Abstract
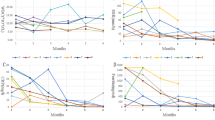
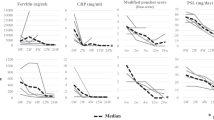
Adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD) is a systemic inflammatory disease of unknown etiology. Recently, it has been reported that quite a few cases of refractory AOSD were successfully treated with tocilizumab (TCZ) and corticosteroids were withdrawn in some of these patients. We report two AOSD patients who were treated successfully with TCZ monotherapy; thus, avoiding corticosteroid treatment. Because both of the patients refused to take corticosteroids, we planned to treat them with 8 mg/kg of TCZ monotherapy at weeks 0, 2, 6 and subsequently every 4 weeks. The efficacy of TCZ was assessed by patients’ clinical symptoms such as fever, arthralgia, skin eruptions, and laboratory markers such as serum levels of CRP, ferritin, and IL-6. We also reviewed 14 previous case reports including 30 cases who had been treated with TCZ for AOSD. Our patients responded rapidly and have been maintained in clinical remission without corticosteroid treatment. In the literature review, concomitant corticosteroid treatment described in 13 cases was successfully tapered in 7 and discontinued in 6 cases. TCZ monotherapy can be a candidate for the first-line therapy for some AOSD patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bywaters EGL (1971) Still’s disease in the adult. Ann Rheum Dis 30:121–133
Yamaguchi M, Ohta A, Tsunematsu T, Kasukawa R, Mizushima Y et al (1992) Preliminary criteria for classification of adult-onset Still’s disease. J Rheumatol 19:424–430
Bagnari V, Colina M, Ciancio G, Govoni M, Trotta F (2010) Adult-onset Still’s disease. Rheumatol Int 30:855–862
Hoshino T, Ohta A, Yang D, Kawamoto M, Kikuchi M et al (1998) Elevated serum interleukin 6, interferon-gamma, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels in patients with adult Still’s disease. J Rheumatol 25:396–398
Efthimiou P, Kontzias A, Ward CM, Ogden NS (2007) Adult-onset Still’s disease: can recent advances in our understanding of its pathogenesis lead to targeted therapy? Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 3:328–335
Fautrel B, Sibilia J, Mariette X, Combe B, Club Rhumatismes et Inflammation (2005) Tumour necrosis factor alpha blocking agents in refractory adult Still’s disease: an observational study of 20 cases. Ann Rheum Dis 64:262–266
Kraetsch HG, Antoni C, Kalden JR, Manger B (2001) Successful treatment of a small cohort of patients with adult-onset of Still's disease with infliximab: first experiences. Ann Rheum Dis 60(suppl 3):iii55–iii57
Fitzgerald AA, Leclercq SA, Yan A, Homik JE, Dinarello CA (2005) Rapid responses to anakinra in patients with refractory adult-onset Still’s disease. Arthritis Rheum 52:1794–1803
Naumann L, Feist E, Natusch A, Langen S, Klause A et al (2010) IL-1-receptor antagonist anakinra provides long-lasting efficacy in the treatment of refractory adult-onset Still’s disease. Ann Rheum Dis 69:466–467
Iwamoto M, Nara H, Hirata D, Minota S, Nishimoto N et al (2002) Humanized monoclonal anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody for treatment of intractable adult-onset Still’s disease. Arthritis Rheum 46:3388–3389
De Bandt M, Saint-Marcoux B (2009) Tocilizumab for multirefractory adult-onset Still’s disease. Ann Rheum Dis 68:153–154
Nakahara H, Mima T, Yoshio-Hoshino N, Matsushita M, Hashimoto J et al (2009) A case report of a patient with refractory adult-onset Still’s disease who was successfully treated with tocilizumab over 6 years. Mod Rheumatol 19:69–72
Matsumoto K, Nagashima T, Takatori S, Kawahara Y, Yagi M et al (2009) Glucocorticoid and cyclosporine refractory adult-onset Still’s disease successfully treated with tocilizumab. Clin Rheumatol 28:485–487
Perdan-Pirkmajer K, Praprotnik S, Tomšič M (2010) A case of refractory adult-onset Still’s disease successfully controlled with tocilizumab and a review of the literature. Clin Rheumatol 29:1465–1467
Naniwa T, Ito R, Watanabe M, Hayami Y, Maeda S, et al. (2010) Case report: successful use of short-term add-on tocilizumab for multirefractory systemic flare of adult-onset Still’s disease. Clin Rheumatol. doi:10.1007/s10067-010-1562-8
Sumida K, Ubara Y, Hoshino J, Suwabe T, Hiramatsu R et al (2010) Etanercept-refractory adult-onset Still’s disease with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura successfully treated with tocilizumab. Clin Rheumatol 29:1191–1194
Yoshimura M, Makiyama J, Koga T, Miyashita T, Izumi Y et al (2010) Successful treatment with tocilizumab in a patient with refractory adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD). Clin Exp Rheumatol 28:141–142
Rech J, Ronneberger M, Englbrecht M, Finzel S, Katzenbeisser J et al (2011) Successful treatment of adult-onset Still’s disease refractory to TNF and IL-1 blockade by IL-6 receptor blockade. Ann Rheum Dis 70:390–392
Kishida D, Okuda Y, Onishi M, Takebayashi M, Matoba K et al (2011) Successful tocilizumab treatment in a patient with adult-onset Still’s disease complicated by chronic active hepatitis B and amyloid A amyloidosis. Mod Rheumatol 21:215–218
Thonhofer R, Hiller M, Just H, Trummer M, Siegel C, et al. (2011) Treatment of refractory adult-onset still’s disease with tocilizumab: report of two cases and review of the literature. Rheumatol Int 31:1653–1656
Kobayashi M, Takahashi Y, Yamashita H, Kaneko H, Mimori A (2011) Benefit and a possible risk of tocilizumab therapy for adult-onset Still’s disease accompanied by macrophage-activation syndrome. Mod Rheumatol 21:92–96
Puéchal X, DeBandt M, Berthelot JM, Breban M, Dubost JJ, Club Rhumatismes Et Inflammation et al (2011) Tocilizumab in refractory adult Still’s disease. Arthritis Care Res 63:155–159
Sabnis GR, Gokhale YA, Kulkarni UP (2011) Tocilizumab in refractory adult-onset Still’s disease with aseptic meningitis—efficacy of interleukin-6 blockade and review of the literature. Semin Arthritis Rheum 40:365–368
Aydintug AO, D’Cruz D, Cervera R, Khamashta MA, Hughes GR (1992) Low dose methotrexate treatment in adult Still’s disease. J Rheumatol 19:431–435
Fujii T, Akizuki M, Kameda H, Matsumura M, Hirakata M et al (1997) Methotrexate treatment in patients with adult-onset Still’s disease—retrospective study of 13 Japanese cases. Ann Rheum Dis 56:144–148
Kalliolias GD, Georgiou PE, Antonopoulos IA, Andonopoulos AP, Liossis SN (2007) Anakinra treatment in patients with adult-onset Still’s disease is fast, effective, safe and steroid sparing: experience from an uncontrolled trial. Ann Rheum Dis 66:842–843
Chen DY, Lan JL, Lin FJ, Hsieh TY et al (2004) Proinflammatory cytokine profiles in sera and pathological tissues of patients with active untreated adult-onset Still’s disease. J Rheumatol 31:2189–2198
Kawaguchi Y, Terajima H, Harigai M, Hara M, Kamatani N (2001) Interleukin-18 as a novel diagnostic marker and indicator of disease severity in adult-onset Still’s disease. Arthritis Rheum 44:1716–1717
Kawashima M, Yamamura M, Taniai M, Yamauchi H, Tanimoto T et al (2001) Levels of interleukin-18 and its binding inhibitors in the blood circulation of patients with adult-onset Still’s disease. Arthritis Rheum 44:550–560
Yokota S, Imagawa T, Takei S, Murata T, Tomiita M et al (2011) Guidance on using tocilizumab for juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Mod Rheumatol 21:563–571
Kaneko K, Kaburaki M, Muraoka S, Tanaka N, Yamamoto T et al (2010) Exacerbation of adult-onset Still’s disease, possibly related to elevation of serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha after etanercept administration. Int J Rheum Dis 13:e67–e69
Conflicts of interest
H.K. has received honoraria from Mitsubishi-Tanabe Pharma, Pfizer, Abbott, Eisai Pharma, and Bristol-Myers KK. T.T. has received research support and consulting or lecture fees from Chugai Pharma. K.A. received research grants from Tanabe-Mitsubishi, Astellas, and Chugai pharmaceutical companies. The other authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakai, R., Nagasawa, H., Nishi, E. et al. Successful treatment of adult-onset Still’s disease with tocilizumab monotherapy: two case reports and literature review. Clin Rheumatol 31, 569–574 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-011-1917-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-011-1917-9