Abstract
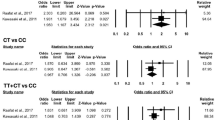
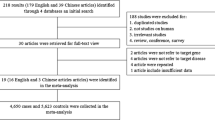
The aim of this study was to explore whether the interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) gene rs2070197 polymorphism was associated with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in multiple ethic populations. A meta-analysis was conducted on the C allele of the IRF5 rs2070197 polymorphism. A total of 7 published case–control studies with 12 comparisons involving 8171 SLE patients and 8904 controls were available for this meta-analysis. This meta-analysis demonstrated the IRF5 rs2070197 polymorphism conferred susceptibility to SLE in all subjects (odds ratio (OR) = 2.128, 95 % confidence interval (CI): 1.856–2.441, P < 0.001) without inter-study heterogeneity. The IRF5 rs2070197 polymorphism was identified as risk factors for SLE in Caucasian populations (OR 1.82, 95 % CI 1.70–1.96), but it had no effects (monomorphic) in Asians. Large-scale multicenter epidemiological studies in selected populations with other risk factors were urgently required.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae SC, Fraser P, Liang MH (1998) The epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus in populations of African ancestry: a critical review of the “prevalence gradient hypothesis”. Arthritis Rheum 41(12):2091–2099
Wakeland EK et al (2001) Delineating the genetic basis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunity 15(3):397–408
Nath SK, Kilpatrick J, Harley JB (2004) Genetics of human systemic lupus erythematosus: the emerging picture. Curr Opin Immunol 16(6):794–800
Deng Y, Tsao BP (2010) Genetic susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in the genomic era. Nat Rev Rheumatol 6(12):683–692
Banchereau J, Pascual V (2006) Type I interferon in systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases. Immunity 25(3):383–392
Niewold TB et al (2010) Interferon alpha in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010:948364
Blanco P et al (2001) Induction of dendritic cell differentiation by IFN-alpha in systemic lupus erythematosus. Science 294(5546):1540–1543
Kariuki SN et al (2009) Cutting edge: autoimmune disease risk variant of STAT4 confers increased sensitivity to IFN-alpha in lupus patients in vivo. J Immunol 182(1):34–38
Graham RR et al (2006) A common haplotype of interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) regulates splicing and expression and is associated with increased risk of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 38(5):550–555
Sigurdsson S et al (2008) Comprehensive evaluation of the genetic variants of interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) reveals a novel 5 bp length polymorphism as strong risk factor for systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum Mol Genet 17(6):872–881
Kavanagh D et al (2008) New roles for the major human 3′-5′ exonuclease TREX1 in human disease. Cell Cycle 7(12):1718–1725
Sigurdsson S et al (2008) A risk haplotype of STAT4 for systemic lupus erythematosus is over-expressed, correlates with anti-dsDNA and shows additive effects with two risk alleles of IRF5. Hum Mol Genet 17(18):2868–2876
Abelson AK et al (2009) STAT4 associates with systemic lupus erythematosus through two independent effects that correlate with gene expression and act additively with IRF5 to increase risk. Ann Rheum Dis 68(11):1746–1753
Takaoka A et al (2005) Integral role of IRF-5 in the gene induction programme activated by Toll-like receptors. Nature 434(7030):243–249
Couzinet A et al (2008) A cell-type-specific requirement for IFN regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) in Fas-induced apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(7):2556–2561
Lien C et al (2010) Critical role of IRF-5 in regulation of B-cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(10):4664–4668
Savitsky DA et al (2010) Contribution of IRF5 in B cells to the development of murine SLE-like disease through its transcriptional control of the IgG2a locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(22):10154–10159
Barnes BJ, Moore PA, Pitha PM (2001) Virus-specific activation of a novel interferon regulatory factor, IRF-5, results in the induction of distinct interferon alpha genes. J Biol Chem 276(26):23382–23390
Schoenemeyer A et al (2005) The interferon regulatory factor, IRF5, is a central mediator of toll-like receptor 7 signaling. J Biol Chem 280(17):17005–17012
Taniguchi T et al (2001) IRF family of transcription factors as regulators of host defense. Annu Rev Immunol 19:623–655
Hughes T et al (2012) Evidence for gene-gene epistatic interactions among susceptibility loci for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 64(2):485–492
Reddy MV et al (2007) Genetic association of IRF5 with SLE in Mexicans: higher frequency of the risk haplotype and its homozygozity than Europeans. Hum Genet 121(6):721–727
Fourati H et al. (2102) Genetic factors contributing to systemic lupus erythematosus in Tunisian patients.J Clin Cell Immunol 03(04)
Lofgren SE et al (2010) Promoter insertion/deletion in the IRF5 gene is highly associated with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in distinct populations, but exerts a modest effect on gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Rheumatol 37(3):574–578
Kozyrev SV et al (2007) Structural insertion/deletion variation in IRF5 is associated with a risk haplotype and defines the precise IRF5 isoforms expressed in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 56(4):1234–1241
Kelly JA et al (2008) Interferon regulatory factor-5 is genetically associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in African Americans. Genes Immun 9(3):187–194
Graham RR et al (2007) Three functional variants of IFN regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) define risk and protective haplotypes for human lupus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(16):6758–6763
Siu HO et al (2008) Association of a haplotype of IRF5 gene with systemic lupus erythematosus in Chinese. J Rheumatol 35(2):360–362
Shin HD et al (2008) Different genetic effects of interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) polymorphisms on systemic lupus erythematosus in a Korean population. J Rheumatol 35(11):2148–2151
Cunninghame GD et al (2007) Association of IRF5 in UK SLE families identifies a variant involved in polyadenylation. Hum Mol Genet 16(6):579–591
Hughes T et al (2012) Analysis of autosomal genes reveals gene-sex interactions and higher total genetic risk in men with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 71(5):694–699
Hom G et al (2008) Association of systemic lupus erythematosus with C8orf13-BLK and ITGAM-ITGAX. N Engl J Med 358(9):900–909
Hu W, Ren H (2011) A meta-analysis of the association of IRF5 polymorphism with systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Immunogenet 38(5):411–417
Acknowledgments
We thank all our colleagues working in the Department of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Key Laboratory of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology.
Disclosures
None.
Funding
This work was supported by funding from the Research Special Fund for Public Welfare Industry of Health (201202004), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China Grants (81172857,81373188), and the Chinese National High Technology Research and Development Program, Ministry of Science and Technology Grants (2011AA02A113).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yuan Li, Si Chen and Ping Li contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Chen, S., Li, P. et al. Association of the IRF5 rs2070197 polymorphism with systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis. Clin Rheumatol 34, 1495–1501 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-3036-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-3036-5