Abstract
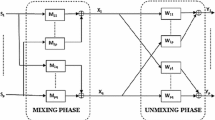
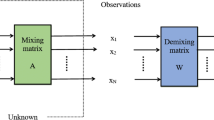
This paper describes a new multi-resolution approach for the blind separation of convolutive image mixtures in transform domain. The proposed method uses an Adaptive Vectorial case of Quincunx Lifting Scheme (AVQLS), based on wavelet decomposition, and a geometric unmixing algorithm. It proceeds in three steps: first, the mixed images are decomposed by AVQLS. Then, the unmixing algorithm is applied to the more relevant component to get a transformed estimate of the original images. An inverse transform is, thereafter, applied to obtain an estimate of the original images. Experiments carried out on medical images showed that the proposed method yields better separation results than many widely used blind source separation algorithms.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cichocki LA, Amari SI (2003) Adaptive blind signal and image processing. Wiley, New York
Comon P (1994) Independent component analysis. A new concept. Signal Process 36:287–314
Do MN, Vetterli M (2002) Wavelet-based texture retrieval using generalized Gaussian density and Kullback–Leibler distance. IEEE Trans Image Process 11(2):146–158
Virtanen I (1982) Entropy correlation coefficient, a measure of statistical dependence for categorized data. Paper presented at the 15th European meeting of statisticians, Palermo, Italy
Elsabrouty M, Bouchard M, Aboulnasr T (2003) A new on-line negentropy-based algorithm for blind source separation. IEEE Int Symp Micro-Nano Mechatron Hum Sci 2:756–759
Amari SI, Cichocki A, Yang HH (1996) A new learning algorithm for blind source separation. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, vol 8, pp 757–763, MIT Press
Bell A (1995) An information-maximization approach to blind separation and blind deconvolution. Neural Comput 7:1129–1159
Hyvarinen A, Karhunen J, Oja E (2001) Independent component analysis. Wiley, New York
Cardoso JF (1997) Infomax and maximum likelifood for blind source separation. IEEE Lect Signal Process 4(4):112–114
Hyvarinen A, Oja E (1997) A fast fixed-point algorithm for independent component analysis. Neural Comput 9(7):1483–1492
Cardoso J-F, Souloumiac A (1993) Blind beamforming for non Gaussian signals. IEEE Proc-F 140(6):362–370
Chan T-H, Ma W-K, Chi C-Y, Wang Y (2008) A convex analysis framework for blind separation of non-negative sources. IEEE Trans Signal Process 56:5120–5134
Naanaa W, Nuzillard J-M (2012) A geometric approach to blind separation of nonnegative and dependent source signals. Signal Process 92(11):2775–2784
Chan T-H, Chi C-Y, Huang Y-M, Ma W-K (2009) A convex analysis based minimum-volume enclosing simplex algorithm for hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans Signal Process 57(11):4418–4432
Torkkola K (1996) Blind separation of convolved sources based on information maximization. In: Proceedings of IEEE workshop on neural networks and dignal processing (NNSP6), Kyoto, Japan, pp 423–432
Lee TW, Girolami M, Lambert R (1997) Blind separation of delayed and convolved sources. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, vol 9, pp 758–764, MIT Press
Smaragdis P (1998) Blind separation of convolved mixtures in frequency domain. Neurocomputing 22:21–34
Dapena A, Bugallo MF, Castedo L (2001) Separation of convolutive mixtures of temporally-white signals: a novel frequency-domain approach, vol 794. In: Ciaramella A, Tagliaferri R, Funaro M (eds) Proceedings of 3rd international workshop on independent component analysis and blind source separation, San Diego, California, pp 179–184
Mitianoudis N, Davies M (2001) New fixed-point ICA algorithm for convolved mixtures. In: Proceedings of 3rd international workshop on independent component analysis and blind source separation, San Diego, California, pp 633–638
Ciaramella A, Tagliaferri R (2006) Separation of convolved mixtures in frequency domain ICA. Int Math Forum 1(16):769–795
Sawada H, Kameoka H, Araki S, Ueda N (2012) Efficient algorithms for Multichannel extensions of Itakura-Saito nonnegative matrix factorization, 978-1-4673-0046-9/12 ICASSP
Schobben DWE, Sommen PCW (2002) A frequency domain blind signal separation method based on de-correlation. IEEE Trans Signal Process 50:1855–1865
Araki S, Mukai R, Makino S, Nishikawa T, Saruwatari H (2003) The fundamental limitation of frequency domain blind source separation for convolutive mixtures of speech. IEEE Trans Speech Audio Process 11(2):109–116
Zibulevsky M, Pearlmutter BA, Bofill P, Kisilev P (2001) Blind source separation by sparse decomposition. In: Roberts SJ, Everson RM (eds) Independent component analysis: principles and practice. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Sweldens W (1995) The lifting scheme: a new philosophy in biorthogonal wavelet constructions. SPIE Wavelet Appl Signal Image Process III 2569:68–79
Hattay J, Benazza-Benyahia A, Pesquet J-C (2004) Adaptive lifting schemes using variablesize block segmentation. In: Proceedings of the ACIVS conference, Brussels, Belgium, August 31–September 3, 2004
Hattay J, Belaid S, Naanaa W (2013) Geometric blind source separation using adaptive lifting scheme. 17th IEEE SPA conference SPA’2013 Spetember 2013 Poland
Macias-Garza F, Bovik AC, Diller KR, Aggarwal SJ, Aggarwal JK (1988) The missing cone problem and low-pass distortion in optical serial sectioning microscopy. In: Proceedings of ICASSP, vol 2, pp 890–893
Schechner YY, Shamir J, Kiryati N (2000) Polarization and statistical analysis of scenes containing a semi-reflector. J Opt Soc Am A 17:276–284
Liew SC, Li M, Kwoh LK, Chen P, Lim H (1998) Cloud-free multi-scene mosaics of spot images. In: IEEE International Proceedings on Geoscience and Remote Sensing Sumposium, 1998, vol 2, pp 1083–1085, Seattle, WA, USA
Calderbank AR, Daubechies I, Sweldens W, Yeo B-L (1998) Wavelet transforms that map integers to integers. Appl Comput Harmon Anal 5:332–369
Hattay J, Benazza-Benyahia A, Pesquet J-C (2005) Adaptive lifting for multicomponent image coding through quadtree partitioning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, signal processing, Philadelphia, USA
Benazza-Benyahia A, Pesquet J-C, Hattay J, Masmoudi H (2007) Blockbased adaptive vector lifting schemes for multichannel image coding. Eurasip Int J Image Video Process (IJIVP) 2007(1):10 (article ID 13421)
Gao LX, Yang ZJ, Cai LG, Wang HQ, Chen P (2011) Roller bearing fault diagnosis based on nonlinear redundant lifting wavelet packet analysis. Sensors 11:260–277
Rao CR, Nayak TK (1985) Cross entropy, dissimilarity measures, and characterizations of quadratic entropy. IEEE Trans Inf Theory IT-31(5):589–593
Antonini M, Barlaud M, Mathieu P, Daubechies I (1992) Image coding using wavelet transform. IEEE Trans Image Process 1(2):205–220
Sharifi K, Garcia L (1995) Estimation of shape parameter for generalized Gaussian distribution in subband decompositions of video. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 5(1):52–56
Gish H, Pierce JN (1968) Asymptotically efficient quantizing. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 14:676–683
Bjrck Å (1996) Numerical methods for least squares problems. SIAM, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden. ISBN 978-0-89871-360-2
Yule GU (1927) On a method of investigating periodicities in disturbed series, with special reference to Wolfer’s sunspot numbers. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser A 226:267–298
Walker G (1931) On periodicity in series of related terms. Proc R Soc Lond Ser A 131:518–532
Donoho D, Johnstone I (1994) Ideal spatial adaptation via wavelet shrinkage. Biometrica 81:425–455
Donoho D, Johnstone IM (1994) Ideal spatial adaptation by wavelet shrinkage. Biometrika 81(3):425–455
Donoho D (1995) Denoising by soft thresholding. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 41(3):613–627
Motzkin T, Raiffa H, Thompson G, Thrall RJ (1953) The double description method. Annals of math studies, vol 8. Princeton University Press, pp 51–73
Cochran D, Gish H, Sinno D (1995) A geometric approach to multiple-channel signal detection. IEEE Trans Signal Process 43(9):2049–2057
Cichocki A, Amari S, Siwek K, Tanaka T, Phan AH et al ICALAB toolboxes. http://www.bsp.brain.riken.jp/ICALAB
Hattay J, Belaid S, Lebrun D, Naanaa W (2014) Digital in-line particle holography: twin-image suppression using sparse blind source separation. Signal Image Video Process 9:1767–1774. doi:10.1007/s11760-014-0646-3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hattay, J., Belaid, S., Naanaa, W. et al. Adaptive vectorial lifting concept for convolutive blind source separation. Pattern Anal Applic 20, 507–518 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-015-0517-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-015-0517-8