Abstract
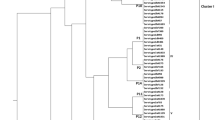
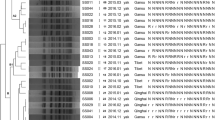
Shigellosis is a public health concern in China. We tested 216 Shigella isolates collected in Shanghai in 2007 for the production of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs). ESBL-producing isolates were characterized using polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based genotyping, conjugation, pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE), and DNA sequence analysis of regions adjacent to bla genes. Plasmids containing genes encoding ESBLs were analyzed using plasmid replicon typing. ESBLs were produced by 18.1 % (39/216) of Shigella isolates, and all 39 ESBL-producing strains harbored bla CTX-M genes. CTX-M-14 was the most frequent variant (69.2 %, 27/39), followed by CTX-M-15 (15.4 %, 6/39). All bla CTX-M genes were transferable by conjugation, and the insertion sequence ISEcp1 was detected upstream of all bla CTX-M genes. The CTX-M-producing Shigella isolates showed high clonal diversity. IncI1, IncFII, IncN, and IncB/O replicons were respectively detected in 23 (58.9 %), 9 (23.1 %), 1 (2.6 %), and 1 (2.6 %) of the 39 transconjugants carrying bla CTX-M. The bla CTX-M-14 genes were most frequently carried by IncI1 (n = 13, 48.1 %) or IncFII (n = 9, 33.3 %) plasmids, and the bla CTX-M-15 genes were closely associated with IncI1 (n = 5, 83.3 %). Our findings demonstrate the high prevalence of ESBL-producing Shigella in Shanghai, the importance of plasmids and ISEcp1 as carriers of bla CTX-M genes, and the close association between certain bla CTX-M genes with a specific plasmid.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bardhan P, Faruque AS, Naheed A, Sack DA (2010) Decrease in shigellosis-related deaths without Shigella spp.-specific interventions, Asia. Emerg Infect Dis 16(11):1718–1723
Salam MA, Bennish ML (1991) Antimicrobial therapy for shigellosis. Rev Infect Dis 13(Suppl 4):S332–S341
Hu GZ, Chen HY, Si HB, Deng LX, Wei ZY, Yuan L, Kuang XH (2008) Phenotypic and molecular characterization of TEM-116 extended-spectrum beta-lactamase produced by a Shigella flexneri clinical isolate from chickens. FEMS Microbiol Lett 279(2):162–166
Fortineau N, Naas T, Gaillot O, Nordmann P (2001) SHV-type extended-spectrum beta-lactamase in a Shigella flexneri clinical isolate. J Antimicrob Chemother 47(5):685–688
Paterson DL, Bonomo RA (2005)Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases: a clinical update. Clin Microbiol Rev 18(4):657–686
Yang Q, Wang H, Chen M, Ni Y, Yu Y, Hu B, Sun Z, Huang W, Hu Y, Ye H, Badal RE, Xu Y (2010) Surveillance of antimicrobial susceptibility of aerobic and facultative Gram-negative bacilli isolated from patients with intra-abdominal infections in China: the 2002–2009 Study for Monitoring Antimicrobial Resistance Trends (SMART). Int J Antimicrob Agents 36(6):507–512
Li B, Sun JY, Liu QZ, Han LZ, Huang XH, Ni YX (2011) High prevalence of CTX-M β-lactamases in faecal Escherichia coli strains from healthy humans in Fuzhou, China. Scand J Infect Dis 43(3):170–174
Clinical and LaboratoryStandards Institute (CLSI) (2013) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; Twenty-third informational supplement. CLSI document M100-S23
Eckert C, Gautier V, Arlet G (2006) DNA sequence analysis of the genetic environment of various bla CTX-M genes. J Antimicrob Chemother 57(1):14–23
Carattoli A, Bertini A, Villa L, Falbo V, Hopkins KL, Threlfall EJ (2005) Identification of plasmids by PCR-based replicon typing. J Microbiol Methods 63(3):219–228
Villa L, García-Fernández A, Fortini D, Carattoli A (2010) Replicon sequence typing of IncF plasmids carrying virulence and resistance determinants. J Antimicrob Chemother 65(12):2518–2529
Ribot EM, Fair MA, Gautom R, Cameron DN, Hunter SB, Swaminathan B, Barrett TJ (2006) Standardization of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis protocols for the subtyping of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella, and Shigella for PulseNet. Foodborne Pathog Dis 3(1):59–67
Tenover FC, Arbeit RD, Goering RV, Mickelsen PA, Murray BE, Persing DH, Swaminathan B (1995) Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: criteria for bacterial strain typing. J Clin Microbiol 33(9):2233–2239
Shen Y, Qian H, Gong J, Deng F, Dong C, Zhou L, Guo H (2013) high prevalence of antibiotic resistance and molecular characterization of integrons among Shigella isolates in Eastern China. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57(3):1549–1551
Yang H, Chen G, Zhu Y, Liu Y, Cheng J, Hu L, Ye Y, Li J (2013) Surveillance of antimicrobial susceptibility patterns among Shigella species isolated in China during the 7-year period of 2005–2011. Ann Lab Med 33(2):111–115
Taneja N, Mewara A, Kumar A, Verma G, Sharma M (2012) Cephalosporin-resistant Shigella flexneri over 9 years (2001–09) in India. J Antimicrob Chemother 67(6):1347–1353
Xiong Z, Li T, Xu Y, Li J (2007) Detection of CTX-M-14 extended-spectrum beta-lactamase in Shigella sonnei isolates from China. J Infect 55(5):e125–e128
Xia S, Xu B, Huang L, Zhao JY, Ran L, Zhang J, Chen H, Pulsrikarn C, Pornruangwong S, Aarestrup FM, Hendriksen RS (2011) Prevalence and characterization of human Shigella infections in Henan Province, China, in 2006. J Clin Microbiol 49(1):232–242
Zhang W, Luo Y, Li J, Lin L, Ma Y, Hu C, Jin S, Ran L, Cui S (2011) Wide dissemination of multidrug-resistant Shigella isolates in China. J Antimicrob Chemother 66(11):2527–2535
Cantón R, González-Alba JM, Galán JC (2012) CTX-M enzymes: origin and diffusion. Front Microbiol 3:110
Carattoli A (2011) Plasmids in Gram negatives: molecular typing of resistance plasmids. Int J Med Microbiol 301(8):654–658
Carattoli A (2009) Resistance plasmid families in Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53(6):2227–2238
Zheng H, Zeng Z, Chen S, Liu Y, Yao Q, Deng Y, Chen X, Lv L, Zhuo C, Chen Z, Liu JH (2012) Prevalence and characterisation of CTX-M β-lactamases amongst Escherichia coli isolates from healthy food animals in China. Int J Antimicrob Agents 39(4):305–310
Zhao WH, Hu ZQ (2013) Epidemiology and genetics of CTX-M extended-spectrum β-lactamases in Gram-negative bacteria. Crit Rev Microbiol 39(1):79–101
Folster JP, Pecic G, Krueger A, Rickert R, Burger K, Carattoli A, Whichard JM (2010) Identification and characterization of CTX-M-producing Shigella isolates in the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54(5):2269–2270
Valverde A, Cantón R, Garcillán-Barcia MP, Novais A, Galán JC, Alvarado A, de la Cruz F, Baquero F, Coque TM (2009) Spread of bla CTX-M-14 is driven mainly by IncK plasmids disseminated among Escherichia coli phylogroups A, B1, and D in Spain. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53(12):5204–5212
Marcadé G, Deschamps C, Boyd A, Gautier V, Picard B, Branger C, Denamur E, Arlet G (2009) Replicon typing of plasmids in Escherichia coli producing extended-spectrum beta-lactamases. J Antimicrob Chemother 63(1):67–71
Ho PL, Lo WU, Wong RC, Yeung MK, Chow KH, Que TL, Tong AH, Bao JY, Lok S, Wong SS (2011) Complete sequencing of the FII plasmid pHK01, encoding CTX-M-14, and molecular analysis of its variants among Escherichia coli from Hong Kong. J Antimicrob Chemother 66(4):752–756
Cao X, Cavaco LM, Lv Y, Li Y, Zheng B, Wang P, Hasman H, Liu Y, Aarestrup FM (2011) Molecular characterization and antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Escherichia coli isolates from patients with urinary tract infections in 20 Chinese hospitals. J Clin Microbiol 49(7):2496–2501
Funding
This work was supported by a Shanghai Science and Technology specific project (grant no. 11ZR1422200).
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Ethical approval
Not required.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jie Li and Bin Li contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Li, B., Ni, Y. et al. Molecular characterization of the extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Shigella spp. in Shanghai. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 34, 447–451 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-014-2244-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-014-2244-2