Abstract
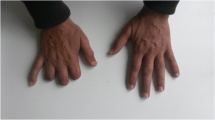
We report two rheumatoid arthritis patients developing sarcoidosis possibly induced by etanercept. Both women, aged 46 and 53, had erosive, rheumatoid-factor-positive rheumatoid arthritis (RA) for 7 and 6 years, respectively. The eldest had received infliximab for over a year with good response, which was stopped because of a perfusion reaction. She developed a cough and dyspnea after 6 months of etanercept treatment. The other developed erythema nodosum and a plaque lesion on the right arm after 1 year of etanercept. Imaging showed, in both cases, mediastinal adenopathies. Biopsies were compatible with sarcoidosis. Etanercept withdrawal led to a complete remission. Recently, there have been reports of noninfectious granulomatous syndromes in patients receiving etanercept for a variety of diseases. In our cases, the temporal association with etanercept therapy and the complete remission after suspension of etanercept suggest a triggering role of this agent. Possible mechanisms of action and supporting evidence are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haraoui B (2005) Differentiating the efficacy of the tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. Semin Arthritis Rheum 34(Suppl 1):7–11
Wallis RS, Ehlers S (2005) Tumor necrosis factor and granuloma biology: explaining the differential infection risk of etanercept and infliximab. Semin Arthritis Rheum 34(5 Suppl1):34–38
Furst DE, Wallis R, Broder M et al (2006) Tumor necrosis factor antagonists: different kinetics and/or mechanisms of action may explain differences in the risk for developing granulomatous infection. Semin Arthritis Rheum 36(3):159–167
Gonzalez-Lopez MA, Blanco R, Gonzalez-Vela MC et al (2006) Development of sarcoidosis during etanercept therapy. Arthritis Rheum 55(5):817–820
Nunes H, Soler P, Valeyre D (2005) Pulmonary sarcoidosis. Allergy 60(5):565–582
Ziegenhagen MW, Muller-Quernheim J (2003) The cytokine network in sarcoidosis and its clinical relevance. J Intern Med 253:18–30
Keystone EC (2004) The utility of tumour necrosis factor blockade in orphan diseases. Ann Rheum Dis 63(Suppl 2):ii79–ii83
Doty JD, Mazur JE, Judson MA (2005) Treatment of sarcoidosis with infliximab. Chest 127:1064–1071
Utz JP, Limper AH, Kalra S et al (2003) Etanercept for the treatment of stage II and III progressive pulmonary sarcoidosis. Chest 124:177–185
Kucera RF (1989) A possible association of rheumatoid arthritis and sarcoidosis. Chest 95(3):604–606
Dinarello CA (2005) Differences between anti-tumor necrosis factor-α monoclonal antibodies and soluble TNF receptors in host defense impairment. J Rheumatol Suppl 74:40–47
Acknowledgement
R. Westhovens is a consultant for Schering–Plough and BMS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verschueren, K., Van Essche, E., Verschueren, P. et al. Development of sarcoidosis in etanercept-treated rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Rheumatol 26, 1969–1971 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-007-0594-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-007-0594-1