Abstract
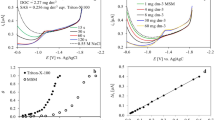
This study demonstrates the potential of the electrochemical methods for the characterization of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in the drainage water of hydroameliorated agricultural areas. A study of drainage water could lead to a better understanding of the distribution and fate of terrestrial DOM in the freshwater systems. We have applied the voltammetric techniques which were developed by our group for the characterization of organic matter in the natural waters in general. Studied samples were collected in the experimental amelioration fields in the Sava river valley (45° 33′ 52″ N/16° 31′ 33″ E, 100 m above sea level), in the hydroameliorated agricultural areas in Croatia. The rough characterization of the type, nature and reactivity of DOM was done through the study of surface activity (SA) of dissolved organic carbon (DOC), copper complexing capacity (CuCC) and apperent stability constants, and measurements of organic and inorganic reduced sulfur species (RSS) fractions. The results confirm that the electrochemical approach gives a valuable and comprehensive insight into physicochemical characteristics of DOM in the drainage water and could be successfully applied to temporal studies in different terrestrial ecosystem.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karlsson J, Byström P, Ask J, Ask P, Persson L, Jansson M (2009) Light limitation of nutrient-poor lake ecosystems. Nature 460:506–509
Ćosović B, Kozarac Z, Frka S, Vojvodić V (2010) Electrochemical adsorption study of natural organic matter in marine and freshwater systems. A plea for use of mercury for scientific purposes. Electroanalysis 22:1994–2000
Ćosović B, Vojvodić V (1998) Voltammetric analysis of surface active substances in natural seawater. Electroanalysis 10:429–434
Kozarac Z, Ćosović B, Vojvodić V (1986) Effects of natural and synthetic surface active substances on the electrochemical reduction of cadmium in natural waters. Water Res 20:295–300
Batina N, Ciglenečki I, Ćosović B (1992) Determinatin of elemental sulfur, sulfide, and their mixtures in electrolyte solutions by ac voltammetry. Anal Chim Acta 267:157–164
Ciglenečki I, Ćosović B (1996) Electrochemical study of sulfur species in seawater and marine phytoplankton cultures. Mar Chem 52:87–97
Gašparović, B (1995) Characterisation of dissolved organic matter in the seawater using o-nitrophenol as a probe, PhD Thesis, University of Zagreb, Croatia
Krznarić D, Ciglenečki I, Ćosović B (2001) Voltammetric investigations of 2-dimethylarsinylethanol sulfide in NaCl and seawater. Anal Chim Acta 431:269–278
Orlović-Leko, P (2001) Physico-chemical interactions of surface active substances with lead in the aquatic systems, PhD thesis, University of Zagreb, Croatia
Orlović-Leko P, Kozarac Z, Ćosović B (2004) Surface active substances (SAS) and dissolved organic matter (DOC) in atmospheric precipitation of urban area of Croatia (Zagreb). Water Air Soil Pollut 158:295–310
Ciglenečki I, Krznarić D, Helz GR (2005) Voltammetry of copper sulfide particles and nanoparticles; investigation of the cluster hypothesis. Environ Sci Technol 39:7492–7498
Ćosović B, Orlović-Leko P, Kozarac Z (2007) Rain water dissolved organic carbon: characterization of surface active substances by electrochemical method. Electroanalysis 19:2077–2084
Plavšić M, Orlović-Leko P, Kozarac Z, Bura-Nakić E, Strmečki S, Ćosović B (2008) Complexation of copper ions in atmospheric precipitation in Croatia. Atmos Res 87(1):80–87
Bura-Nakić E, Helz GR, Ciglenečki I, Ćosović B (2009) Reduced sulfur species in a stratified seawater lake (Rogonica Lake, Croatia); seasonal variations and argument for organic carriers of reactive sulfur. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73:3738–3751
Orlović-Leko P, Kozarac Z, Ćosović B, Strmečki S, Plavšić M (2011) Characterization of atmospheric surfactants in the bulk precipitation by electrochemical tools. J Atmos Chem 66(11–26)
Orlović-Leko P, Vidović K, Plavšić M, Ciglenečki I, Šimunić I, Minkina, T Characterization of Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) in the Drainage Water of Hydroameliorated Agricultural Areas in Croatia. The Proceeding of the International Soil science Congress on Soil Science in International Year of Soils. Article book, Shein E (ed), 19–23 October, 2015. Sochi, Russia
Filella M (2009) Freshwaters: which NOM matters? Environ Chem Lett 7:21–35
Milne E (2008) Soil organic carbon. In: Cleveland CJ (ed) Encyclopedia of Earth. Environmental Information Coalition, National Council for Science and the Environment, Washington, DC
Strobel BW (2001) Influence of vegetation on low-molecular-weight carboxylic acids in soil solution—a review. Geoderma 99:169–198
Yavitt JB, Fahey TJ (1984) An experimental analysis of solution chemistry in a lodgepole pine forest floor. Oikos 43:222–234
Kalbitz K, Solinger S, Park JH, Michalzik B, Matzner E (2000) Controls on the dynamics of dissolved organic matter in soils: a review. Soil Sci 165:277–304
Kleber M, Johnson MG (2010) Chapter three—advances in understanding the molecular structure of soil organic matter: implications for interactions in the environment. Adv Agron 106:77–142
Kaiser K, Guggenberger G (2005) Dissolved organic sulphur in soil water under Pinus sylvestris L. and Fagus sylvatica L. Stands in northeastern Bavaria, Germany-variations with seasons and soil depth. Biogeochemistry 72:337–364
Wang Z, Zhang X, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Li B, Vogt R (2012) Dissolved organic sulfur in streams draining forested catchments in southern China. J Environ Sci (China) 24(4):704–710
Evans CD, Monteith DT, Cooper DM (2005) Long-term increases in surface water dissolved organic carbon: observations, possible causes and environmental impacts. Environ Pollut 137:55–71
Delpla I, Jung AV, Baures E, Clement M, Thomas O (2009) Impacts of climate change on surface water quality in relation to drinking water production. Environ Int 35(8):1225–1233
Dafner EV, Wangersky PJ (2002) A brief overview of modern directions in marine DOC studies part II—recent progress in marine DOC studies. J Environ Monit 4:55–69
Šimunić I, Mesić M, Sraka M, Likso T, Čoga L (2011) Influence of drainpipe spacing on nitrate leaching and maize yield. Cereal Res Commun 39(2):274–283
Ciglenečki I, Ćosović B (1997) Electrochemical determination of thiosulfate in seawater in the presence of elemental sulfur and sulfide. Electroanalysis 9:1–7
Milanović I, Krznarić D, Bura-Nakić E, Ciglenečki I (2014) Deposition and dissolution of metal sulfide layers at a Hg electrode surface in seawater electrolyte conditions. Environ Chem 11(2):167–172
Tipping E, Woof C (1990) Humic substances in acid organic soils: modeling their release to the soil solution in terms of humic charge. J Soil Sci 41:573–586
Tate KR, Theng, BKG (1980) Organic matter and its interactions with inorganic soil constituents In: Theng BKG (ed) Soils with Variable Charge, N.Z. Soc. Soil Sci., Lower Hutt, New Zealand 225–249
Orlović-Leko P, Plavšić M, Bura-Nakić E, Kozarac Z, Ćosović B (2009) Organic matter in the bulk precipitations in Zagreb and Šibenik, Croatia. Atmos Environ 43(4):805–811
McDonald S, Bishop AG, Prenzler PD, Robards K (2004) Analytical chemistry of freshwater humic substances. Anal Chim Acta 527(2):105–124
Michalzik B, Kalbitz K, Park JH, Solinger S, Matzner E (2001) Fluxes and concentrations of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen—a synthesis for temperate forests. Biogeochemistry 52(2):173–205
Šimunić I, Tomić F, Ostojić Z (2002) Concentration and leaching of atrazine into drainage water in Gleyic Podzoluvisol. Rostlinná Výroba 48(4):167–174
Guggenberger G, Kaiser K (2003) Dissolved organic matter in soil: challenging the paradigm of sorptive preservation. Geoderma 113:293–310
Yu CH, Newton SQ, Norman MA, Schäfer L, Miller DM (2003) Molecular dynamics simulations of adsorption of organic compounds at the clay mineral/aqueous solution Interface. Struct Chem 14(2):175–185
Ružić I (1982) Theoretical aspects of the direct titration of natural waters and its information yield for trace metal speciation. Anal Chim Acta 140:99–113
van den Berg CMG (1982) Determination of copper complexation with natural organic ligands in seawater by equilibration with manganese dioxide: I Theory. Mar Chem 11:307–322
Scoullos M, Plavšić M, Karavoltsos S (2004) Copper speciation in the Gulf of Elefsis, the role of macroalgae Ulva rigida. Mar Chem 86:51–63
Plavšić M, Lee C, Ćosović B (2006) Copper complexing properties of melanoidins and marine humic material. Sci Total Environ 366:310–319
Acknowledgments
This work is fully supported by the project “The Sulphur and Carbon Dynamics in the Sea and Fresh-Water Environment” (IP-11-2013-1205 SPHERE) and partly by the project AMBIOMERES (IP-11-2013-8607) from the Croatian Science Foundation. The authors thank Zdeslav Zovko for DOC measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orlović-Leko, P., Vidović, K., Plavšić, M. et al. Voltammetry as a tool for rough and rapid characterization of dissolved organic matter in the drainage water of hydroameliorated agricultural areas in Croatia. J Solid State Electrochem 20, 3097–3105 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-016-3245-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-016-3245-0