Abstract
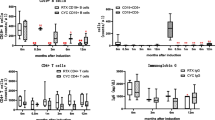
Rituximab (RTX) was reported effective in ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV). We aimed to evaluate clinical efficacy of RTX in AAV along with its impact on immunological parameters. Eighteen RTX-treated AAV patients (M/F 11/7; median age 37.5; 15× PR3-ANCA, 3× MPO-ANCA; 16× relapsing/refractory, 2× first-line therapy) were enrolled. Clinical response, ANCA, total serum IgG levels and cellular immunity parameters were examined. The patients were followed up (FU) for a median of 26 months (range 3–82, 15 for ≥6 months). All patients achieved B cell depletion (lasting 3–24 months). No significant increase was noted in T cell or NK cell subpopulations. At 6 months, partial remission was achieved in 5/15 patients (33 %) and complete in 8 (53 %). The median prednisone dose (30..10 mg/d) and ANCA levels (17.2..2.7 IU/mL) decreased (p < 0.01). RTX retreatment was used in nine (8× pre-emptive, 1× relapse). Six patients relapsed (none of the pre-emptively treated). Three patients died of infection. IgG levels at 3 months decreased compared to baseline (9.0 vs 5.7 g/L, p < 0.01). Higher percentage of HLA-DR+CD3+ cells and lower percentage of CD4+CD45RA+ naive T cells persisted during FU. IFN-γ production increased at 6 months compared to baseline (27.3 vs 41.5 %). No significant change was noted in the intracellular IL-10 and IL-12 production. RTX helped to lower the glucocorticosteroids dose and withdraw cytotoxic drugs in most AAV patients. Hypogammaglobulinaemia was common but well tolerated. Peripheral circulating T cells remained activated despite B cell depletion.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keogh KA, Ytterberg SR, Fervenza FC, Carlson KA, Schroeder DR, Specks U (2006) Rituximab for refractory Wegener’s granulomatosis: report of a prospective, open-label pilot trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 173:180–187
Stasi R, Stipa E, Del Poeta G, Amadori S, Newland AC, Provan D (2006) Long-term observation of patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis treated with rituximab. Rheumatology 45:1432–1436
Jones RB, Ferraro AJ, Chaudhry AN, Brogan P, Salama AD, Smith KG, Savage CO, Jayne DR (2009) A multicenter survey of rituximab therapy for refractory antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum 60:2156–2168
Jones RB, Tervaert JW, Hauser T, Luqmani R, Morgan MD, Peh CA, Savage CO, Segelmark M, Tesar V, van Paassen P, Walsh D, Walsh M, Westman K, Jayne DR, European Vasculitis Study Group et al (2010) Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis. N Engl J Med 363:211–220
Stone JH, Merkel PA, Spiera R, Seo P, Langford CA, Hoffman GS et al (2010) RAVE-ITN research group. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide for ANCA-associated vasculitis. N Engl J Med 363:221–232
Smith RM, Jones RB, Guerry MJ, Laurino S, Catapano F, Chaudhry A et al (2012) Rituximab for remission maintenance in relapsing ANCA-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. doi:10.1002/art.34583
Cartin-Ceba R, Golbin JM, Keogh KA, Peikert T, Sánchez-Menéndez M, Ytterberg SR et al (2012) Rituximab for remission induction and maintenance in refractory granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s): a single-center ten-year experience. Arthritis Rheum. doi:10.1002/art.34584
Liossis SN, Sfikakis PP (2008) Rituximab-induced B cell depletion in autoimmune diseases: potential effects on T cells. Clin Immunol 127:280–285
Venhoff N, Effelsberg NM, Salzer U, Warnatz K, Peter HH, Lebrecht D, Schlesier M, Voll RE, Thiel J (2012) Impact of rituximab on immunoglobulin concentrations and B cell numbers after cyclophosphamide treatment in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitides. PLoS One 7:e37626
Roccatello D, Sciascia S, Rossi D, Alpa M, Naretto C, Russo A, Menegatti E, Baldovino S (2011) Long-term effects of rituximab added to cyclophosphamide in refractory patients with vasculitis. Am J Nephrol 34:175–180
Wilk E, Witte T, Marquardt N, Horvath T, Kalippke K, Scholz K, Wilke N, Schmidt RE, Jacobs R (2009) Depletion of functionally active CD20+ T cells by rituximab treatment. Arthritis Rheum 60:3563–3571
van de Veerdonk FL, Lauwerys B, Marijnissen RJ, Timmermans K, Di Padova F, Koenders MI, Gutierrez-Roelens I, Durez P, Netea MG, van der Meer JW, van den Berg WB, Joosten LA (2011) The anti-CD20 antibody rituximab reduces the Th17 cell response. Arthritis Rheum 63:1507–1516
Xiang Y, Peng J, Tai N, Hu C, Zhou Z, Wong FS, Wen L (2012) The dual effects of B cell depletion on antigen-specific T cells in BDC2.5NOD mice. J Immunol 188:4747–4758
Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA, Basu N, Cid MC, Ferrario F et al (2012) 2012 revised international chapel hill consensus conference nomenclature of vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. doi:10.1002/art.37715
Flossmann O, Bacon P, de Groot K, Jayne D, Rasmussen N, Seo P, Westman K, Luqmani R (2007) Development of comprehensive disease assessment in systemic vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis 66:283–292
Hruskova Z, Rihova Z, Mareckova H, Jancova E, Rysava R, Zavada J, Merta M, Löster T, Tesar V (2009) Intracellular cytokine production in ANCA-associated vasculitis: low levels of interleukin-10 in remission are associated with a higher relapse rate in the long-term follow-up. Arch Med Res 40:276–284
Alberici F, Jayne DR (2013) Impact of rituximab trials on the treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 0:1–12. doi:10.1093/ndt/gft318
Marinaki S, Kälsch AI, Grimminger P, Breedijk A, Birck R, Schmitt WH et al (2006) Persistent T-cell activation and clinical correlations in patients with ANCA-associated systemic vasculitis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:1825–1832
Sfikakis PP, Boletis JN, Lionaki S, Vigklis V, Fragiadaki KG, Iniotaki A, Moutsopoulos HM (2005) Remission of proliferative lupus nephritis following B cell depletion therapy is preceded by down-regulation of the T cell costimulatory molecule CD40 ligand: an open-label trial. Arthritis Rheum 52:501–513. doi:10.1002/art.20858
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by PRVOUK-P25/LF1/2, GAUK-442611, 2013.
Conflict of interest
Authors Chocova Z, Hruskova Z, Mareckova H, Svobodova B, Duskova D, Bednarova V, Jancova E and Rysava R declare that they have no conflict of interest. Prof. Tesar received honoraria from Roche.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chocova, Z., Hruskova, Z., Mareckova, H. et al. Rituximab use in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis: clinical efficacy and impact on immunological parameters. Clin Rheumatol 34, 107–115 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2816-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2816-7