Abstract
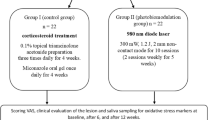
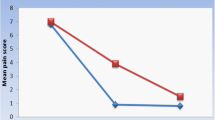
Recently, photodynamic therapy (PDT) has been suggested as a new treatment option that is free from side effects for erosive-atrophic oral lichen planus (OLP). The purpose of this study was to compare the effect of toluidine blue-mediated photodynamic therapy (TB-PDT) with local corticosteroids on treatment of erosive-atrophic OLP. In this randomized clinical trial, 25 patients with keratotic-atrophic-erosive oral lichen planus were allocated randomly into two groups. Group 1 (experimental): topical application of toluidine blue with micropipette was applied, and after 10 min, the patients were treated with a 630-nm GaAlAs laser (power density: 10 mW/cm2) during two visits. Group 2 (control) used mouthwash diluted with dexamethasone (tab 0/5 in 5 ml water) for 5 min, and then, it was spat out, and after 30 min, the mouth was rinsed with 30 drops of nystatin 100,000 units for 5 min and again spat out. Demographic data, type, and severity of the lesions and pain were recorded before and after treatment and then at the 1-month follow-up visit. Response rate was defined based on changes in intensity of the lesions and pain. In the experimental and control groups, sign scores of changes significantly reduced after treatment respectively (p = 0.021) and (p = 0.002), but between the two groups, no significant difference was observed (p = 0.72). In the experimental (p = 0.005) and control groups (p = 0.001), the intensity of lesions significantly reduced after treatment and there was a significant difference between the two groups (p = 0.001). The mean amount of improvement in pain was significantly greater in the control group compared with the experimental group (p < 0.001) (α = 0.05). Our study showed that TB-PDT with laser was effective in the management of OLP.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mollaoglu N (2000) Oral lichen planus: a review. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 38:370–377
Edwards PC, Kelsh R (2002) Oral lichen planus: clinical presentation and management. J Can Dent Assoc 68:494–499
Sharma S, Saimbi CS, Koirala B (2008) Erosive oral lichen planus and its management: a case series. J Nepal Med Assoc 47:86–90
Eisen D, Carrozzo M, Bagan Sebastian JV, Thongprasom K (2005) Oral lichen planus: clinical features and management. Oral Dis 11:338–349
Mccreary CE, Mccartan BE (1999) Clinical management of oral lichen planus. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 37:338–343
Van der Waal I (2009) Oral lichen planus and oral lichenoid lesions; a critical appraisal with emphasis on the diagnostic aspects. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 14:310–314
Vente C, Reich K, Rupprecht R, Neumann C (1999) Erosive mucosal lichen planus: response to topical treatment with tacrolimus. Br J Dermatol 140:338–342
Little J, Falace D, Miller C (2007) Dental management of the compromised patient. 7 the ed Mosby, pp 236-245
Usacheva MN, Teichert MC, Biel MA (2001) Comparison of the methylene blue and toluidine blue photobactericidal efficacy against gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. Lasers Surg Med 29:165–173
Luan XL, Qin YL, Bi LJ, Hu CY, Zhang ZG, Lin J, Zhou CN (2009) Histological evaluation of the safety of toluidine blue-mediated photosensitization to periodontal tissues in mice. Lasers Med Sci 24:162–166
Aghahosseini F, Arbabi-kalati F, Fashtami LA, Fateh M, Djavid GE (2006) Treatment of oral lichen planus with photodynamic therapy mediated methylene blue. Case Rep Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 11:126–129
Taub AF (2007) Photodynamic therapy: other uses. Dermatol Clin 25:101–109
Zanin IC, Lobo MM, Rodrigues LK, Pimenta LA, Ho¨fling JF, Concalves RB (2006) Photosensitization of in vitro biofilms by toluidine blue O combined with a light-emitting diode. Eur J Oral Sci 114:64–69
Aghahosseini F, Arabi-kalati F, Fashtami LA, Djavid GE, Beithollahi JM (2006) Methylene blue-mediated photodynamic therapy: a possible alternative treatment for oral lichen planus. Laser Surg Med 38:33–38
Sabnis RW (2010) Hand book of biological dyes and stains. johnwiley&sons, p 470
Jajarm HH, Falaki F, Mahdavi O (2011) A comparative pilot study of low intensity laser versus topical corticosteroids in the treatment of erosive-atrophic oral lichen planus. Photomed Laser Surg 29:421–425
Thongprasom K, Luangjarmekom L, Sererat T, Taweesap W (1992) Relative efficacy of fluocinolone acetonide compared with triamcinolone acetonide in treatment of oral lichen planus. J Oral Pathol Med 21:456–458
Liu J, Zeng X, Chen Q, Cai Y, Chen F, Wang Y (2006) An evaluation on the efficacy and safety of amlexanox oral adhesive tablets in the treatment of recurrent minor aphthous ulceration in a Chinese cohort: a randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, unparallel multicenter clinical trial. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 102:475–481
Eduardo F, Bueno DF, de Freitas PM, Marques MM, Passos-Bueno MR, Eduardo C et al (2008) Stem cell proliferation under low intensity laser irradiation: a preliminary study. Laser Surg Med 40:433–438
Almeida‐Lopes L, Rigau J, Amaro Zângaro R, Guidugli‐Neto J, Marques Jaeger MM (2001) Comparison of the low intensity laser therapy effects on cultured human gingival fibroblasts proliferation using different irradiance and same fluency. Laser Surg Med 29:179–184
Byrnes KR, Barna L, Chenault VM, Waynant RW, Ilev IK, Longo L et al (2004) Photo biomodulation improves cutaneous wound healing in an animal model of type II diabetes. Photomed Laser Surg 22:281–290
Sadaksharam J, Nayaki KP, Selvam NP (2012) Treatment of oral lichen planus with methylene blue mediated photodynamic therapy: a clinical study. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 28:97–101
Trehan M, Taylor C (2004) Low dose excimer 308 nm laser for the treatment of oral lichen planus. Arch Dermatol 140:415–420
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the research vice chancellor of the Mashhad University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jajarm, H.H., Falaki, F., Sanatkhani, M. et al. A comparative study of toluidine blue-mediated photodynamic therapy versus topical corticosteroids in the treatment of erosive-atrophic oral lichen planus: a randomized clinical controlled trial. Lasers Med Sci 30, 1475–1480 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-014-1694-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-014-1694-1