Abstract
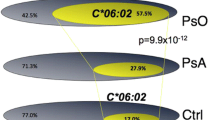
In psoriatic arthritis (PsA), genetic factors play a substantial role in disease susceptibility as well as in its expression. This study aims to determine the distribution of class I and class II HLA antigens in PsA patients and secondly to analyze the influence of genetic factors in the clinical expression of the disease. Consecutive PsA patients (CASPAR criteria) with less than 1 year of disease duration were included. Sociodemographic and clinical data were recorded. Blood samples were obtained, DNA was extracted by polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and class I (A, B, and C) and class II (DR) HLA antigens were determined by oligotyping. A control group of 100 nonrelated healthy controls from the general population served as control. p values were corrected (pc) according to the number of alleles tested. A total of 73 patients were included, 37 were females (50.7 %) with a median disease duration of 72 months (interquartile range (IQR) 24–149). Thirty-three patients (45.2 %) had a family history of psoriasis. When analyzing all the class I and class II HLA antigens, a significantly higher frequency of B38 (odds ratio (OR) 2.95, p = 0.03) and Cw6 (OR 2.78, p = 0.009) was found in PsA patients compared to the control group. On the contrary, the HLA-A11 (OR 0.14, p = 0.04) and B7 (OR 0.31, p = 0.03) were significantly more frequent among healthy controls. Furthermore, B18 was significantly more frequent in patients with early arthritis onset (less than 40 years): seven patients (22.6 %) with early onset compared to two patients (4.8 %) with late onset (p = 0.03). No association between HLA-B27 and spondylitis or HLA-DR4 with polyarticular involvement was observed. The HLA-B38 and Cw6 alleles are associated with a greater PsA susceptibility in Argentine population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nograles KE, Brasington RD, Bowcock AM (2009) New insights into the pathogenesis and genetics of psoriatic arthritis. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 5(2):83–91
Moll JMH, Wright V (1973) Psoriatic arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 3(1):55–78
Fournie B, Crognier L, Arnaud C, Zabraniecki L, Lascaux-Lefebvre V, Marc V et al (1999) Proposed classification criteria of psoriatic arthritis: a preliminary study in 260 patients. Rev Rhum Engl Ed 66(10):446–456
Taylor WJ, Marchesoni A, Arreghini M, Sokoll K, Helliwell PS (2004) A comparison of the performance characteristics of classification criteria for the diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 34(3):575–584
Taylor W, Gladman D, Helliwell P, Marchesoni A, Mease P, Mielants H, the CASPAS Study Group (2006) Classification criteria for psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 54(8):2665–2673
Duffin KC, Chandran V, Gladman DD, Krueger GG, Elder JT, Rahman P (2008) Genetics of psoriasis arthritis: update and future direction (GRAPPA 2007). J Rheumatol 35(7):1449–1453
Barton AC (2002) Genetic epidemiology Psoriatic arthritis. Rev Arthritis Res 4(4):247–251
Burden AD, Javed S, Bailey M, Hodgins M, Connor M, Tilman D (1998) Genetics of psoriasis: paternal inheritance and a locus on chromosome 6p. J Investig Dermatol 110(6):958–960
Bowcock A, Cookson WO (2004) The genetics of psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and atopic dermatitis. Hum Mol Genet 13:R43–R55
Ho P, Barton A, Worthington J, Plant D, Griffiths C, Young H et al (2008) Investigating the role of the HLA-Cw*06 and HLA-DRB1 genes in susceptibility to psoriatic arthritis: comparison with psoriasis and undifferentiated inflammatory arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 67(5):677–682
Espinoza LR, Vasey FB, Oh JH, Wilkinson R, Osterland CK (1978) Association between HLA-BW38 and peripheral psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 21(1):72–75
Murray C, Mann DL, Gerber LN, Barth W, Perlmann S, Decker JL et al (1980) Histocompatibility alloantigens in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Evidence for the influence of multiple genes in the major histocompatibility complex. J Clin Invest 66(4):670–675
Gladman DD, Anhorn KA, Schachter R, Mervat H (1986) HLA antigens in psoriatic arthritis. J Rheumatol 13(3):586–592
Armstrong RD, Panayi GS, Welsh KL (1983) Histocompatibility antigens in psoriasis, psoriasis arthropathy, and ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 42(2):142–146
Gerber LH, Murray CL, Perlman SG, Barth WF, Decker JL, Nigra TA et al (1982) Human lymphocyte antigens characterizing psoriatic arthritis and its subtypes. J Rheumatol 9(5):703–707
Szczerkowska DA, Rebala K, Szczerkowska Z, Nedoszylko B (2005) HLA-C locus alleles distribution in patients from northern Poland with psoriatic arthritis-preliminary report. Int J Immunogenet 32(6):389–391
Queiro R, Gonzalez S, López-Larrea C, Alperi M, Sarasqueta C, Riestra JL et al (2006) HLA-C locus alleles may modulate the clinical expression of psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 8(6):1–5
Gladman DD, Farewell VT (2003) HLA Studies in psoriatic arthritis: current situation and future needs. J Rheumatol 30(1):4–6
Gladman DD, Farewell VT (1995) The role of HLA antigens as indicators of disease progression in psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 38(6):845–850
González S, Brautbar C, Martínez-Borra J, López-Vásquez A, Segal R, Blanco-Gelaz MA et al (2001) Polymorphism in MICA rather than HLA-B/C genes is associated with psoriatic arthritis in the Jewish population. Hum Immunol 62(6):632–638
Ettehadi P, Greaves MW, Wallach D, Aderka D, Camp RD (1994) Elevated tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) biological activity in psoriatic skin lesions. Clin Exp Immunol 96(1):146–151
Williams F, Meenagh A, Sleator C, Cook D, Fernández-Vina M, Bowcock AM et al (2005) Activating killer cell immunoglobin-like receptor gene KIR2DS1 is associated with psoriatic arthritis. Hum Immunol 66(7):836–841
Helliwell PS, Taylor WJ (2005) Classification and diagnostic criteria for psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 64(Suppl 2):ii3–ii8
Gladman DD, Shuckett R, Russell ML, Thorne JC, Schachter RK (1987) Psoriatic arthritis: an analysis of 220 patients. Q J Med 62(238):127–141
Bennett PH, Burch TA Amsterdam. Excerpta Media Foundation International Congress Series 148, 1966:456–457
Moll JM, Wright V (1973) Familial occurrence of PsA. Ann Rheum Dis 32(3):181–201
Rahman P, Elder JT (2005) Genetic epidemiology of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 64(Suppl II):ii37–ii39
González S, Martínez-Borra J, Torre-Alonso JC, González-Roces S, Sánchez del Río J, Rodríguez Pérez A et al (1999) The MICA-A9 triplet repeat polymorphism in the transmembrane region confers additional susceptibility to the development of psoriatic arthritis and its independent of the association of Cw*0602 in psoriasis. Arthritis Rheum 42(5):1010–1016
Karason A, Gudjonsson JE, Upmanyu R, Antonsdottir AA, Hauksson VB, Runasdottir EH et al (2003) A susceptibility gene for psoriatic arthritis maps to chromosome 16q: evidence for imprinting. Am J Hum Genet 72(1):125–131
Rahman P, Sun S, Peddle L, Snelgrove T, Melay W, Greenwood C et al (2006) Association between the interleukin-1 family gene cluster and psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 54(7):2321–2325
Nelson WN, Martin MP, Gladman D, Wade J, Trowsdale J, Carrington M (2004) Cutting Edge: Heterozygote advantage in autoimmune disease: hierarchy of protection/susceptibility conferred by HLA and killer Ig-like receptor combinations in psoriatic arthritis. J Immunol 173:4273–4276
Gladman DD, Farewell VT (2003) HLA studies in psoriatic arthritis: current situation and future needs. J Rheumatol 30(1):4–6
Gladman DD, Farewell VT, Kopciuk KA, Cook RJ (1998) HLA markers and progression in psoriatic arthritis. J Rheumatol 25(4):730–733
Ho PY, Barton A, Worthington J, Thomson W, Silman AJ, Bruce IN (2007) HLA-Cw6 and HLA-DRB1*07 together are associated with less severe joint disease in psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 66(6):807–811
Ho P, Barton A, Worthington J (2004) Genetic epidemiology of psoriatic arthritis. Mod Rheumatol 14(2):91–100
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schneeberger, E.E., Citera, G., Rodríguez Gil, G. et al. Clinical and immunogenetic characterization in psoriatic arthritis patients. Clin Rheumatol 34, 1413–1418 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2739-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2739-3