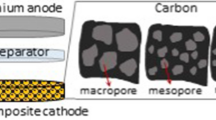
Abstract
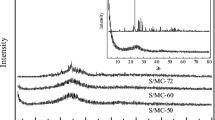
To get a high sulfur loaded porous carbon/sulfur cathode material with an excellent performance, we investigated four different sulfur loading treatments. The samples were analyzed by the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET), X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns, thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). We proved that it is more effective to introduce the sulfur into the pores of porous carbon at 300 °C than at 155 °C. Especially, the porous carbon/sulfur composite heated in a sealed reactor at 300 °C for 8 h presents a fine sulfur load with sulfur content of 78 wt.% and exhibits an excellent electrochemical performance. The discharge capacity is 760, 727, 744, 713, and 575 mAh g−1 of sulfur at a current density of 80, 160, 320, 800, and 1,600 mA g−1 based on the sulfur/carbon composite, respectively. What is more, there is almost no decay at the current density of 800 mA g−1 for 50 cycles and coulombic efficiency remains over 95 %.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aricò AS, Bruce PG, Scrosati B, Tarascon J, Schalkwijk W (2005) Nanostructured materials for advanced energy conversion and storage devices. Nat Mater 4:366–377
Guo YG, Hu JS, Wan LJ (2008) Nanostructured materials for electrochemical energy conversion and storage devices. Adv Mater 20:2878–2887
Yamin H, Penciner J, Gorenshtain A, Elam M, Peled E (1985) The electrochemical behavior of polysulfides in tetrahydrofuran. J Power Sources 14:129–134
Yang Y, McDowell MT, Jackson A, Cha JJ, Hong SS, Cui Y (2010) New nanostructured Li2S/silicon rechargeable battery with high specific energy. Nano Lett 10:1486–1491
Whittingham MS (2004) Lithium batteries and cathode materials. Chem Rev 10:4271–4302
Armand M, Tarascon JM (2008) Building better batteries. Nature 451:652–657
Tarascon JM, Armand M (2001) Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 414:359–367
Ji XL, Lee KT, Nazar LF (2009) A highly ordered nanostructured carbon–sulphur cathode for lithium–sulphur batteries. Nat Mater 8:500–506
Cheon SE, Ko KS, Cho JH, Kim SW, Chin EY, Kim HT (2003) Rechargeable lithium sulfur battery I. Structural change of sulfur cathode during discharge and charge. J Electrochem Soc 150:A796–A799
He XM, Pu WH, Ren JG, Wang L, Wang JL, Jiang CY, Wan CR (2007) Charge/discharge characteristics of sulfur composite cathode materials in rechargeable lithium batteries. Electrochim Acta 52:7372–7376
Dean JA (1985) Lange's handbook of chemistry [J]. McGrawHill, New York
Mikhaylik YV, Akridge JR (2004) Polysulfide shuttle study in the Li/S battery system. J Electrochem Soc 151:A1969–A1976
Ji X, Evers S, Black R, Nazar LF (2011) Stabilizing lithium–sulphur cathodes using polysulphide reservoirs. Nat Commun 2:325
Schuster J, He G, Mandlmeier B, Yim T, Lee KT, Bein T, Nazar LF (2012) Spherical ordered mesoporous carbon nanoparticles with high porosity for lithium–sulfur batteries. Angew Chem 51:3591–3595
Wang HL, Yang Y, Liang YY, Robinson JT, Li YG, Jackson A, Cui Y, Dai HJ (2011) Graphene-wrapped sulfur particles as a rechargeable lithium sulfur battery cathode material with high capacity and cycling stability. Nano Lett 11:2644–2647
Ji LW, Rao MM, Zheng HM, Zhang L, Li YC, Duan WH, Guo JH, Cairns EJ, Zhang YG (2011) Graphene oxide as a sulfur immobilizer in high performance lithium/sulfur cells. J Am Chem Soc 133:18522–18525
Xiao LF, Cao YL, Xiao J, Schwenzer B, Engelhard MH, Saraf LV, Nie Z, Exarhos GJ, Liu J (2012) A soft approach to encapsulate sulfur: polyaniline nanotubes for lithium–sulfur batteries with long cycle life. Adv Mater 24:1176–1181
Fu YZ, Manthiram A (2012) Core-shell structured sulfur-polypyrrole composite cathodes for lithium–sulfur batteries. R Soc Chem Adv 2:5927–5929
Seh ZW, Li WY, Cha JJ, Zheng GY, Yang Y, McDowell MT, Hsu PC, Cui Y (2013) Sulphur–TiO2 yolk–shell nanoarchitecture with internal void space for long-cycle lithium–sulphur batteries. Nat Commun 4:1331–1336
Guo JC, Xu YH, Wang CS (2011) Sulfur-impregnated disordered carbon nanotubes cathode for lithium–sulfur batteries. Nano Lett 11:4288–4294
Zhang B, Lai C, Zhou Z, Gao XP (2009) Preparation and electrochemical properties of sulfur–acetylene black composites as cathode materials. Electrochim Acta 54:3708–3713
SenGupta AK (2002) Environmental separation of heavy metals. Engineering processes [M]. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton
Zhang WH, Qiao D, Pan JX, Cao YL, Yang HX, Ai XP (2013) A Li+-conductive microporous carbon–sulfur composite for Li–S batteries. Electrochim Acta 87:497–502
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, Ll., Liu, Gb., Wang, Y. et al. A comparison of sulfur loading method on the electrochemical performance of porous carbon/sulfur cathode material for lithium–sulfur battery. J Solid State Electrochem 18, 935–940 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-013-2337-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-013-2337-3