ABSTRACT
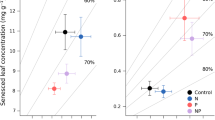
The native tree Metrosideros polymorpha dominates Hawaiian forests across a very wide range of soil fertility, including both sites where forest production is limited by nitrogen (N) and others where it is limited by phosphorus (P). Five long-term fertilization experiments have further broadened the range of nutrient availabilities experienced by Metrosideros. Adding P to P-limited sites increased foliar P concentrations threefold and litter P concentrations up to 10-fold; lignin concentrations decreased, and the decomposability of leaf litter increased from 32%–35% to 36%–46% mass loss in the first year. Adding N to N-limited sites increased leaf and litter N concentrations by only 15%–20%, with little or no effect on the decomposability of tissue.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 22 January 1998; accepted 4 May 1998.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vitousek, P. Foliar and Litter Nutrients, Nutrient Resorption, and Decomposition in Hawaiian Me t rosideros polymorpha . Ecosystems 1, 401–407 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100219900033
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100219900033