Abstract
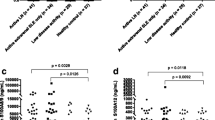
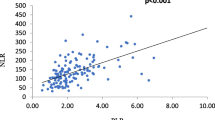
In patients with rheumatic diseases, reliable markers for determining disease activity are scarce. One potential parameter is the level of immunoglobulin free light chains (FLCs), which is known to be elevated in the blood of patients with certain rheumatic diseases. Few studies have quantified FLCs in urine, a convenient source of test sample, in patients with different rheumatic diseases. We carried out a retrospective analysis of patients with rheumatic disease attending the University hospital of Goettingen, Germany. Subjects were included if they had urine levels of both κ and λ FLCs available and did not have myeloma. Data regarding systemic inflammation and kidney function were recorded, and FLC levels were correlated with inflammatory markers. Of the 382 patients with rheumatic disease, 40.1 % had chronic polyarthritis, 21.2 % connective tissue disease, 18.6 % spondyloarthritis and 15.7 % vasculitis. Elevated levels of κ FLCs were found for 84 % of patients and elevated λ for 52.7 %. For the patients with rheumatoid arthritis, FLCs correlated with C-reactive protein (κ, r = 0.368, p < 0.001; λ, r = 0.398, p < 0.001) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (κ, r = 0.692, p < 0.001; λ, r = 0.612, p < 0.001). Patients being treated with rituximab displayed FLC levels similar to those of the reference group. There were clear elevations in both κ and λ FLCs in patients with rheumatic disease, but not in κ/λ ratio. The correlation between FLCs and inflammatory markers in patients with rheumatoid arthritis demonstrates their potential for predicting disease activity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal R (2013) Urinary free light chains: a potential biomarker in lupus nephritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 52:2106–2107
Aggarwal R, Sequeira W, Kokebie R, Mikolaitis RA, Fogg L, Finnegan A, Plaas A, Block JA, Jolly M (2011) Serum free light chains as biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 63:891–898
Bradwell AR (2005) Serum free light chain measurements move to center stage. Clin Chem 51:805–807
Brebner JA, Stockley RA (2013) Polyclonal free light chains: a biomarker of inflammatory disease or treatment target? F1000 Med Rep 5:4
Brouwer J, Otting-van de Ruit M, Busking-van der Lely H (1985) Estimation of free light chains of immunoglobulins by enzyme immunoassay. Clin Chim Acta 150:267–274
Carubbi F, Alunno A, Cipriani P, Bartoloni E, Ciccia F, Triolo G, Gerli R, Giacomelli R (2014) Rituximab in primary Sjogren’s syndrome: a ten-year journey. Lupus 23:1337–1349
Chiche L, Cournac JM, Mancini J, Bardin N, Thomas G, Jean R, Schleinitz N, Kaplanski G, Durand JM, Boucraut J, Harle JR (2011) Normalization of serum-free light chains in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus upon rituximab treatment and correlation with biological disease activity. Clin Rheumatol 30:685–689
Draborg AH, Lydolph MC, Westergaard M, Olesen Larsen S, Nielsen CT, Duus K, Jacobsen S, Houen G (2015) Elevated concentrations of serum immunoglobulin free light chains in systemic lupus erythematosus patients in relation to disease activity, inflammatory status, B cell activity and Epstein-Barr Virus antibodies. PLoS One 10:e0138753
Gottenberg JE, Aucouturier F, Goetz J, Sordet C, Jahn I, Busson M, Cayuela JM, Sibilia J, Mariette X (2007) Serum immunoglobulin free light chain assessment in rheumatoid arthritis and primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 66:23–27
Gottenberg JE, Miceli-Richard C, Ducot B, Goupille P, Combe B, Mariette X (2009) Markers of B-lymphocyte activation are elevated in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis and correlated with disease activity in the ESPOIR cohort. Arthritis Res Ther 11:R114
Hanaoka M, Gono T, Kawaguchi Y, Uchida K, Koseki Y, Katsumata Y, Kaneko H, Takagi K, Ichida H, Nitta K, Yamanaka H (2013) Urinary free light chain is a potential biomarker for ISN/RPS class III/IV lupus nephritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 52:2149–2157
Hopper JE, Golbus J, Meyer C, Ferrer GA (2000) Urine free light chains in SLE: clonal markers of B-cell activity and potential link to in vivo secreted Ig. J Clin Immunol 20:123–137
Hutchison CA, Harding S, Hewins P, Mead GP, Townsend J, Bradwell AR, Cockwell P (2008) Quantitative assessment of serum and urinary polyclonal free light chains in patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3:1684–1690
Hutchison CA, Landgren O (2011) Polyclonal immunoglobulin free light chains as a potential biomarker of immune stimulation and inflammation. Clin Chem 57:1387–1389
Jolly M, Francis S, Aggarwal R, Mikolaitis RA, Niewold TB, Chubinskaya S, Block JA, Scanzello C, Sequeira W (2014) Serum free light chains, interferon-alpha, and interleukins in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 23:881–888
Jones RB (2014) Rituximab in the treatment of anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitis. Nephron Clin Pract 128:243–249
Kormelink TG, Tekstra J, Thurlings RM, Boumans MH, Vos K, Tak PP, Bijlsma JW, Lafeber FP, Redegeld FA, van Roon JA (2010) Decrease in immunoglobulin free light chains in patients with rheumatoid arthritis upon rituximab (anti-CD20) treatment correlates with decrease in disease activity. Ann Rheum Dis 69:2137–2144
Lopez-Olivo MA, Amezaga Urruela M, McGahan L, Pollono EN, Suarez-Almazor ME (2015) Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 1:Cd007356
Nakano T, Nagata A, Takahashi H (2004) Ratio of urinary free immunoglobulin light chain kappa to lambda in the diagnosis of Bence Jones proteinuria. Clin Chem Lab Med 42:429–434
Segal R, Yaron M, Tartakovsky B (1990) Methotrexate: mechanism of action in rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 20:190–200
Sieper J, Braun J, Rudwaleit M, Boonen A, Zink A (2002) Ankylosing spondylitis: an overview. Ann Rheum Dis 61(Suppl 3):iii8–ii18
Stokes MB, Valeri AM, Herlitz L, Khan AM, Siegel DS, Markowitz GS, D’Agati VD (2015) Light chain proximal tubulopathy: clinical and pathologic characteristics in the modern treatment era. J Am Soc Nephrol
van Gestel AM, Prevoo ML, van ‘t Hof MA, van Rijswijk MH, van de Putte LB, van Riel PL (1996) Development and validation of the European League Against Rheumatism response criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Comparison with the preliminary American College of Rheumatology and the World Health Organization/International League Against Rheumatism Criteria. Arthritis Rheum 39:34–40
Waldmann TA, Strober W, Mogielnicki RP (1972) The renal handling of low molecular weight proteins. II. Disorders of serum protein catabolism in patients with tubular proteinuria, the nephrotic syndrome, or uremia. J Clin Invest 51:2162–2174
Zhang R, Li M, Chouhan KK, Simon EE, Hamm LL, Batuman V (2013) Urine free light chains as a novel biomarker of acute kidney allograft injury. Clin Transpl 27:953–960
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study received ethical approval from the ethical commission of the university Goettingen (11/2/14AN) and was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Disclosures
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bramlage, C.P., Froelich, B., Wallbach, M. et al. The significance and predictive value of free light chains in the urine of patients with chronic inflammatory rheumatic disease. Clin Rheumatol 35, 2939–2946 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3437-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3437-0