrared laser. Lasers Med Sci 32, 389–396 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-016-2129-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-016-2129-y