Abstract
Purpose
Incisional hernia is a common long-term complication after laparotomy. This study investigated whether prophylactic mesh reinforcement of laparotomy reduced the rate of incisional hernia, with emphasis on trial design and quality.
Methods
A systematic review of published literature was performed for studies comparing incisional hernia presence following conventional closure or prophylactic mesh reinforcement. Studies were assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool, the Jadad score and the Newcastle Ottawa Scale (NOS). The primary endpoint was incisional hernia, assessed by meta-analysis.
Results
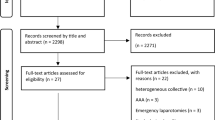
Seven studies [four randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and three prospective trials] included 588 patients; 262 received mesh reinforcement. All studies included elective patients at high risk of incisional hernia. Six incorporated a polypropylene mesh and one a biologic mesh. Four studies were judged high quality by NOS and two of four RCTs were at low risk of bias, although overall outcome assessment from all studies was either poor or mediocre. Mesh significantly reduced the rate of incisional hernia [odds ratio (OR) 0.15, p < 0.001]; the same effect was seen in RCTs only (OR 0.17, p < 0.001). A borderline increase of seroma seen with a fixed effect model (OR 1.82, p = 0.050) was not seen with a random effect model (OR 1.86, p = 0.210, I 2 = 45 %).
Conclusion
Mesh reinforcement of laparotomy significantly reduced the rate of incisional hernia in high-risk patients. However, poor assessment of secondary outcomes limits applicability; routine placement in all patients cannot yet be recommended. More evidence regarding the rates of adverse events, cost-benefits and quality of life are needed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
van’t Riet M, Steyerberg EW, Nellensteyn J, Bonjer HJ, Jeekel J (2002) Meta-analysis of techniques for closure of midline abdominal incisions. Br J Surg 89:1350–1356
Diener MK, Voss S, Jensen K, Buchler MW, Seiler CM (2010) Elective midline laparotomy closure: the INLINE systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg 251:843–856
Gecim IE, Kocak S, Ersoz S, Bumin C, Aribal D (1996) Recurrence after incisional hernia repair: results and risk factors. Surg Today 26:607–609
Llaguna OH, Avgerinos DV, Nagda P, Elfant D, Leitman IM, Goodman E (2011) Does prophylactic biologic mesh placement protect against the development of incisional hernia in high-risk patients? World J Surg 35:1651–1655
Capella RF, Iannace VA, Capella JF (2007) Reducing the incidence of incisional hernias following open gastric bypass surgery. Obes Surg 17:438–444
Wells G SB, O’Connell D et al (2000) The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of non-randomised studies in meta-analyses. In: 3rd Symposium on systematic reviews: beyond the basics. Improving quality and impact, Oxford, UK
Bhangu A, Nepogodiev D, Gupta A, Torrance A, Singh P (2012) Systematic review and meta-analysis of outcomes following emergency surgery for Clostridium difficile colitis. Br J Surg 99:1501–1513
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gotzsche PC, Juni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, Savovic J, Schulz KF, Weeks L, Sterne JA (2011) The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 343:d5928
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, McQuay HJ (1996) Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials 17:1–12
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. Brit Med J 339:b2700
Lau J, Ioannidis JP, Schmid CH (1997) Quantitative synthesis in systematic reviews. Ann Intern Med 127:820–826
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7:177–188
Bevis PM, Windhaber RA, Lear PA, Poskitt KR, Earnshaw JJ, Mitchell DC (2010) Randomized clinical trial of mesh versus sutured wound closure after open abdominal aortic aneurysm surgery. Br J Surg 97:1497–1502
El-Khadrawy OH, Moussa G, Mansour O, Hashish MS (2009) Prophylactic prosthetic reinforcement of midline abdominal incisions in high-risk patients. Hernia 13:267–274
Gutierrez de la Pena C, Medina Achirica C, Dominguez-Adame E, Medina Diez J (2003) Primary closure of laparotomies with high risk of incisional hernia using prosthetic material: analysis of usefulness. Hernia 7:134–136
Strzelczyk JM, Szymanski D, Nowicki ME, Wilczynski W, Gaszynski T, Czupryniak L (2006) Randomized clinical trial of postoperative hernia prophylaxis in open bariatric surgery. Br J Surg 93:1347–1350
Curro G, Centorrino T, Low V, Sarra G, Navarra G (2012) Long-term outcome with the prophylactic use of polypropylene mesh in morbidly obese patients undergoing biliopancreatic diversion. Obes Surg 22:279–282
Strzelczyk J, Czupryniak L, Loba J, Wasiak J (2002) The use of polypropylene mesh in midline incision closure following gastric by-pass surgery reduces the risk of postoperative hernia. Langenbecks Arch Surg 387:294–297
Hartling L, Ospina M, Liang Y, Dryden DM, Hooton N, Krebs Seida J, Klassen TP (2009) Risk of bias versus quality assessment of randomised controlled trials: cross sectional study. Brit Med J 339:b4012
Deeks JJ, Dinnes J, D’Amico R, Sowden AJ, Sakarovitch C, Song F, Petticrew M, Altman DG (2003) Evaluating non-randomised intervention studies. Health Technol Assess 7:iii-x, 1–173
Anthony T, Murray BW, Sum-Ping JT, Lenkovsky F, Vornik VD, Parker BJ, McFarlin JE, Hartless K, Huerta S (2011) Evaluating an evidence-based bundle for preventing surgical site infection: a randomized trial. Arch Surg 146:263–269
Eklund A, Montgomery A, Bergkvist L, Rudberg C (2010) Chronic pain 5 years after randomized comparison of laparoscopic and Lichtenstein inguinal hernia repair. Br J Surg 97:600–608
Herbert GS, Tausch TJ, Carter PL (2009) Prophylactic mesh to prevent incisional hernia: a note of caution. Am J Surg 197:595–598 (discussion 598)
Pollock AV, Evans M (1989) Early prediction of late incisional hernias. Brit J Surg 76:953–954
Bhangu A, Fletcher L, Kingdon S, Smith E, Nepogodiev D, Janjua U (2012) A clinical and radiological assessment of incisional hernias following closure of temporary stomas. Surgeon 10:321–325
Lopez-Cano M, Armengol M, Quiles MT, Biel A, Velasco J, Huguet P, Mestre A, Delgado LM, Gil FX, Arbos MA (2012) Preventive midline laparotomy closure with a new bioabsorbable mesh: an experimental study. J Surg Res 181:160–169
Itani KM, Rosen M, Vargo D, Awad SS, Denoto G 3rd, Butler CE (2012) Prospective study of single-stage repair of contaminated hernias using a biologic porcine tissue matrix: the RICH Study. Surgery 152:498–505
Bhangu A, Nepogodiev D, Futaba K (2012) Systematic review and meta-analysis of the incidence of incisional hernia at the site of stoma closure. World J Surg 36:973–983
Conflicts of interest
All authors declares no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
On behalf of the West Midlands Research Collaborative.
Committee of the West Midlands Research Collaborative—David Bartlett, Kaori Futaba, Pritesh Mistry, Caroline Richardson, Elizabeth Hepburn, Abhilasha Patel, Paul Marriott, Andrew Torrance, Dion Morton.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhangu, A., Fitzgerald, J.E., Singh, P. et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of prophylactic mesh placement for prevention of incisional hernia following midline laparotomy. Hernia 17, 445–455 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-013-1119-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-013-1119-2