Abstract
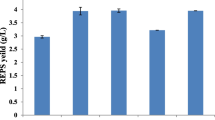
In the last two decades, many studies have been reported that a high concentration of NaCl suppresses exopolysaccharide (EPS) production in lactic acid bacteria. In the present study, however, the enhancement of EPS production by Lactobacillus confusus under high salinity stress in submerged fermentation was demonstrated using response surface methodology via a full factorial design. Under the optimized conditions of 3.33% NaCl, 20 g/L sucrose, and 35 h of incubation, the EPS yield was 10.87 g/ L with 178% higher than the maximum yield (6.12 g/L of EPS) produced from the modified MRS medium without NaCl. Biomass production was independent of EPS production. A high yield of biomass was obtained in the culture with 0.23% NaCl. This results indicate that high salinity stress by NaCl can enhance EPS production in submerged fermentation in uncontrolled pH cultivations by inducing the production of cell-associated dextransucrase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Vuyst L, Degeest B. Heteropolysaccharides from lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 23: 153–177 (1999)
De Vuyst L, De Vin F, Vaningelgem F, Degeest B. Recent developments in the biosynthesis and applications of heteropolysaccharides from lactic acid bacteria. Int. Dairy J. 11: 687–707 (2001)
Malik A, Radji M, Kralj S, Dijkhuizen L. Screening of lactic acid bacteria from Indonesia reveals glucansucrase and fructansucrase genes in two different Weissella confusa strains from soya. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 300: 131–138 (2009)
Svensson M, Waak E, Svensson U, Radstrom P. Metabolically improved exopolysaccharide production by Streptococcus thermophilus and its influence on the rheological properties of fermented milk. Appl. Environ. Microb. 71: 6398–6400 (2005)
Boels IC, van Kranenburg R, Kanning MW, Chong BF, de Vos WM, Kleerebezem M. Increased exopolysaccharide production in Lactococcus lactis due to increased levels of expression of the NIZO B40 eps gene cluster. Appl. Environ. Microb. 69: 5029–5031 (2003)
Jolly L, Vincent SJ, Duboc P, Neeser JR. Exploiting expolysaccharides from lactic acid bacteria. Anton. Leeuw. Int. J. G. 82: 367–374 (2002)
Looijesteijn PJ, Hugenholtz J. Uncoupling of growth and exopolysaccharide production by Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris NIZO B40 and optimization of its synthesis. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 88: 178–182 (1999)
Looijesteijn PJ, Trapet L, de Vries E, Abee T, Hugenholtz J. Physiological function of exopolysaccharides produced by Lactococcus lactis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 64: 71–80 (2001)
Torino MI, Hebert EM, Mozzi F, Font de Valdez G. Growth and exopolysaccharide production by Lactobacillus helveticus ATCC 15807 in an adenine-supplemented chemically defined medium. J. Appl. Microbiol. 99: 1123–1129 (2005)
Velasco S, Arskold E, Paese M, Grage H, Irastorza A, Radstrom P, van Niel EW. Environmental factors influencing growth of and exopolysaccharide formation by Pediococcus parvulus 2.6. Int. J. Food. Microbiol. 111: 252–258 (2006)
Maina NH, Tenkanen M, Maaheimo H, Juvonen R, Virkki L. NMR spectroscopic analysis of exopolysaccharides produced by Leuconostoc citreum and Weissella confusa. Carbohyd. Res. 343: 1446–1455 (2008)
Bounaix MS, Robert H, Gabriel V, Morel S, Remaud-Simeon M, Gabriel B, Fontagne-Faucher C. Characterization of dextranproducing Weissella strains isolated from sourdoughs and evidence of constitutive dextransucrase expression. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 311: 18–26 (2010)
Bounaix MS, Gabriel V, Morel S, Robert H, Rabier P, Remaud-Siméon M, Gabriel B, Fontagn-Faucher C. Biodiversity of exopolysaccharides produced from sucrose by sourdough lactic acid bacteria. J. Agr. Food Chem. 57: 10889–10897 (2009)
Ahmed ZR, Siddiqui K, Arman M, Ahmed N. Characterization of high molecular weight dextran produced by Weissella cibaria CMGDEX3. Carbohyd. Res. 90: 441–446 (2012)
Kuntiya A, Hanmoungjai P, Techapun C, Sasaki K, Seesuriyachan P. Influence of pH, sucrose concentration, and agitation speed on exopolysaccharide production by Lactobacillus confusus TISTR 1498 using coconut water as a raw material substitute. Maejo Int. J. Sci. Tech. 4: 318–330 (2010)
Seesuriyachan P, Techapun C, Shinkawa H, Sasaki K. Solid state fermentation for extracellular polysaccharide production by Lactobacillus confusus with coconut water and sugar cane juice as renewable wastes. Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. 74: 423–426 (2010)
Seesuriyachan P, Kuntiya A, Hanmoungjai P, Techapun C. Exopolysaccharide production by Lactobacillus confusus TISTR 1498 using coconut water as an alternative carbon source: The effect of peptone, yeast extract, and beef extract. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 33: 379–387 (2011)
Duenas M, Munduate A, Perea A, Irastorza A. Exopolysaccharide production by Pediococcus damnosus 2.6 in a semidefined medium under different growth conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 87: 113–120 (2003)
Seesuriyachan P, Kuntiya A, Hanmoungjai P, Techapun C, Chaiyaso T, Leksawasdi N. Optimization of exopolysaccharide overproduction by Lactobacillus confusus in solid state fermentation under high salinity stress. Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. 76: 912–917 (2012)
Miller GL. Use of dinitrosalicilic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 31: 426–428 (1959)
Kang YS, Park W. Protection against diesel oil toxicity by sodium chloride-induced exopolysaccharides in Acinetobacter sp. strain DR1. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 109: 118–123 (2010)
Shaileshkumar DS, Lele SS. Statistical optimization of media for dextran production by Leuconostoc sp., isolated from fermented idli batter. Food. Sci. Biotechnol. 19: 471–478 (2010)
Prasertsan P, Wichienchot S, Doelle H, Kennedy JF. Optimization for biopolymer production by Enterobacter cloacae WD7. Carbohyd. Res. 71: 468–475 (2008)
Dols M, Chraibi W, Remaud-Simeon M, Lindley ND, Monsan PF. Growth and energetics of Leuconostoc mesenteroides NRRL B-1299 during metabolism of various sugars and their consequences for dextransucrase production. Appl. Environ. Microb. 63: 2159–2165 (1997)
Cerning J. Exocellular polysaccharides produced by lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 87: 113–130 (1990)
van Geel-Schutten GH, Flesch F, Ten Brink B, Smith MR, Dijkhuizen L. Screening and characterization of Lactobacillus strains producing large amounts of exopolysaccharides. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 50: 697–703 (1998)
Cerning J. Exocellular polysaccharides produced by lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 7: 113–130 (1990)
Shukla S, Goyal A. 16S rRNA-based identification of a glucanhyperproducing Weissella confusa. Enzyme Res. doi:10.4061/2011/250842 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seesuriyachan, P. Statistical modeling and optimization for exopolysaccharide production by Lactobacillus confusus in submerged fermentation under high salinity stress. Food Sci Biotechnol 21, 1647–1654 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-012-0219-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-012-0219-6