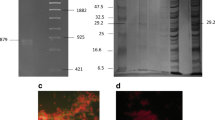
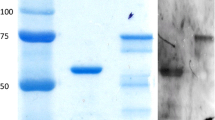
Abstract
Chlamydia pneumoniae causes diseases in humans, including community-acquired pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinusitis. It is also associated with atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, and hyperlipidemia. In this study, we investigated novel materials with which to develop a sensitive and specific method to identify early C. pneumoniae infection, to allow more effective clinical treatment and prevention. We prepared novel monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against a recombinant protein equivalent to the immunodominant region of chlamydial protease-like activity factor (CPAF) from C. pneumoniae. The mAbs specifically reacted with the endogenous CPAF antigen of the C. pneumoniae type strain in immunoblotting and indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) assays, but did not react with C. trachomatis type strains or genital secretions from patients with acute C. trachomatis infection. The mAb with the highest titer was used to develop a new IIF assay and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to detect the C. pneumoniae antigen in clinical specimens from child patients suspected of pneumonia. The sensitivity, specificity, and concordance rate of the mAb-based IIF and ELISA tests were compared with those of polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Our results show that these mAbs have excellent specificity and may be used to develop new screening tools for the diagnosis of early pediatric pneumonia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
She RC, Thurber A, Hymas WC, Stevenson J, Langer J, Litwin CM, Petti CA (2010) Limited utility of culture for Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydophila pneumoniae for diagnosis of respiratory tract infections. J Clin Microbiol 48:3380–3382
Thurman KA, Warner AK, Cowart KC, Benitez AJ, Winchell JM (2011) Detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydia pneumoniae, and Legionella spp. in clinical specimens using a single-tube multiplex real-time PCR assay. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 70:1–9
Chu DJ, Guo SG, Pan CF, Wang J, Du Y, Lu XF, Yu ZY (2012) An experimental model for induction of lung cancer in rats by Chlamydia pneumoniae. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 13:2819–2822
Luque A, Turu MM, Rovira N, Juan-Babot JO, Slevin M, Krupinski J (2012) Early atherosclerotic plaques show evidence of infection by Chlamydia pneumoniae. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 4:2423–2432
Hilden J, Lind I, Kolmos HJ, Als-Nielsen B, Damgaard M, Hansen JF, Hansen S, Helø OH, Hildebrandt P, Jensen GB, Kastrup J, Kjøller E, Nielsen H, Petersen L, Jespersen CM, Gluud C; CLARICOR Trial Group (2010) Chlamydia pneumoniae IgG and IgA antibody titers and prognosis in patients with coronary heart disease: results from the CLARICOR trial. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 66:385–392
Gaona-Flores V, García-Elorriaga G, Valerio-Minero M, González-Veyrand E, Navarrete-Castro R, Palacios-Jiménez N, Del Rey-Pineda G, González-Bonilla C, Monasta L (2008) Anti-Chlamydophila pneumoniae antibodies as associated factor for carotid atherosclerosis in patients with AIDS. Curr HIV Res 6:267–271
Dowell SF, Peeling RW, Boman J, Carlone GM, Fields BS, Guarner J, Hammerschlag MR, Jackson LA, Kuo CC, Maass M, Messmer TO, Talkington DF, Tondella ML, Zaki SR; C. pneumoniae Workshop Participants (2001) Standardizing Chlamydia pneumoniae assays: recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (USA) and the Laboratory Centre for Disease Control (Canada). Clin Infect Dis 33:492–503
Phoon MC, Yee GW, Koh WP, Chow VT (2011) Comparative seroepidemiologic analysis of Chlamydophila pneumoniae infection using microimmunofluorescence, enzyme immunoassay and neutralization test: implications for serodiagnosis. Indian J Microbiol 51:223–229
Pesonen E, Tiirola T, Andsberg E, Jauhiainen M, Paldanius M, Persson K, Saikku P, Sarna S, Ohlin H, Leinonen M (2009) Serum chlamydial lipopolysaccharide as a prognostic factor for a new cardiovascular event. Heart Lung 38:176–181
Sueur JM, Beaumont K, Cabioch T, Orfila J, Betsou F (2006) Diagnostic value of an ELISA using a recombinant 54-kDa species-specific protein from Chlamydia pneumoniae. Clin Microbiol Infect 12:470–477
Zhong G, Fan P, Ji H, Dong F, Huang Y (2001) Identification of a chlamydial protease-like activity factor responsible for the degradation of host transcription factors. J Exp Med 193:935–942
Sharma J, Bosnic AM, Piper JM, Zhong G (2004) Human antibody responses to a Chlamydia-secreted protease factor. Infect Immun 72:7164–7171
Dong F, Zhong Y, Arulanandam B, Zhong G (2005) Production of a proteolytically active protein, chlamydial protease/proteasome-like activity factor, by five different Chlamydia species. Infect Immun 73:1868–1872
Sharma J, Dong F, Pirbhai M, Zhong G (2005) Inhibition of proteolytic activity of a chlamydial proteasome/protease-like activity factor by antibodies from humans infected with Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun 73:4414–4419
Zhang RY, Shen WD (2012) Monoclonal antibody expression in mammalian cells. Methods Mol Biol 907:341–358
Balakrishna K, Radhika M, Murali HS, Batra HV, Bawa AS (2012) Specific identification of pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica by monoclonal antibodies generated against recombinant attachment invasion locus (rAil) protein. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:533–539
Zheng J, Wu Y, Liu J, Liu G, Chen C (2008) Early diagnosis using recombinant protein of immunodominant region gene of chlamydial protease-like activity factor from Chlamydophila pneumoniae. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 48:520–525
Fazekas de St Groth S, Scheidegger D (1980) Production of monoclonal antibodies: strategy and tactics. J Immunol Methods 35:1–21
Beatty JD, Beatty BG, Vlahos WG (1987) Measurement of monoclonal antibody affinity by non-competitive enzyme immunoassay. J Immunol Methods 100:173–179
Benitez AJ, Thurman KA, Diaz MH, Conklin L, Kendig NE, Winchell JM (2012) Comparison of real-time PCR and a microimmunofluorescence serological assay for detection of Chlamydophila pneumoniae infection in an outbreak investigation. J Clin Microbiol 50:151–153
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (81372318), the 12th Five-Year Infectious Disease Research Project (2012ZX10001-003), the Medicine Bootstrap Class Project of the Shanghai Science and Technology Commission (134119a5300), the Shanghai Natural Science Foundation (13ZR1435000), the Shanghai Education Board Scientific Research Innovation Project (13YZ049), the Shanghai Health Bureau Scientific Research Project (20124309), and the Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center Research Fund (201309).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, J., Ding, T., Chen, Z. et al. Preparation and evaluation of monoclonal antibodies against chlamydial protease-like activity factor to detect Chlamydia pneumoniae antigen in early pediatric pneumonia. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 34, 1319–1326 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-015-2343-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-015-2343-8