Abstract
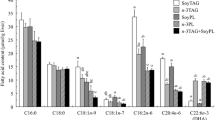
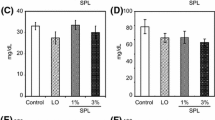
This study evaluated phospholipids (PLs) containing n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 PUFAs) for their specific inherent effects and effects due to a combination of the presence of glycerophosphate structure and n-3 PUFAs on cholesterol metabolism in rats. Rats were fed a diet of AIN-93G containing soybean oil (SO, 7%), SO (5.8%)+fish oil (1.2%), SO (5.2%)+soybean PLs (1.8%), SO (5.2%)+PLs containing n-3 PUFAs (1.8%), and SO (4.0%)+fish oil (1.2%)+soybean PLs (1.8%). Diets with PLs containing n-3 PUFAs, and soybean PLs in combination with fish oil, resulted in decreased serum and liver cholesterol levels through enhancement of fecal cholesterol excretion and suppression of liver sterol regulatory element binding protein-2 mRNA expression compared with the diet containing soybean oil alone. This study shows that soybean PLs with added triacylglycerol that included n-3 PUFAs have the same effects on cholesterol metabolism as PLs containing n-3 PUFAs, and that these could be of benefit to people.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lands WE, Hamazaki T, Yamazaki K, Okuyama H, Sakai K, Goto Y, Hubbard VS. Changing dietary patterns. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 51: 991–993 (1990)
Toshima H. Coronary artery disease trends in Japan. Jpn. Circ. J. 58: 166–172 (1994)
Martin MJ, Hulley SB, Browner WS, Kuller LH, Wentworth D. Serum cholesterol, blood pressure, and mortality: Implications from a cohort of 361,662 men. Lancet 2: 933–936 (1986)
Knopp RH, Paramsothy P, Atkinson B, Dowdy A. Comprehensive lipid management versus aggressive low-density lipoprotein lowering to reduce cardiovascular risk. Am. J. Cardiol. 101: 48B–57B (2008)
Childs MT, Bowlin JA, Ogilvie JT, Hazzard WR, Albers JJ. The contrasting effects of a dietary soya lecithin product and corn oil on lipoprotein lipids in normolipidemic and familial hypercholesterolemic subjects. Atherosclerosis 38: 217–228 (1981)
Rampone AJ, Machida CM. Mode of action of lecithin in suppressing cholesterol absorption. J. Lipid Res. 22: 744–752 (1981)
LeBlanc MJ, Brunet S, Bouchard G, Lamireau T, Yousef IM, Gavino V, Lévy E, Tuchweber B. Effects of dietary soybean lecithin on plasma lipid transport and hepatic cholesterol metabolism in rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 14: 40–48 (2003)
Chung SY, Moriyama T, Uezu E, Uezu K, Hirata R, Yohena N, Masuda Y, Kokubu T, Yamamoto S. Administration of phosphatidylcholine increases brain acetylcholine concentration and improves memory in mice with dementia. J. Nutr. 125: 1484–1489 (1995)
McDaniel MA, Maier SF, Einstein GO. “Brain-specific” nutrients: A memory cure? Nutrition 19: 957–975 (2003)
Ma X, Zhao J, Lieber CS. Polyenylphosphatidylcholine attenuates non-alcoholic hepatic fibrosis and accelerates its regression. J. Hepatol. 24: 604–613 (1996)
Hu FB, Bronner L, Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, Rexrode KM, Albert CM, Hunter D, Manson JE. Fish and ω-3 fatty acid intake and risk of coronary heart disease in women. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 287: 1815–1821 (2002)
Robinson DR, Xu LL, Tateno S, Guo M, Colvin RB. Suppression of autoimmune disease by dietary n-3 fatty acids. J. Lipid Res. 34: 1435–1444 (1993)
Larson MK, Ashmore JH, Harris KA, Vogelaar JL, Pottala JV, Sprehe M, Harris WS. Effects of ω-3 acid ethyl esters and aspirin, alone and in combination, on platelet function in healthy subjects. Thromb. Haemostasis 100: 634–641 (2008)
Shirouchi B, Nagao K, Inoue N, Ohkubo T, Hibino H, Yanagita T. Effect of dietary ω-3 phosphatidylcholine on obesity-related disorders in obese Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima fatty rats. J. Agr. Food Chem. 55: 7170–7176 (2007)
Ikemoto A, Ohishi M, Sato Y, Hata N, Misawa Y, Fujii Y, Okuyama H. Reversibility of n-3 fatty acid deficiency-induced alterations of learning behavior in the rat: Level of n-6 fatty acids as another critical factor. J. Lipid Res. 42: 1655–1663 (2001)
Hiratsuka S, Ishihara K, Kitagawa T, Wada S, Yokogoshi H. Effect of dietary docosahexaenoic acid connecting phospholipids on the lipid peroxidation of the brain in mice. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 54: 501–506 (2008)
Hosokawa M, Sato A, Ishigamori H, Kohno H, Tanaka T, Takahashi K. Synergistic effects of highly unsaturated fatty acid-containing phosphatidyl-ethanolamine on differentiation of human leukemia HL-60 cells by dibutyryl cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 92: 666–672 (2001)
Hosomi R, Fukunaga K, Arai H, Kanda S, Nishiyama T, Kanada T, Yoshida M. Effect of phospholipid n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on rat lipid metabolism. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Tech. 112: 537–544 (2010)
Reeves PG, Nielsen FH, Fahey GC Jr. AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: Final report of the American Institute of Nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J. Nutr. 123: 1939–1951 (1993)
Prevot AF, Mordret FX. Utilisation des colonnes capillaries de verre pour lánalyse des corps gras par chromotographie en phase gazeuse (Using glass capillaries columns for the analysis of fats by chromatography in gaseous phase). Rev. Fse. Corps Gras. 23: 409–423 (1976)
Erdahl WL, Stolyhwo A, Privett OS. Analysis of soybean lecithin by thin layer and analytical liquid chromatography. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 50: 513–515 (1973)
Horton JD, Bashmakov Y, Shimomura I, Shimano H. Regulation of sterol regulatory element binding proteins in livers of fasted and refed mice. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 5987–5992 (1998)
Bligh E, Dyer WJ. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 37: 911–917 (1959)
Bruusgaard A, Sorensen H, Gilhuus-Moe CC, Skålhegg BA. Bile acid determination with different preparations of 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Clin. Chim. Acta 77: 387–389 (1977)
Cohn JS, Kamili A, Wat E, Chung RW, Tandy S. Reduction in intestinal cholesterol absorption by various food components: Mechanisms and implications. Atherosclerosis Suppl. 11: 45–48 (2010)
Imaizumi K, Mawatari K, Murata M, Ikeda I, Sugano M. The contrasting effect of dietary phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine on serum lipoproteins and liver lipids in rats. J. Nutr. 113: 2403–2411 (1983)
Mastellone I, Polichetti E, Grès S, de la Maisonneuve C, Domingo N, Marin V, Lorec AM, Farnarier C, Portugal H, Kaplanski G, Chanussot F. Dietary soybean phosphatidylcholines lower lipidemia: Mechanisms at the levels of intestine, endothelial cell, and hepatobiliary axis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 11: 461–466 (2000)
Altmann SW, Davis HR Jr, Zhu LJ, Yao X, Hoos LM, Tetzloff G, Iyer SP, Maguire M, Golovko A, Zeng M, Wang L, Murgolo N, Graziano MP. Niemann-Pick C1 Like 1 protein is critical for intestinal cholesterol absorption. Science 303: 1201–1204 (2004)
Ordovas JM, Tai ES. The babel of the ABCs: Novel transporters involved in the regulation of sterol absorption and excretion. Nutr. Rev. 60: 30–33 (2002)
Mathur SN, Watt KR, Field FJ. Regulation of intestinal NPC1L1 expression by dietary fish oil and docosahexaenoic acid. J. Lipid Res. 48: 395–404 (2007)
Imaizumi K, Murata M, Sugano M. Effect of dietary polyunsaturated phospholipid on the chemical composition of serum lipoproteins in rat. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 28: 281–294 (1982)
Shirouchi B, Nagao K, Furuya K, Inoue N, Inafuku M, Nasu M, Otsubo K, Koga S, Matsumoto H, Yanagita T. Effect of dietary phosphatidylinositol on cholesterol metabolism in Zucker (fa/fa) rats. J. Oleo Sci. 58: 111–115 (2009)
Vlahcevic ZR, Pandak WM, Stravitz RT. Regulation of bile acid biosynthesis. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. 28: 1–25 (1999)
Frøyland L, Vaagenes H, Asiedu DK, Garras A, Lie O, Berge RK. Chronic administration of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid as ethyl esters reduced plasma cholesterol and changed the fatty acid composition in rat blood and organs. Lipids 31: 169–178 (1996)
Brown MS, Goldstein JL. The SREBP pathway: Regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell 89: 331–340 (1997)
Brown MS, Goldstein JL. A proteolytic pathway that controls the cholesterol content of membranes, cells, and blood. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 11041–11048 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosomi, R., Fukunaga, K., Fukao, M. et al. Combination effect of phospholipids and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on rat cholesterol metabolism. Food Sci Biotechnol 21, 1335–1342 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-012-0176-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-012-0176-0